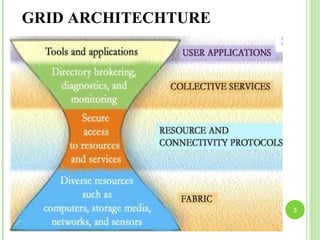
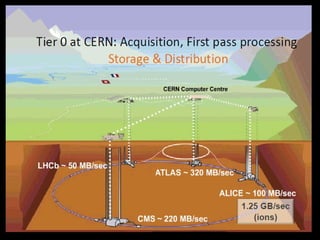
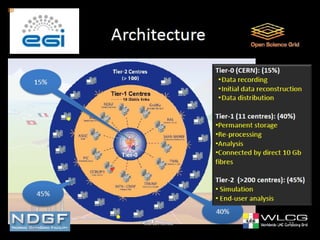
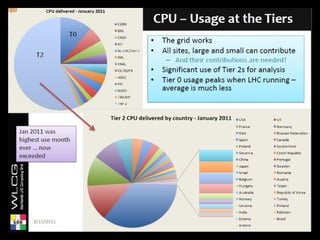
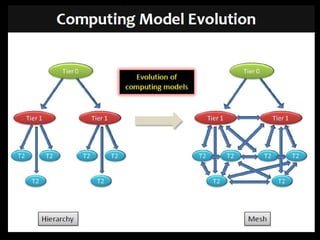
Grid computing involves distributing computing resources across a network to tackle large problems. The Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG) was established to support the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) experiment, which produces around 15 petabytes of data annually. The WLCG uses a four-tiered model, with raw data stored at Tier-0 (CERN), copies distributed to Tier-1 data centers, computational resources provided by Tier-2 centers, and Tier-3 facilities providing additional analysis capabilities. This distributed model has proven effective in supporting the first year of LHC data collection and analysis through globally shared computing resources.