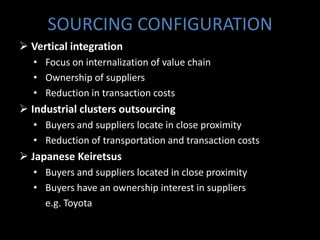
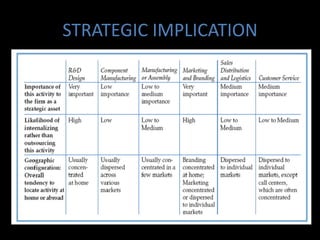
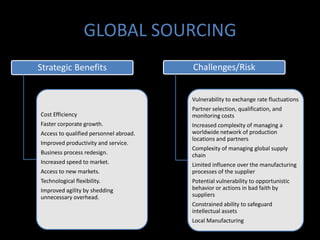
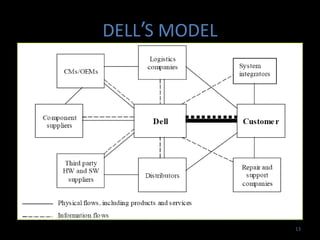
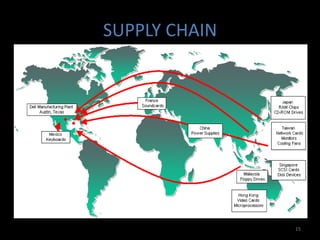
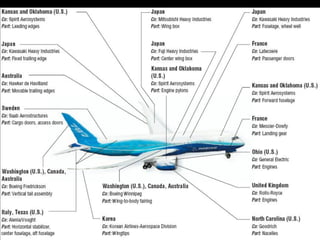
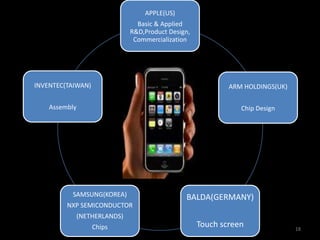
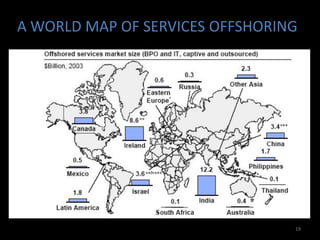
Global sourcing refers to procuring products or services from independent foreign suppliers or subsidiaries located abroad. Companies adopt global sourcing strategies to lower costs, improve quality, ensure reliable supply, enter new markets, access new technologies, and react to competitor moves. Key considerations in global sourcing include make-or-buy decisions, sourcing configurations like vertical integration or outsourcing to industrial clusters, and strategies to minimize risks like currency fluctuations, weak legal environments, and over-reliance on suppliers. Large companies like Apple, Dell, and Samsung employ complex multi-country global supply chain models for assembly, manufacturing, and component sourcing.