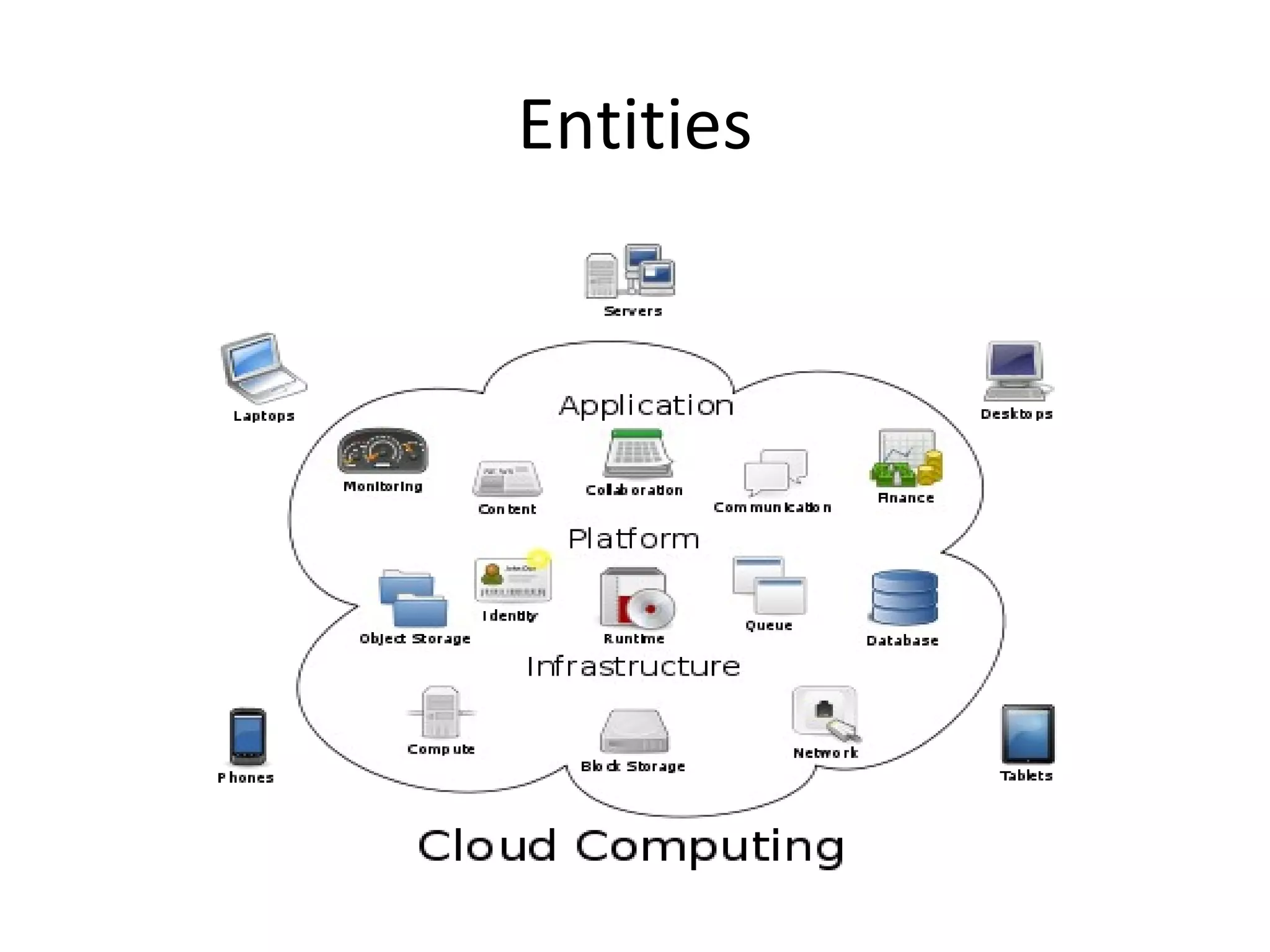
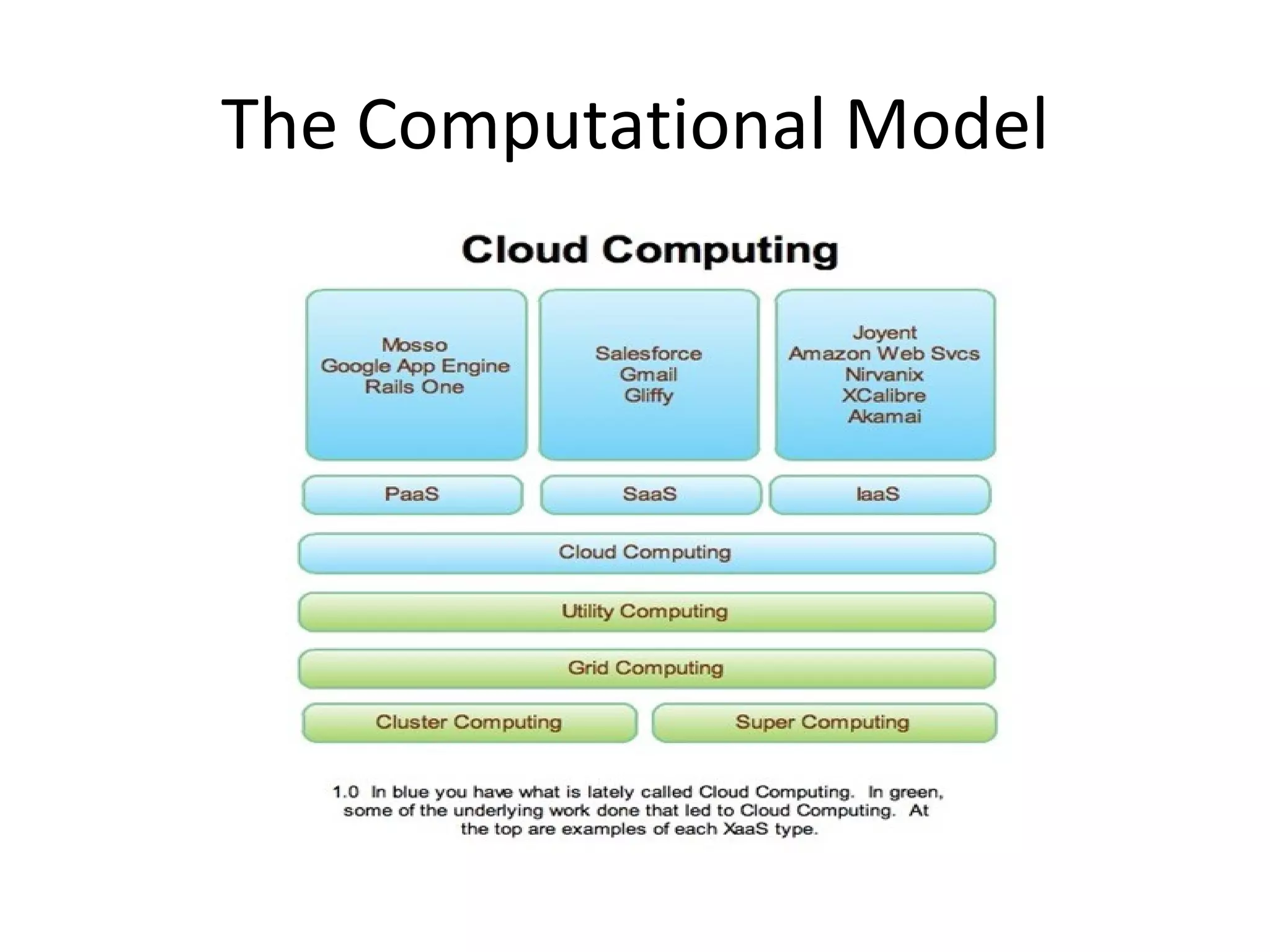
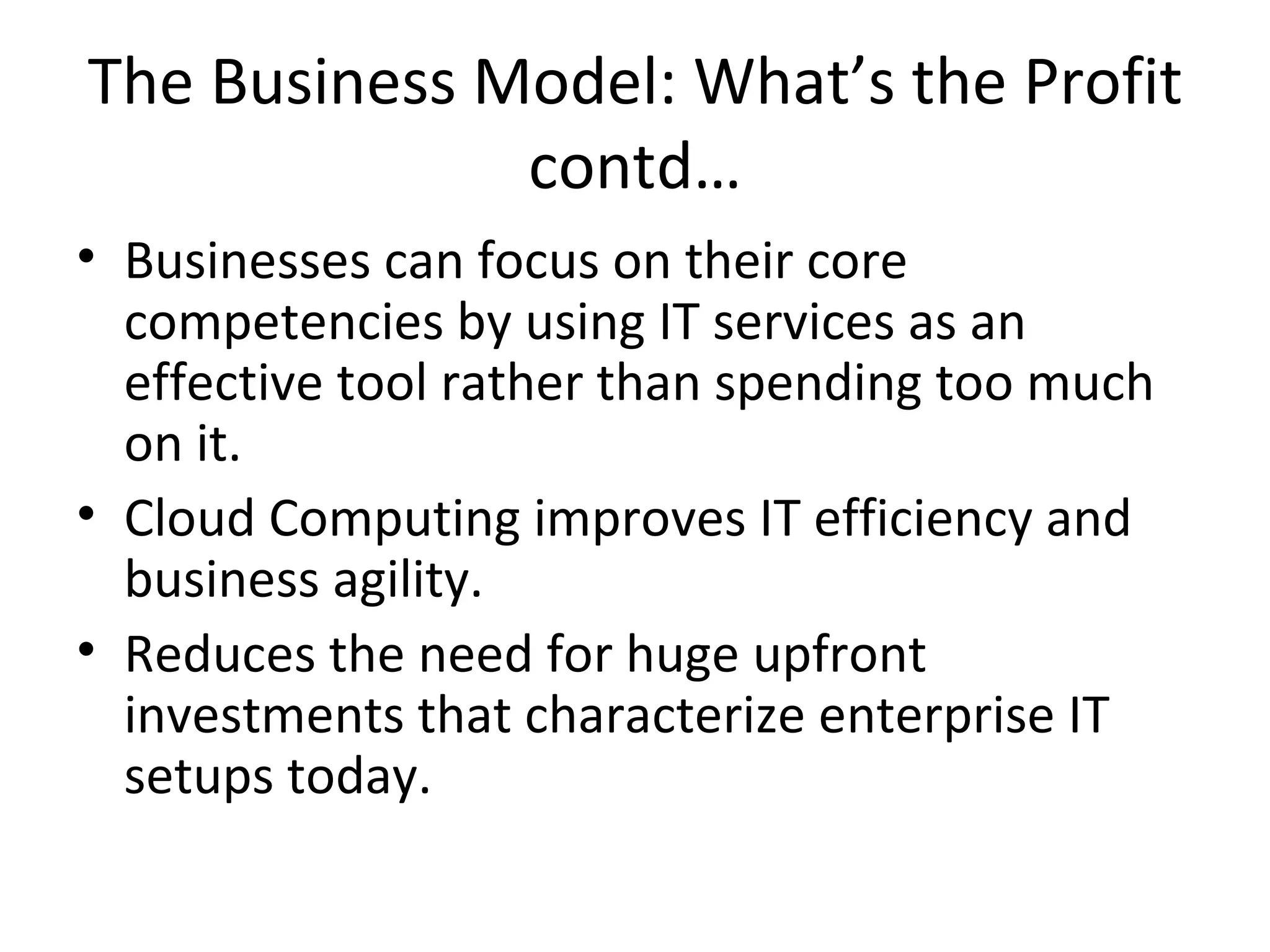
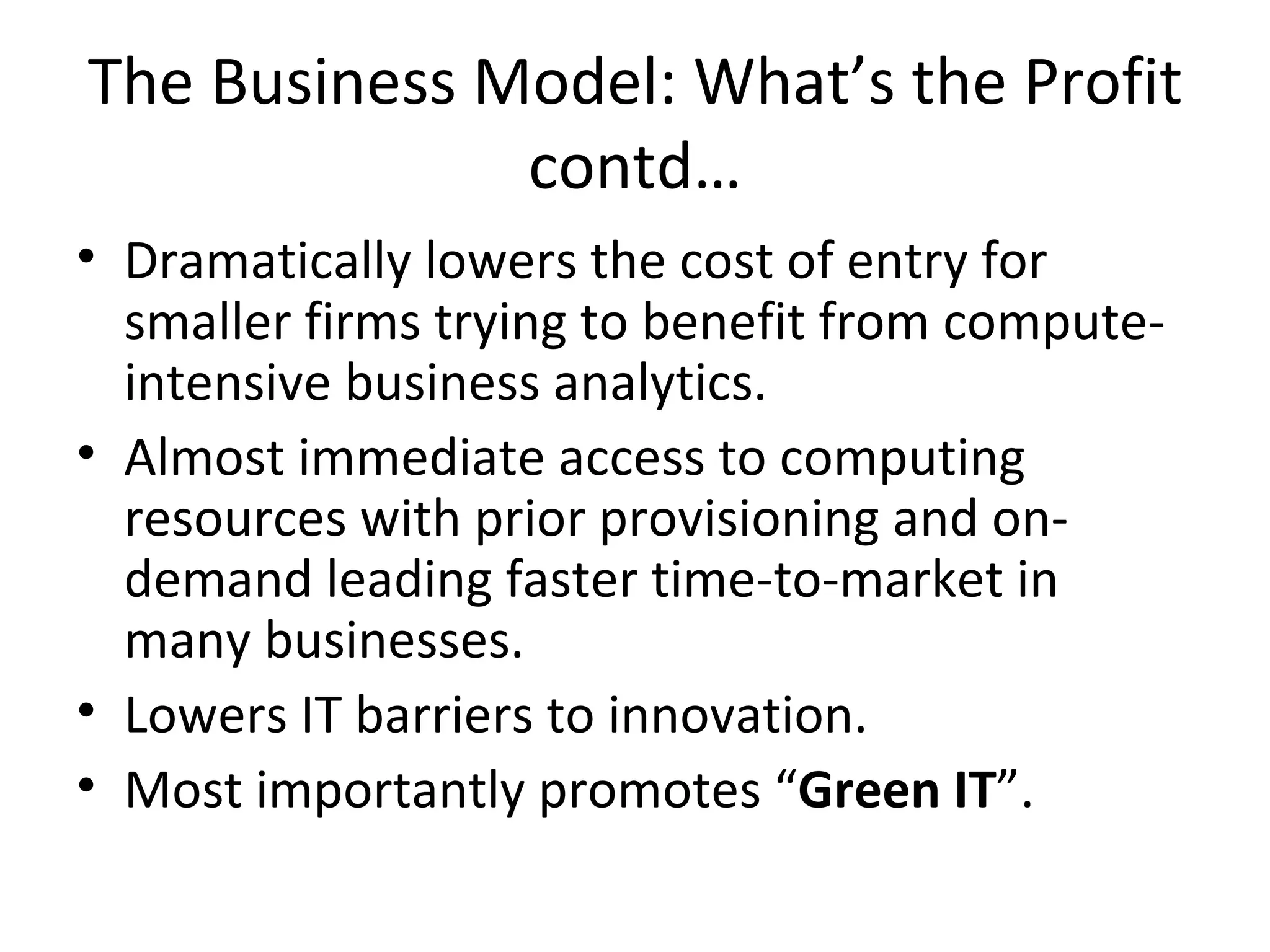
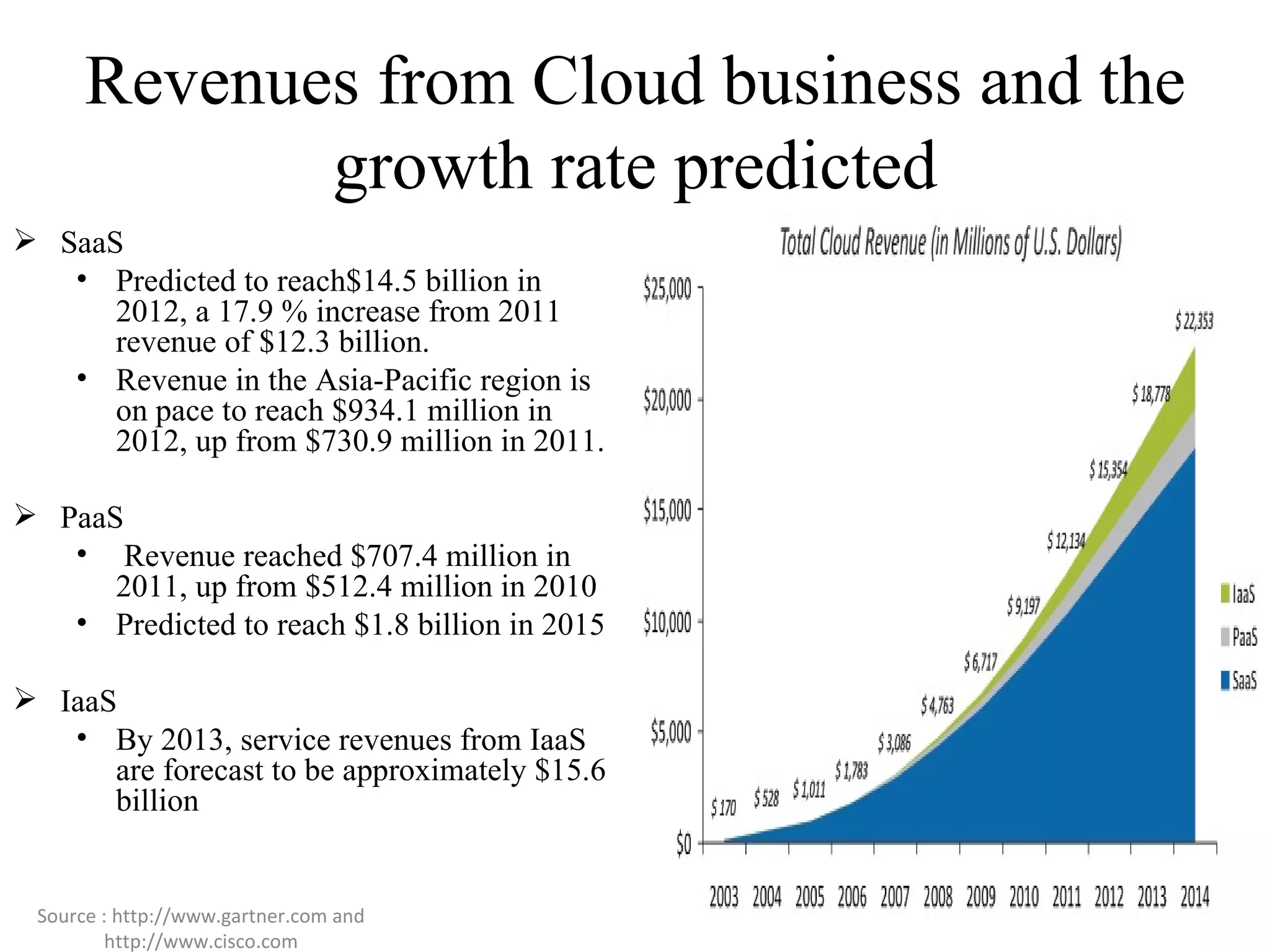
Cloud computing refers to applications and services delivered over the Internet. It provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like servers, storage, databases and software that can be provisioned with minimal management effort. Major cloud service models include SaaS, PaaS and IaaS. The cloud computing market is growing rapidly with major players like Amazon, Microsoft and Google dominating different segments. Emerging services like STaaS, Daas and Caas are facilitating wider cloud adoption.