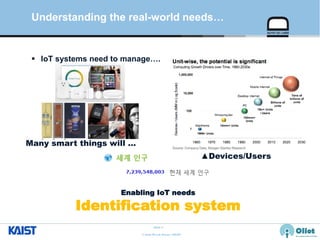
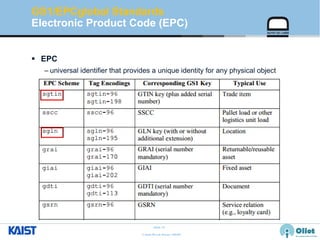
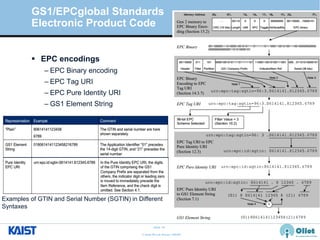
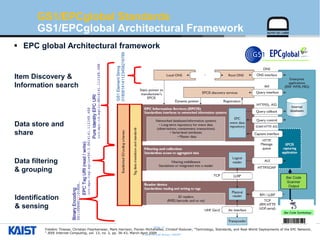
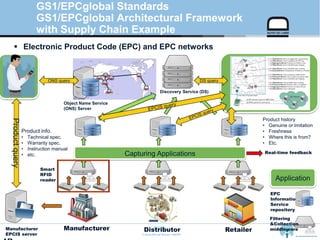
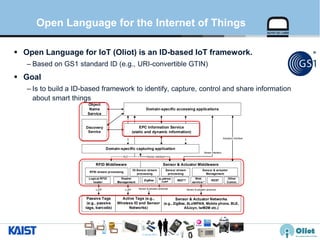
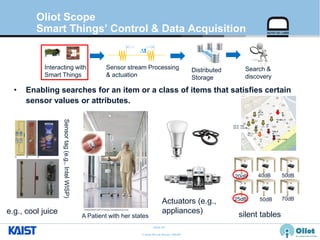
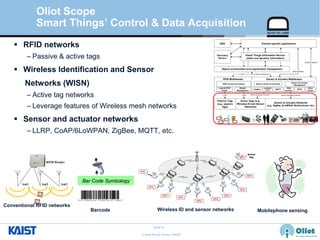
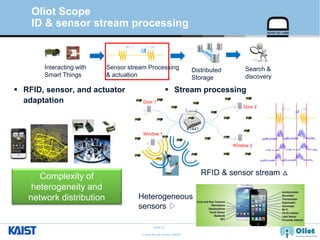
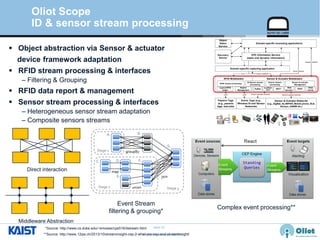
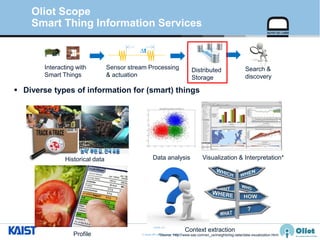
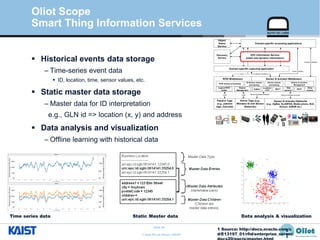
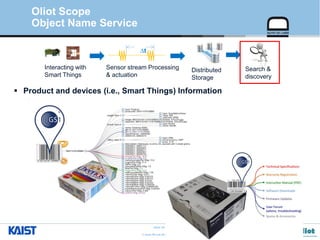
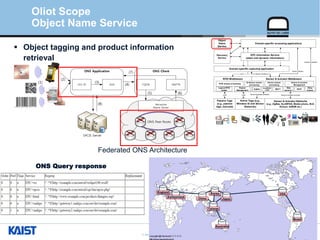
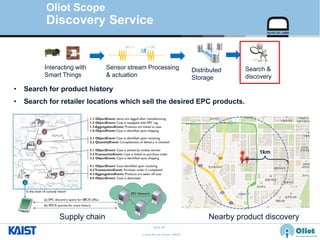
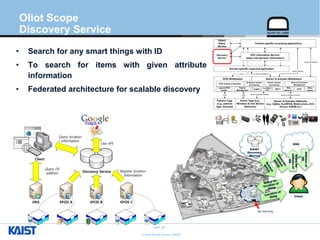
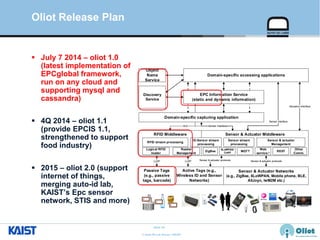
The document provides an overview of the GS1/EPCglobal standards and the Oliot project. It discusses key aspects of the GS1/EPCglobal standards including the Global Product Classification, Application Identifiers, GS1 Keys like the Global Trade Item Number and Serial Shipping Container Code, and the Electronic Product Code. It also provides an overview of the scope and components of the Oliot project, an open source IoT framework based on GS1 standards that aims to identify, capture, control and share information about smart things through technologies like RFID, sensors and actuators.