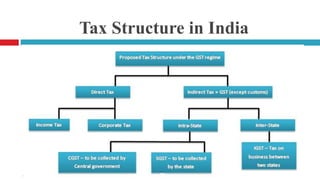
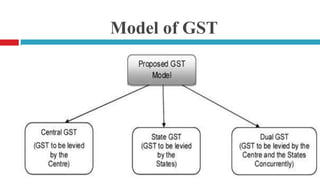
The document summarizes a presentation on Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. It provides an introduction to GST, outlines India's past tax system, describes the history and implementation of GST, discusses the different GST models and rates, and highlights both the advantages and disadvantages of GST. Some key impacts of GST mentioned are increased foreign investment, fewer taxes and reduced business costs, as well as effects on sectors like real estate. The conclusion states that GST is a major tax reform that will replace indirect taxes and require new legislation, but could be effective if laws are identical across states and the central government.