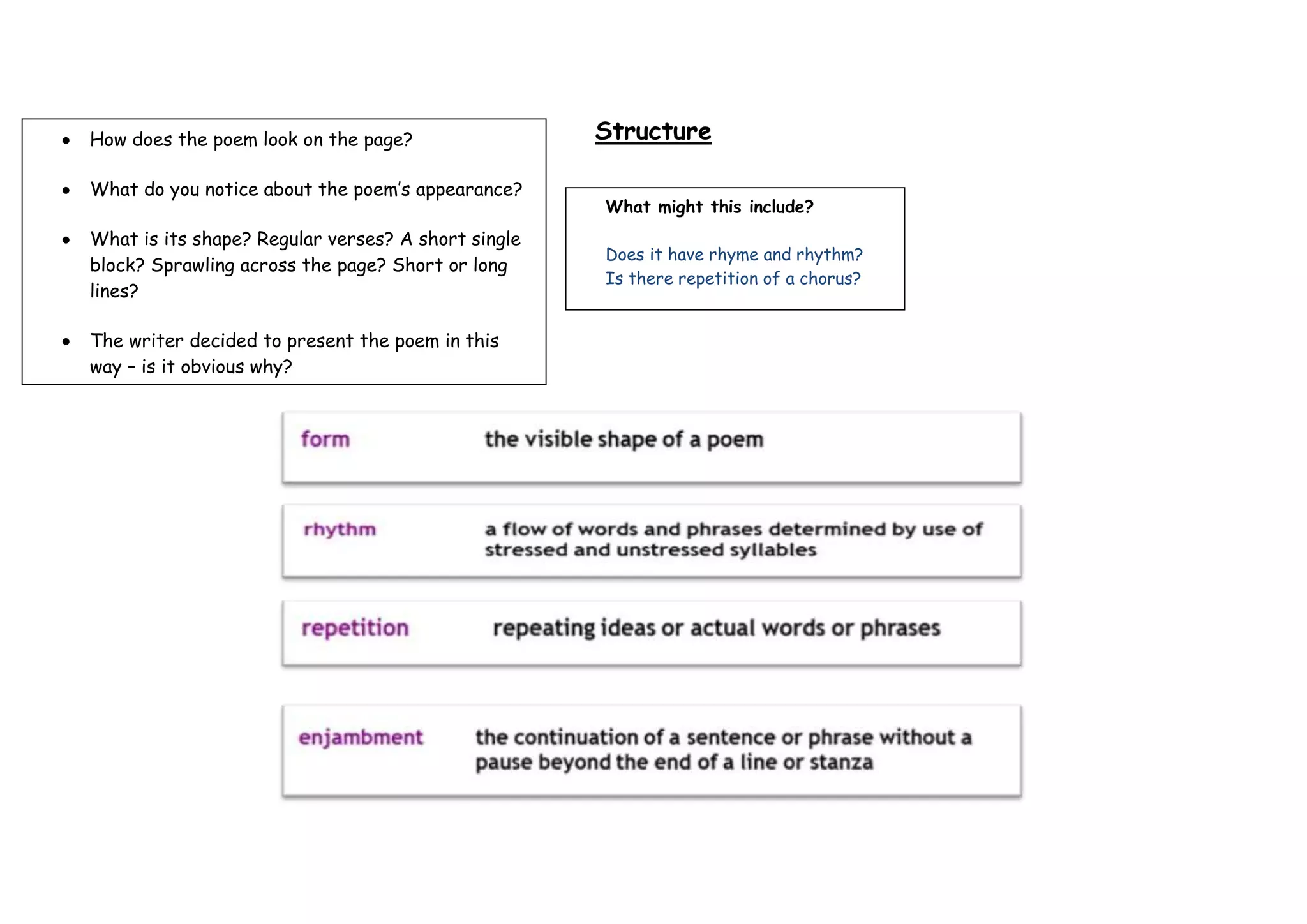
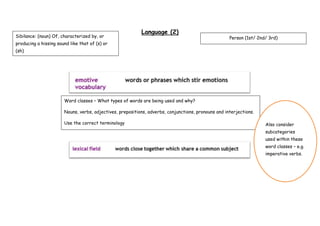
The document provides guidance on analyzing different elements of a poem, including its structure, meaning, viewpoint, imagery, language, and effect on the reader. It suggests examining the poem's appearance on the page, its rhyme and rhythm, repetition, themes, narrative elements, imagery like similes and metaphors, the speaker's perspective, word choice, tone and more to fully understand the poet's intent. The goal is to interpret how these various components work together to convey the writer's message and perspective.