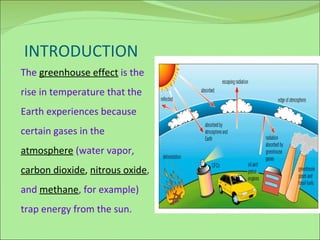
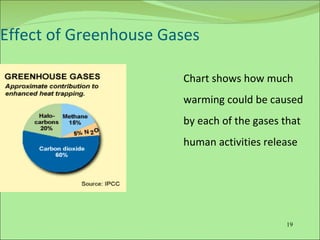
The document discusses the greenhouse effect and greenhouse gases. It explains that certain gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun, causing the greenhouse effect. It then describes the major greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and chlorofluorocarbons. The document outlines the various human activities that contribute to increased levels of these gases in the atmosphere, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, agriculture, and industrial processes. It concludes by discussing some of the potential consequences of rising global temperatures like sea level rise and disruption of ecosystems.