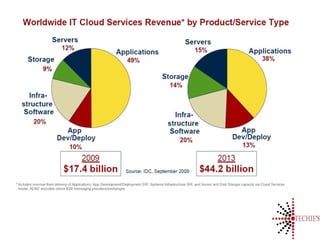
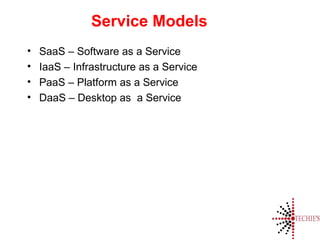
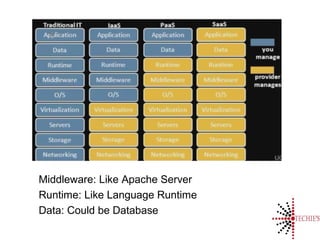
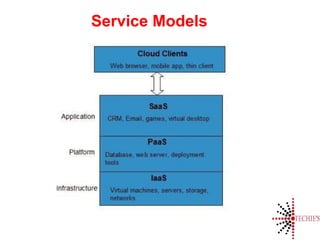
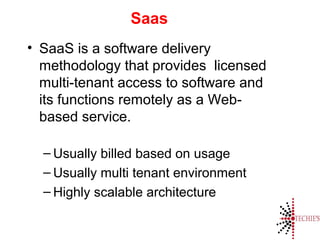
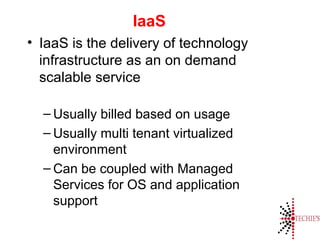
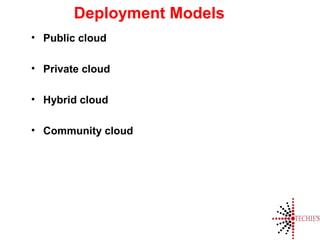
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet with a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for large upfront hardware investments. It evolved from the 1950s and gained public traction with Amazon Web Services in 2006. Key service models include SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS, offering scalable and customizable solutions while providing advantages like reduced complexity and better reliability.