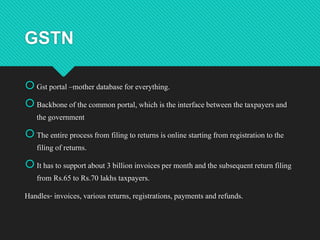
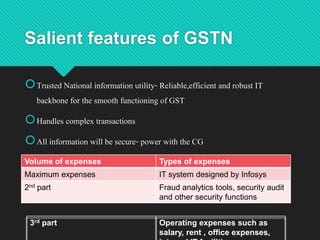
The document discusses India's Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), which provides the IT infrastructure and services necessary to implement the GST system. Key points:
1) GSTN is a non-profit company owned jointly by the central and state governments, as well as other financial institutions. It manages the common GST portal and backbone that allows taxpayers to file returns and make payments online.
2) The GSTN infrastructure handles large volumes of invoices, returns, registrations, payments and refunds for millions of taxpayers across India.
3) GST Suvidha Providers (GSPs) assist taxpayers in complying with GST requirements through their online platforms and interfaces with