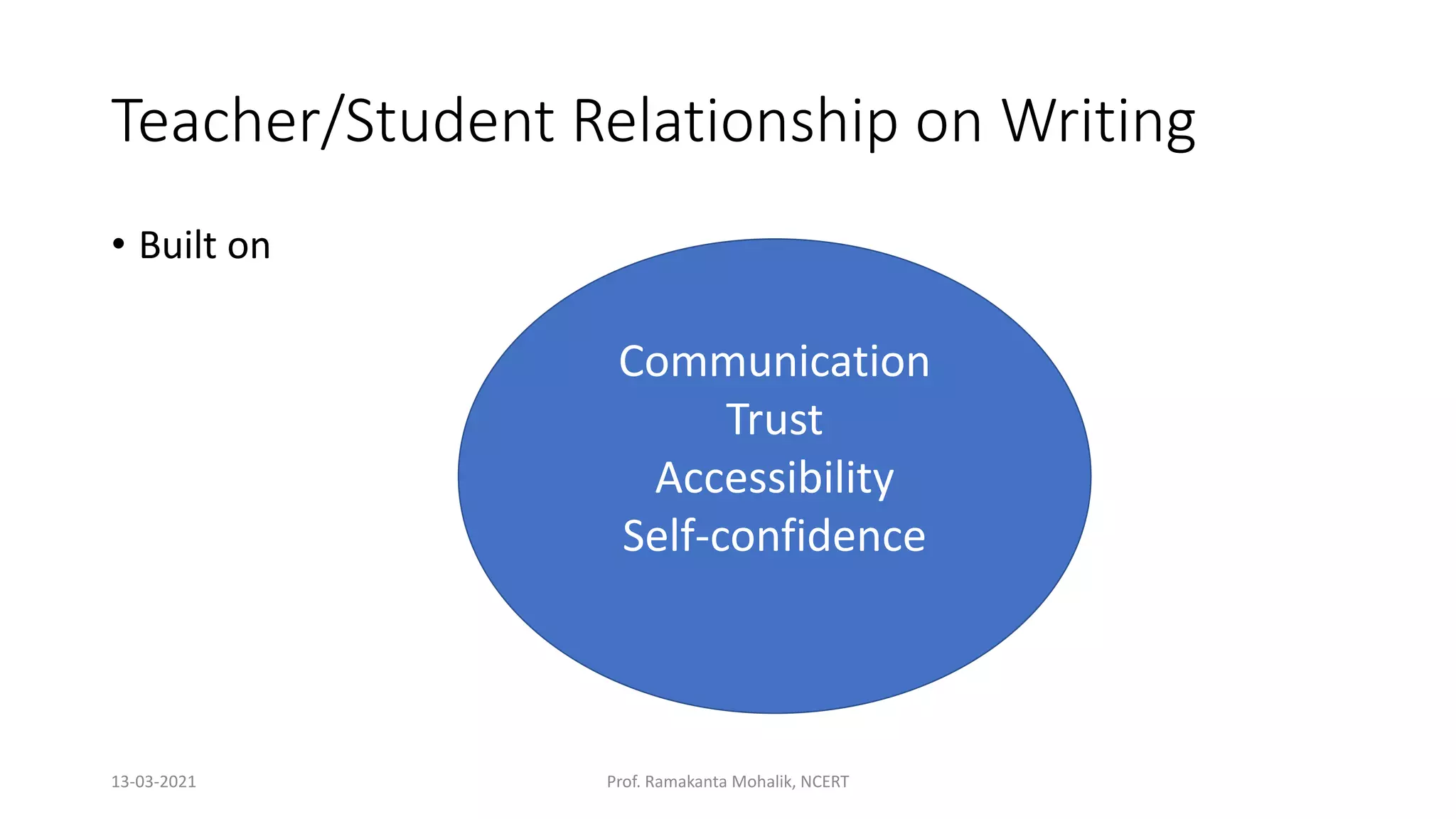
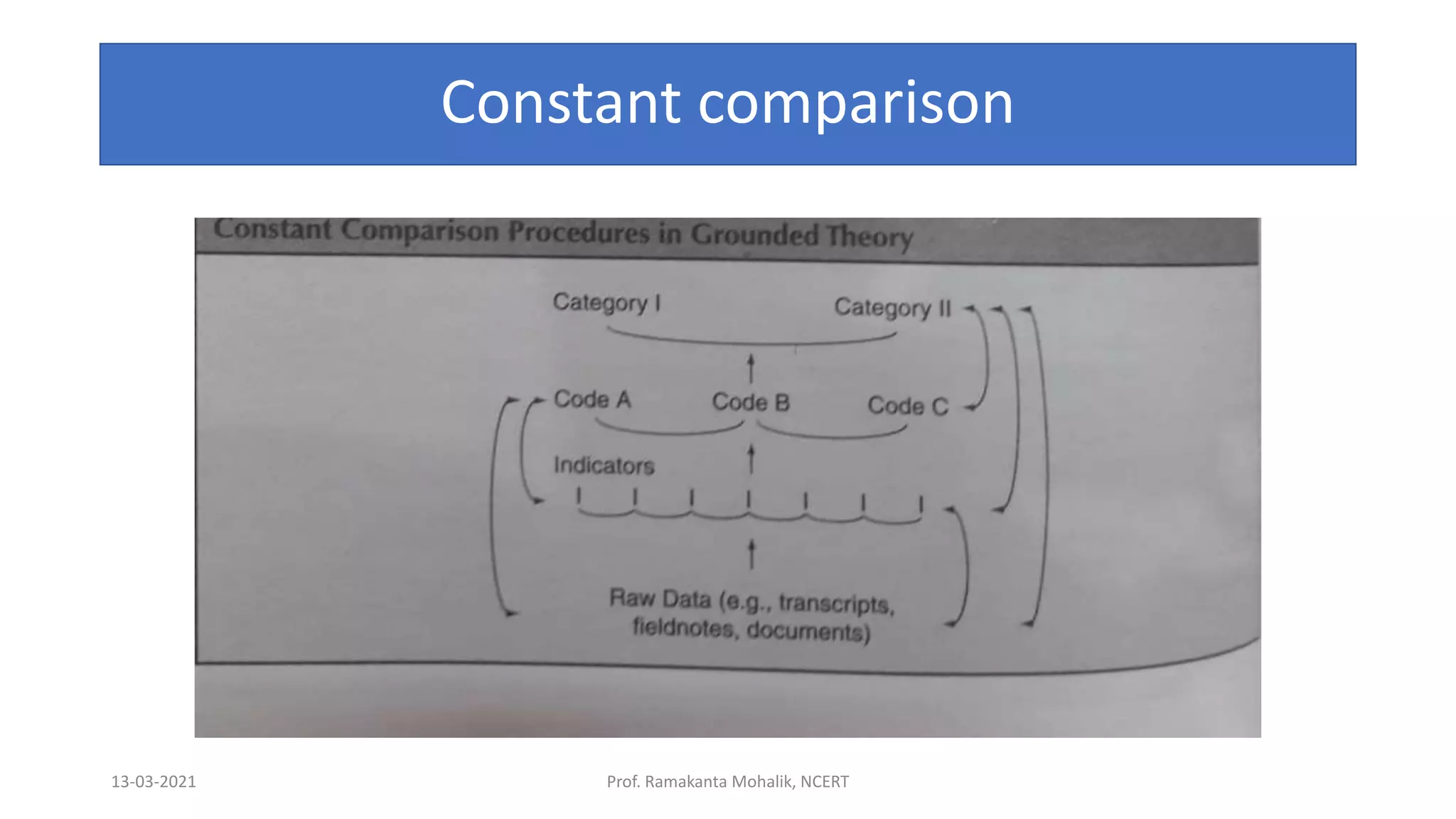
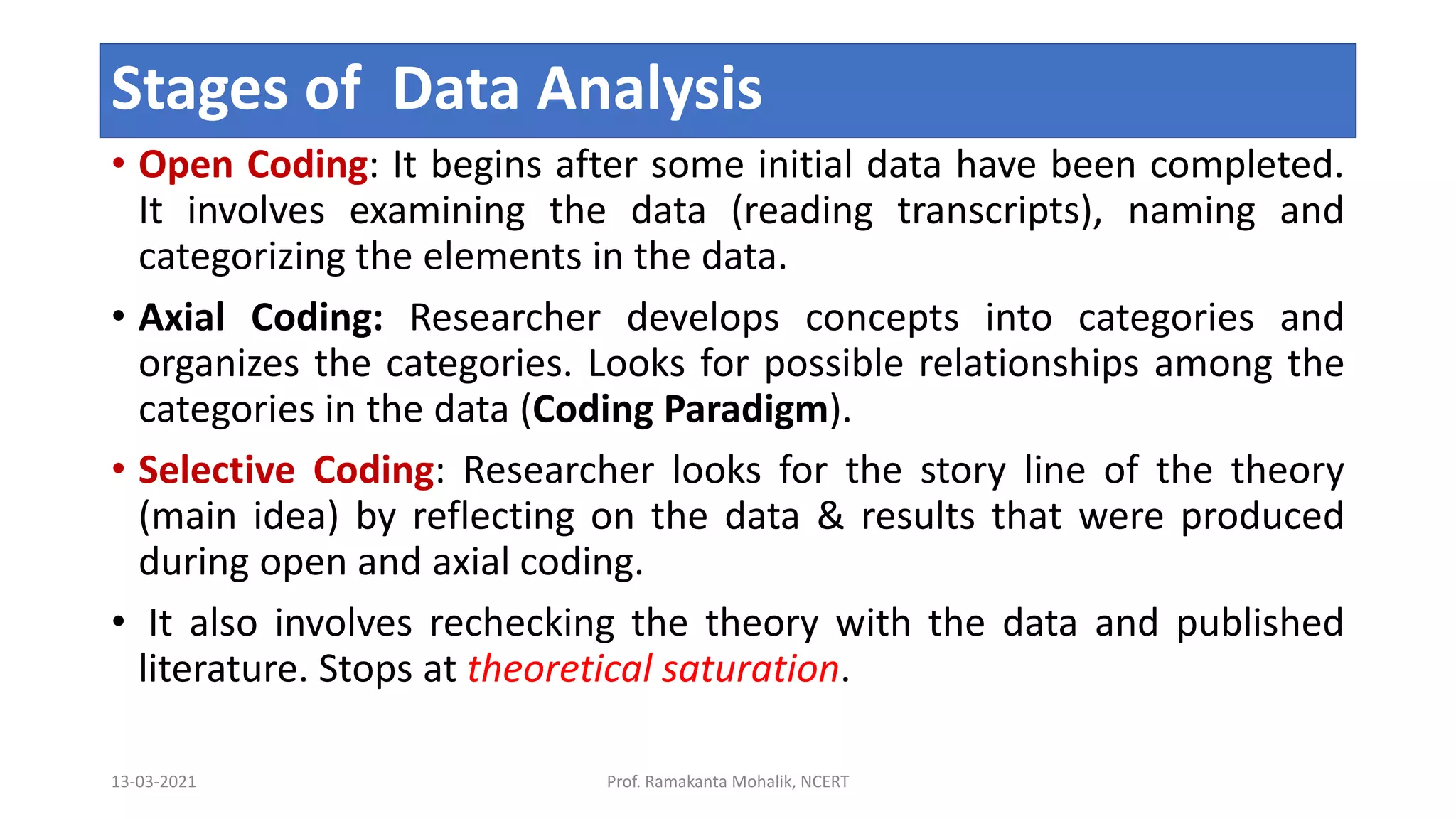
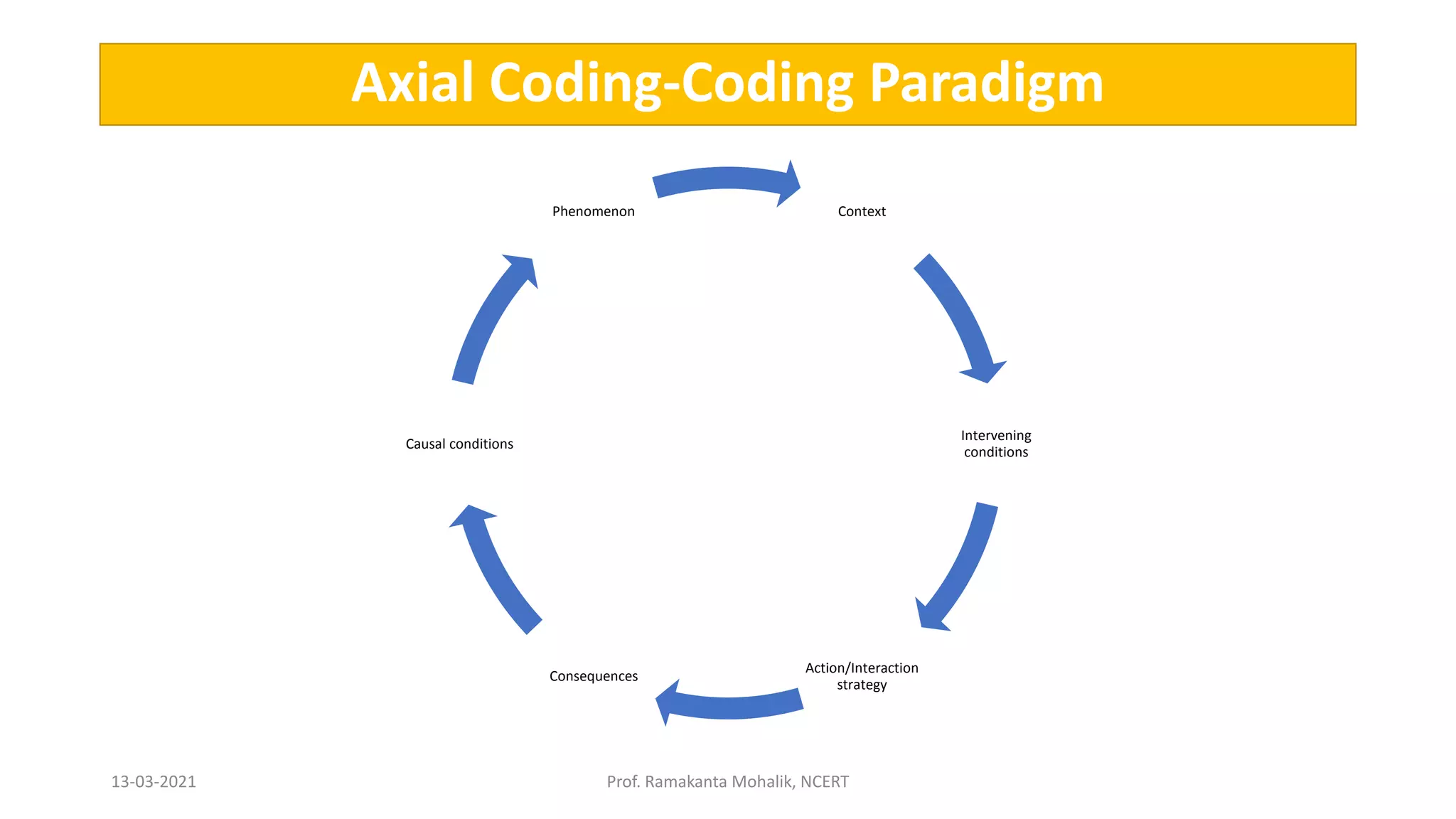
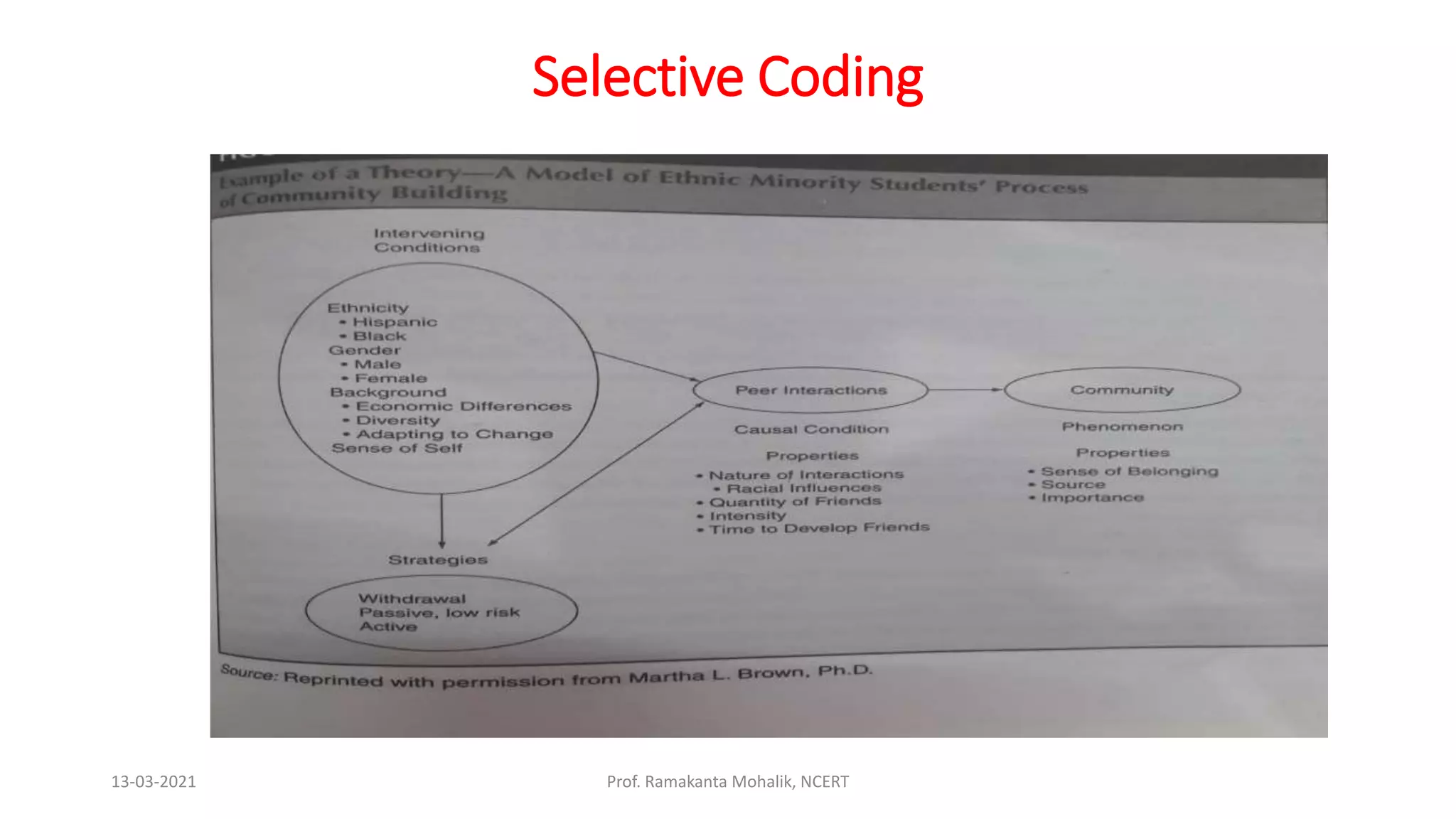
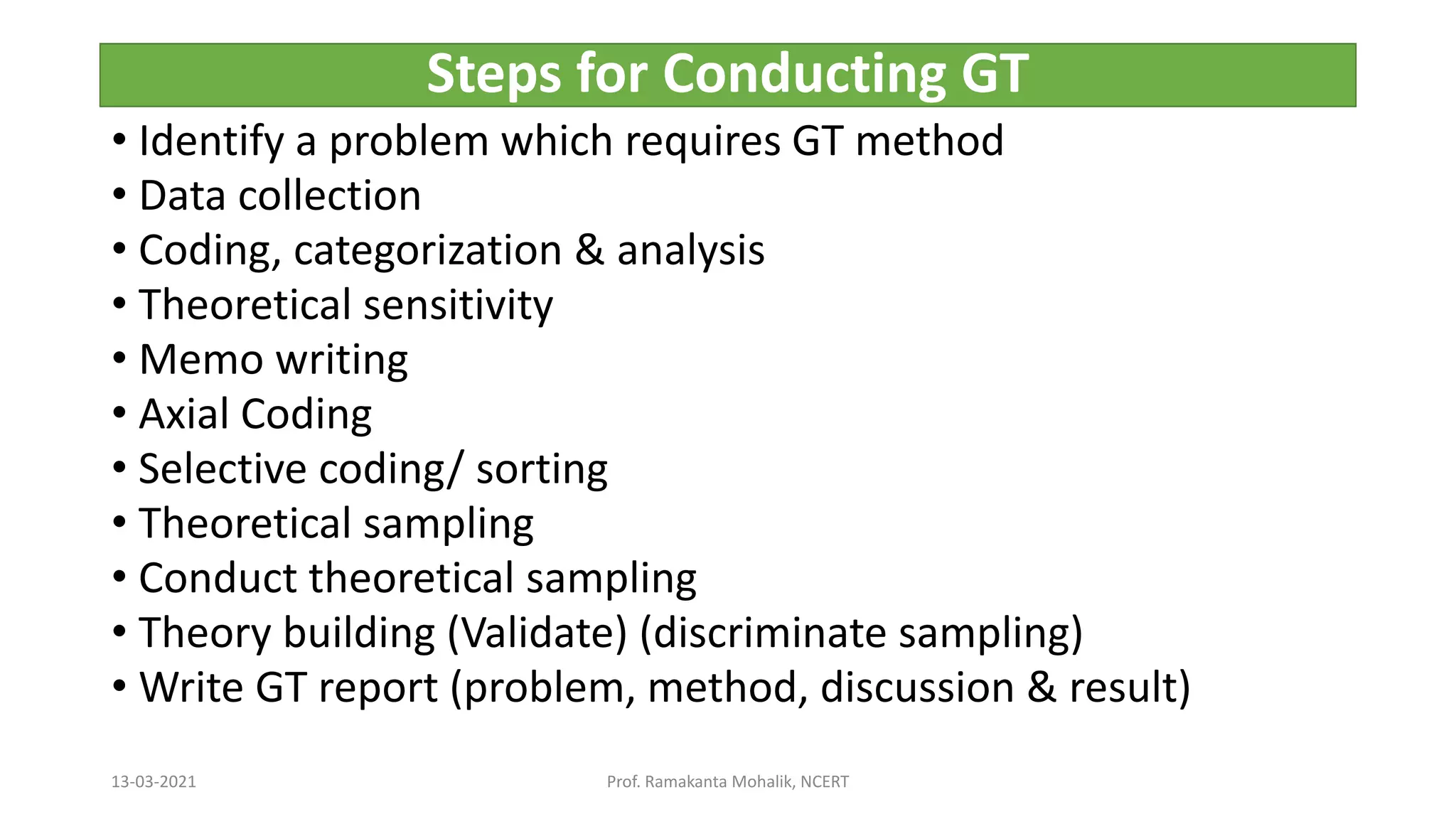
- The document discusses grounded theory as a research method for understanding the teacher-student relationship in an English writing classroom. It outlines the research questions and describes collecting data through classroom observations, student and teacher interviews, and analyzing the data using open, axial and selective coding to develop a theory grounded in the data. The goal is to discover the elements of the teacher-student relationship that most impact student writing improvement and outcomes.