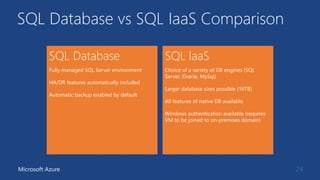
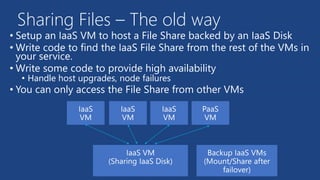
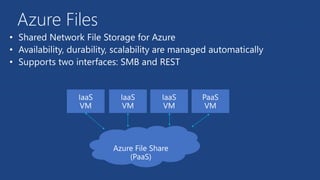
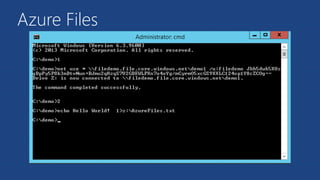
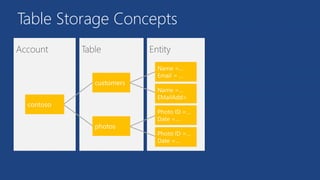
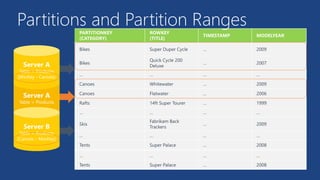
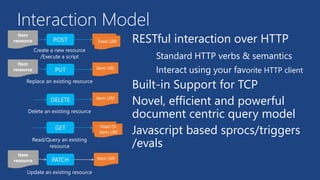
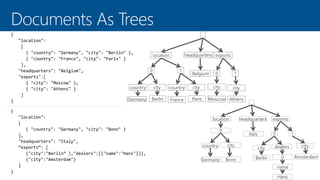
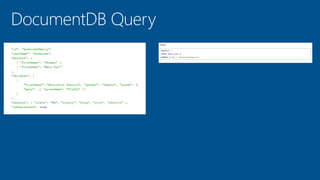
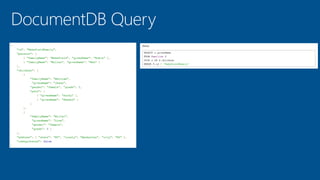
This document summarizes key components of Microsoft Azure's data platform, including SQL Database, NoSQL options like Azure Tables, Blob Storage, and Azure Files. It provides an overview of each service, how they work, common use cases, and demos of creating resources and accessing data. The document is aimed at helping readers understand Azure's database and data storage options for building cloud applications.






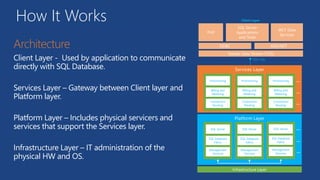











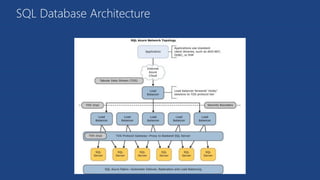
![Application Connectivity
1. TDS (Tabular Data Stream) protocol over TCP/IP supported
2. SSL required
3. Use firewall rules to connect from outside Microsoft data center
ASP.NET EXAMPLE:
1. login: [login]@[server]
2. Idle connections
3. Long running transactions
4. DoS guard
5. Failover events
6. Throttling
7. Connection pooling and Retry logic
8. Latency introduced for updates
9. No cross-database dependencies
<connectionStrings>
<addname="AdventureWorks"connectionString=
"Data
Source=[server].database.windows.net;
Integrated Security=False;
Initial Catalog=ProductsDb;
User Id=[login];
Password=[password];
Trusted_Connection=False;
Encrypt=true;"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient"/>
</connectionStrings>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datashared-150109103618-conversion-gate02/85/Azure-Data-Platform-20-320.jpg)