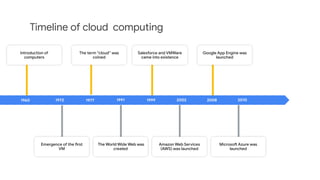
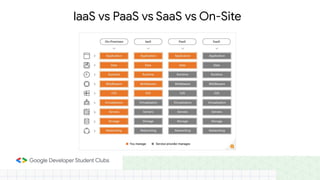
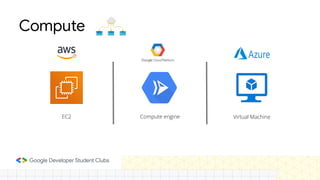
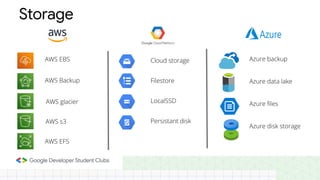
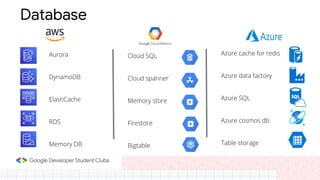
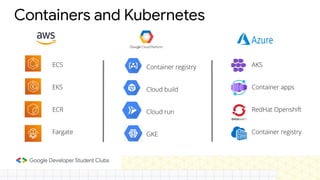
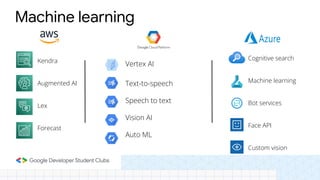
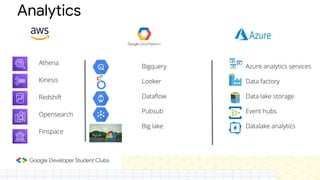
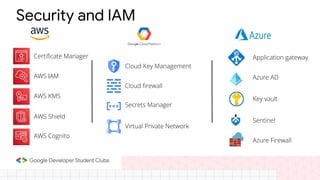
The document discusses the evolution and importance of cloud computing, detailing its benefits over traditional IT infrastructure, including cost savings, scalability, and data security. It explores various cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and cloud types (public, private, hybrid), along with pricing models and product categories offered by cloud providers. Additionally, it emphasizes the growing career opportunities in cloud computing and the significance of cloud certifications.