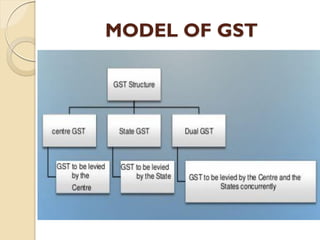
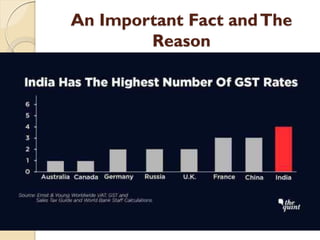
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is the biggest tax reform in India since independence. It is a comprehensive indirect tax on manufacture, sale, and consumption of goods and services throughout India. GST replaces many indirect taxes and aims to reduce tax cascading. It will simplify and harmonize the indirect tax regime in India. However, there were some hurdles in implementing GST, such as disputes between the central and state governments over tax sharing and the need for advanced IT infrastructure. Most countries have implemented some form of GST with rates typically between 15-20%.