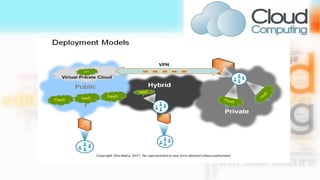
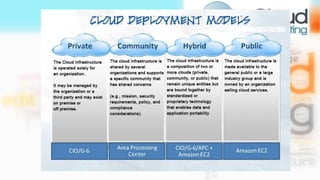
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including:
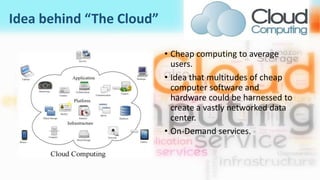
1) Cloud computing involves using networked computers and virtualization to provide on-demand services and resources over the internet. It aims to provide cheap, scalable computing resources to users.
2) Key aspects include vast data centers and resource pools that users can dynamically access on-demand, with resources that tend to be priced like utilities based on usage.
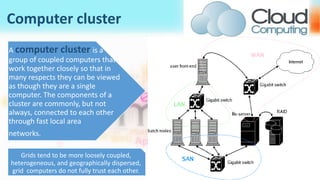
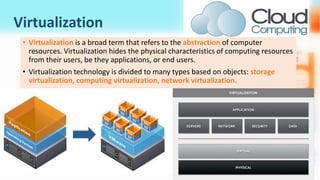
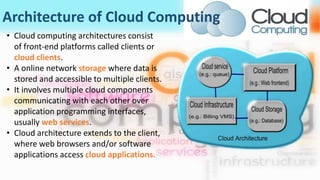
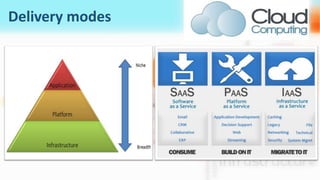
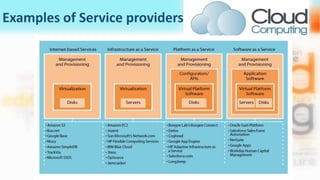
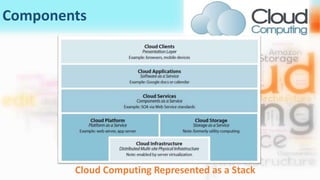
3) Cloud computing delivers resources, platforms, and software as services through models like SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, using virtualization technology and computer clusters behind interfaces like web services.



![Cloud Computing
• Every user can get it’s own private resource from the
cloud, the cloud resource are provided by the specific
service provider, the user need not contribute its
resource.
• Computing resources, such as servers, can be
dynamically shaped or carved out from its underlying
hardware infrastructure and made available to a
workload.
• Long-lived services based on hardware virtualization.
• Resource side middleware- proprietary.
• User Interface-HTTP[S] ,REST, SOAP, java, API, BitTorrent.
• Commercially funded.
Grid Computing
• Grid computing emphasizes on resource sharing,
every grid node can apply for resource from other
nodes and vice-versa.
• The focus of grid computing is on the ability of
moving a workload to the location of the needed
computing resources, which are mostly remote
and are readily available.
• Short-lived batch-style processing (job execution).
• Resource side middleware-Open source Apache
2.0 .
• User Interface-High Level interface.
• Publicly funded.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputingpresenatation-final2013-130505040921-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-presentation-6-320.jpg)