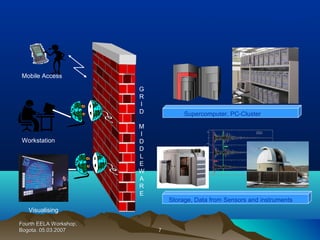
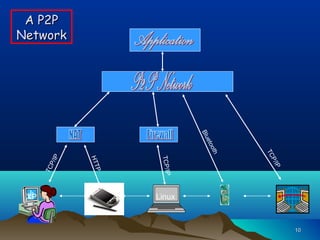
Grid computing involves connecting geographically distributed computers and resources into a single network to create a virtual supercomputer. Resources may include computers, storage devices, instruments, and data owned by diverse organizations. Users can access these heterogeneous resources through a single account, similar to how an electrical power grid provides power from different sources. Key aspects of grid computing include distributed supercomputing, high-throughput computing, on-demand computing, and data-intensive computing. Major companies involved in developing grid computing include IBM, Intel, and Sun Microsystems. Limitations include the need for standardization and use of command line interfaces or programming.