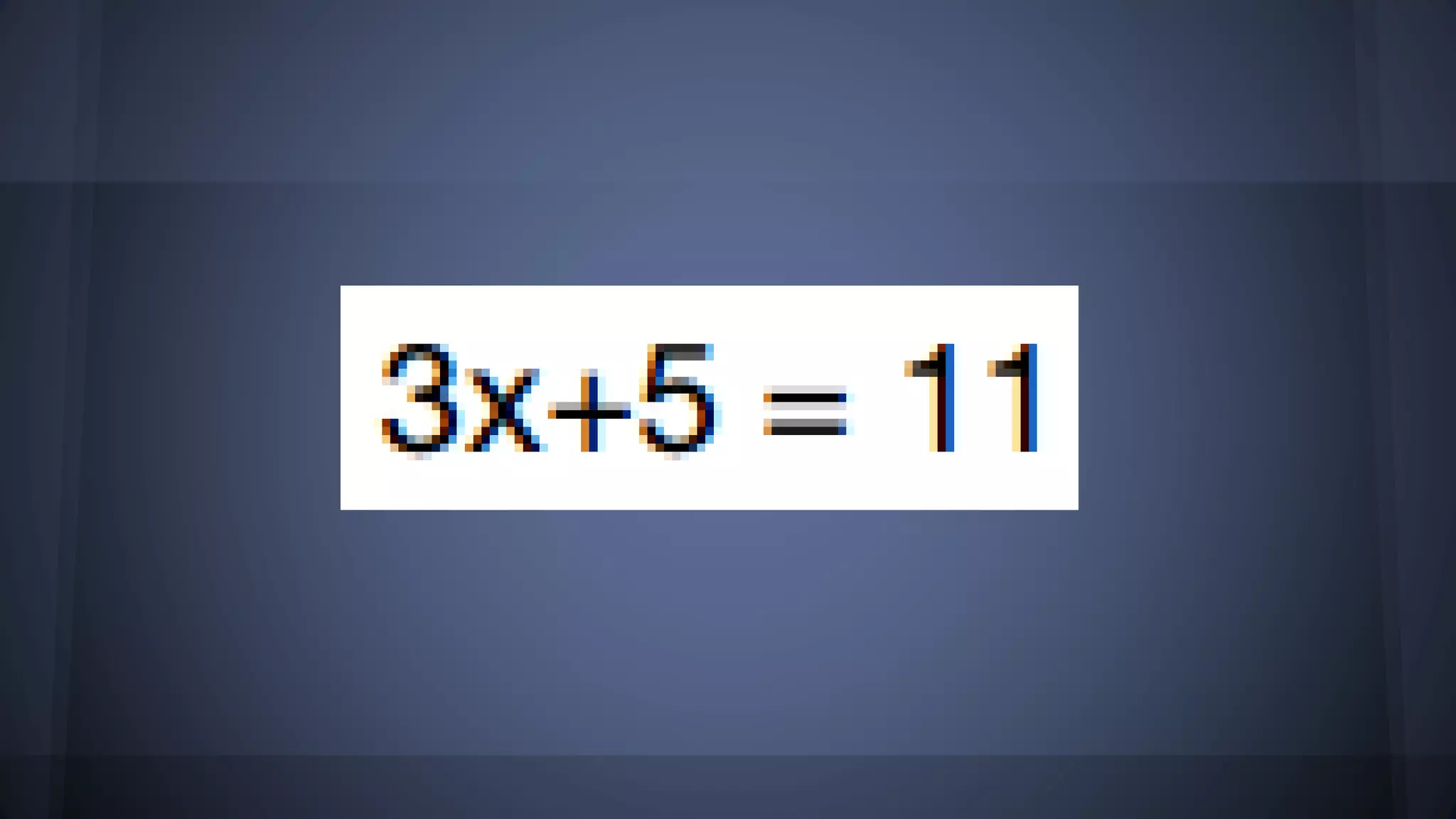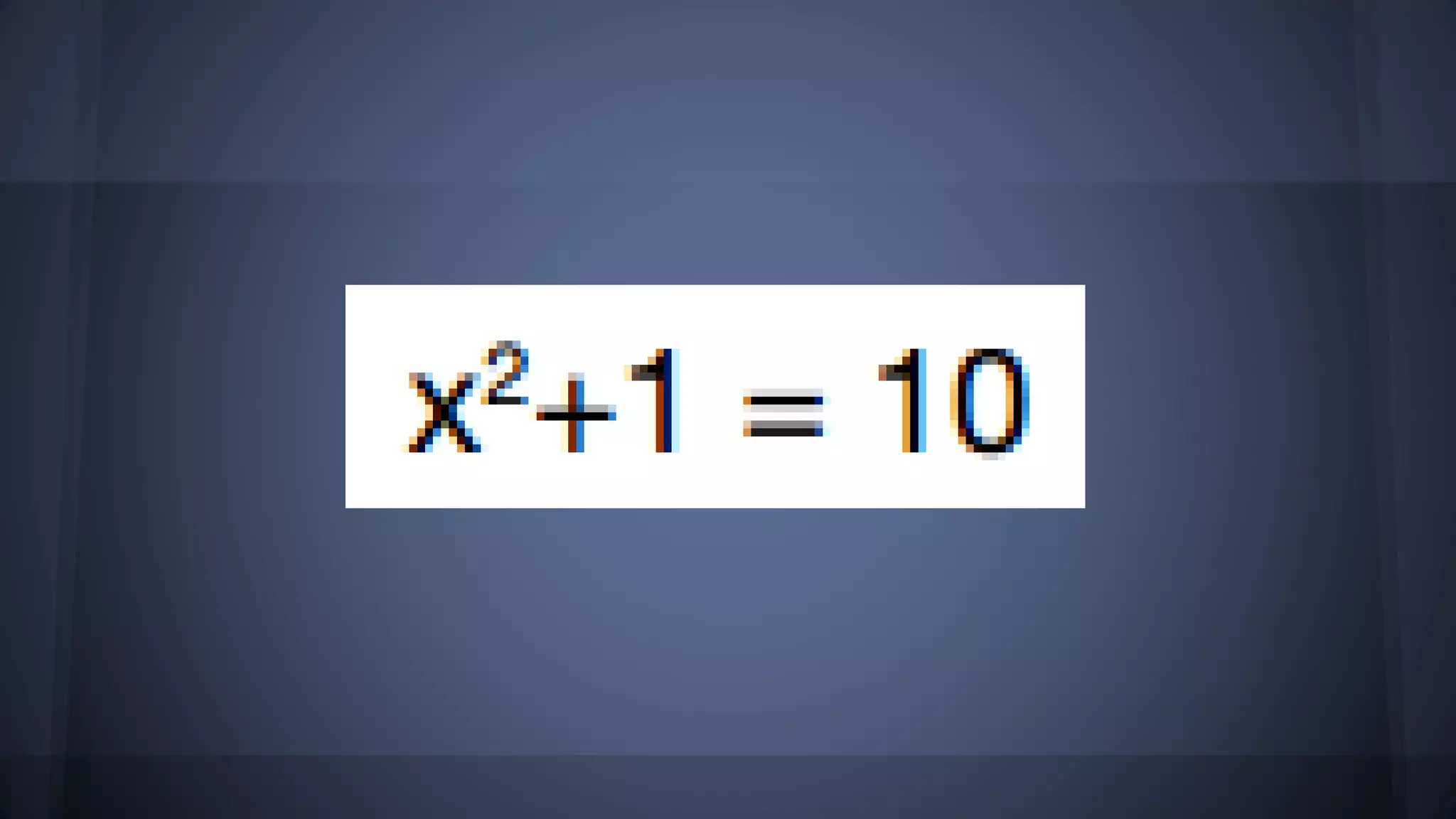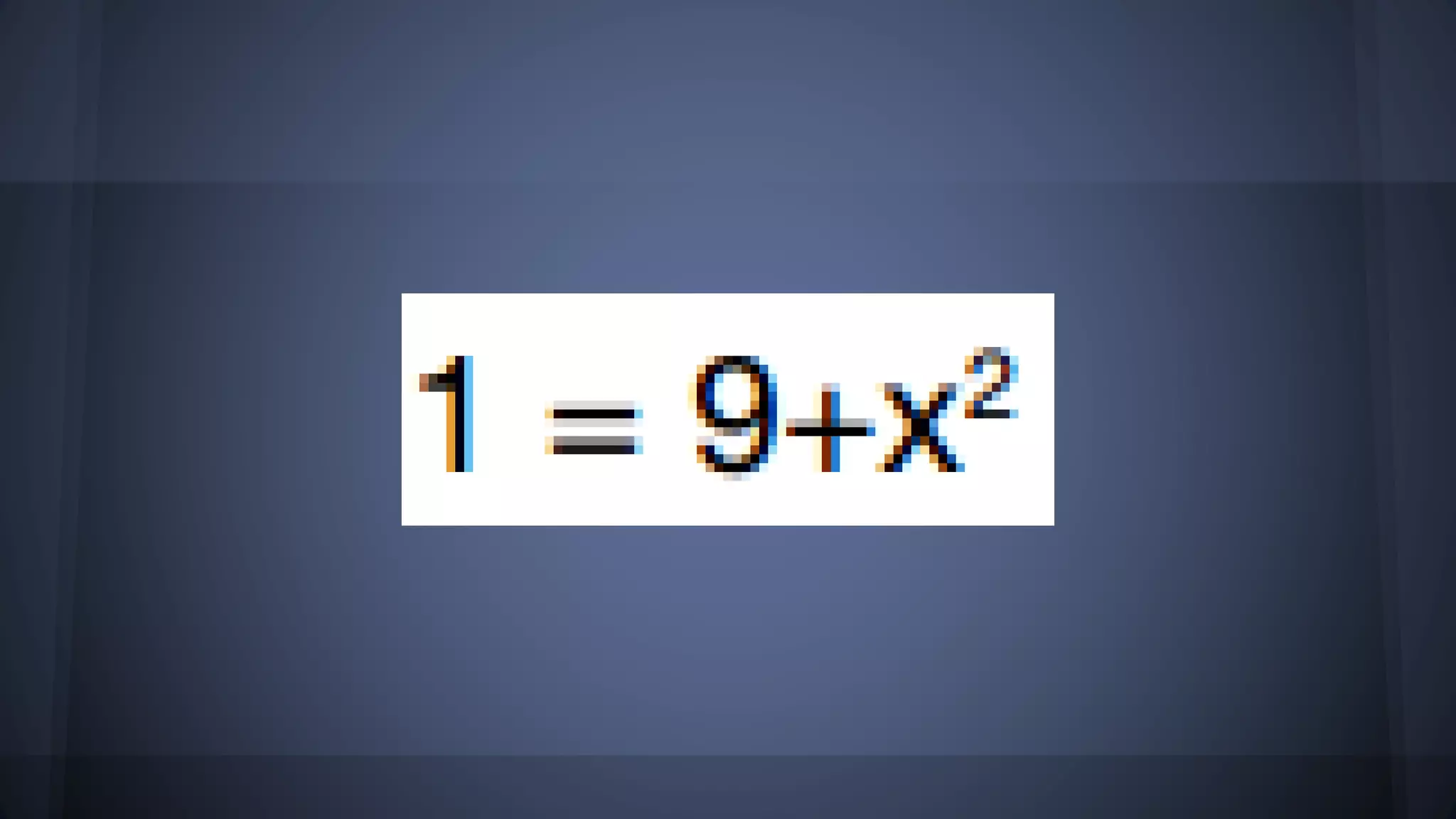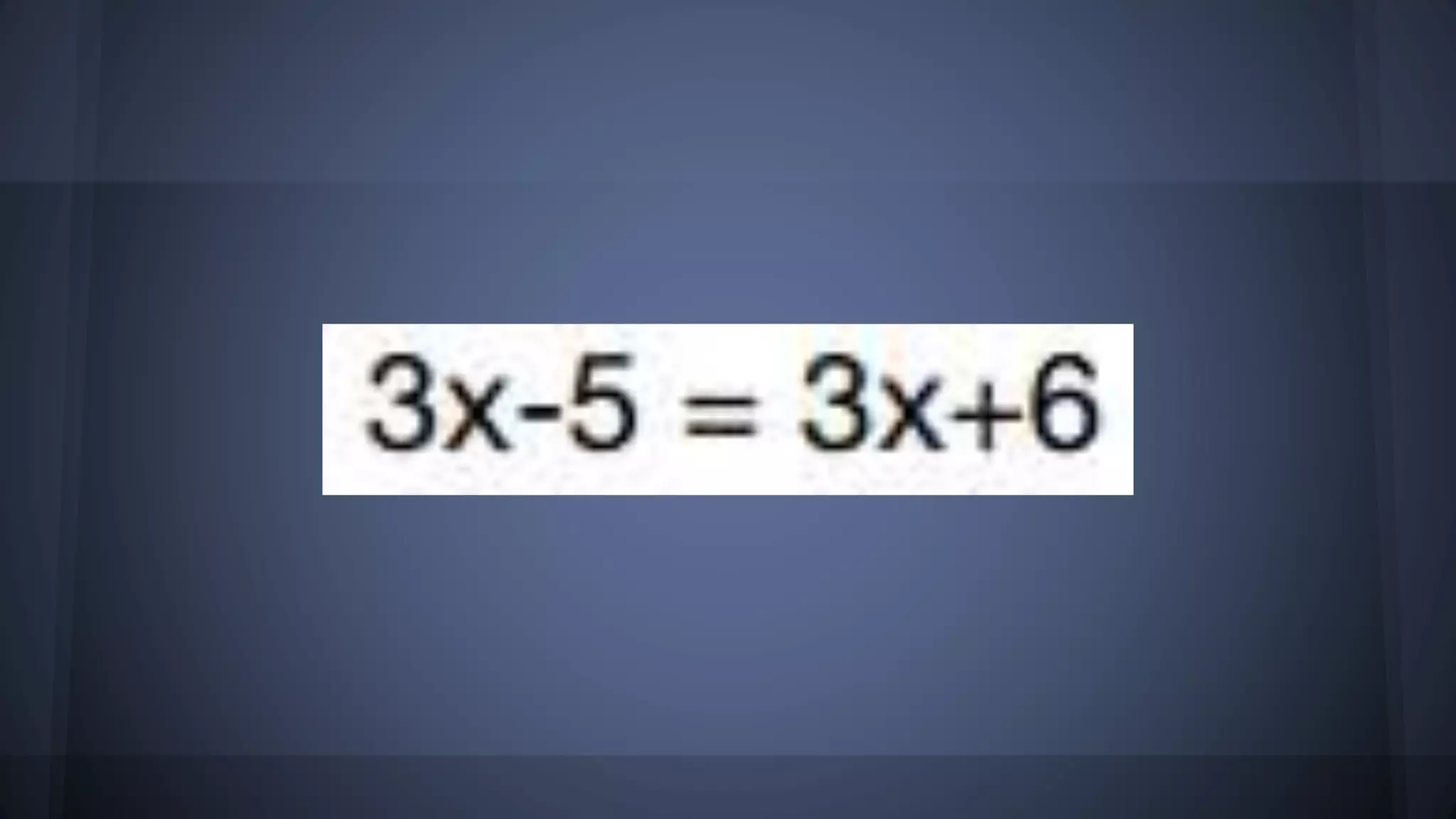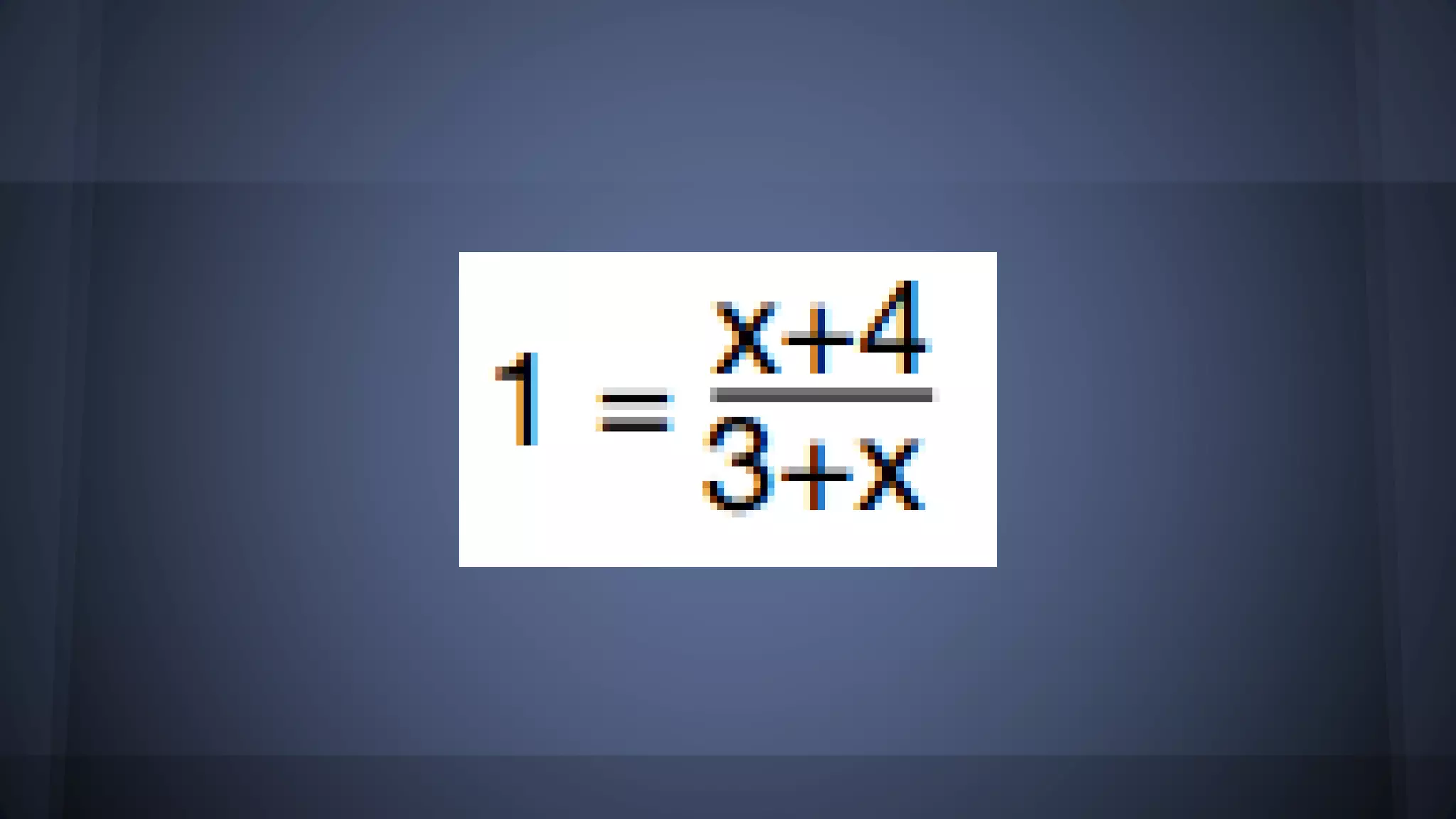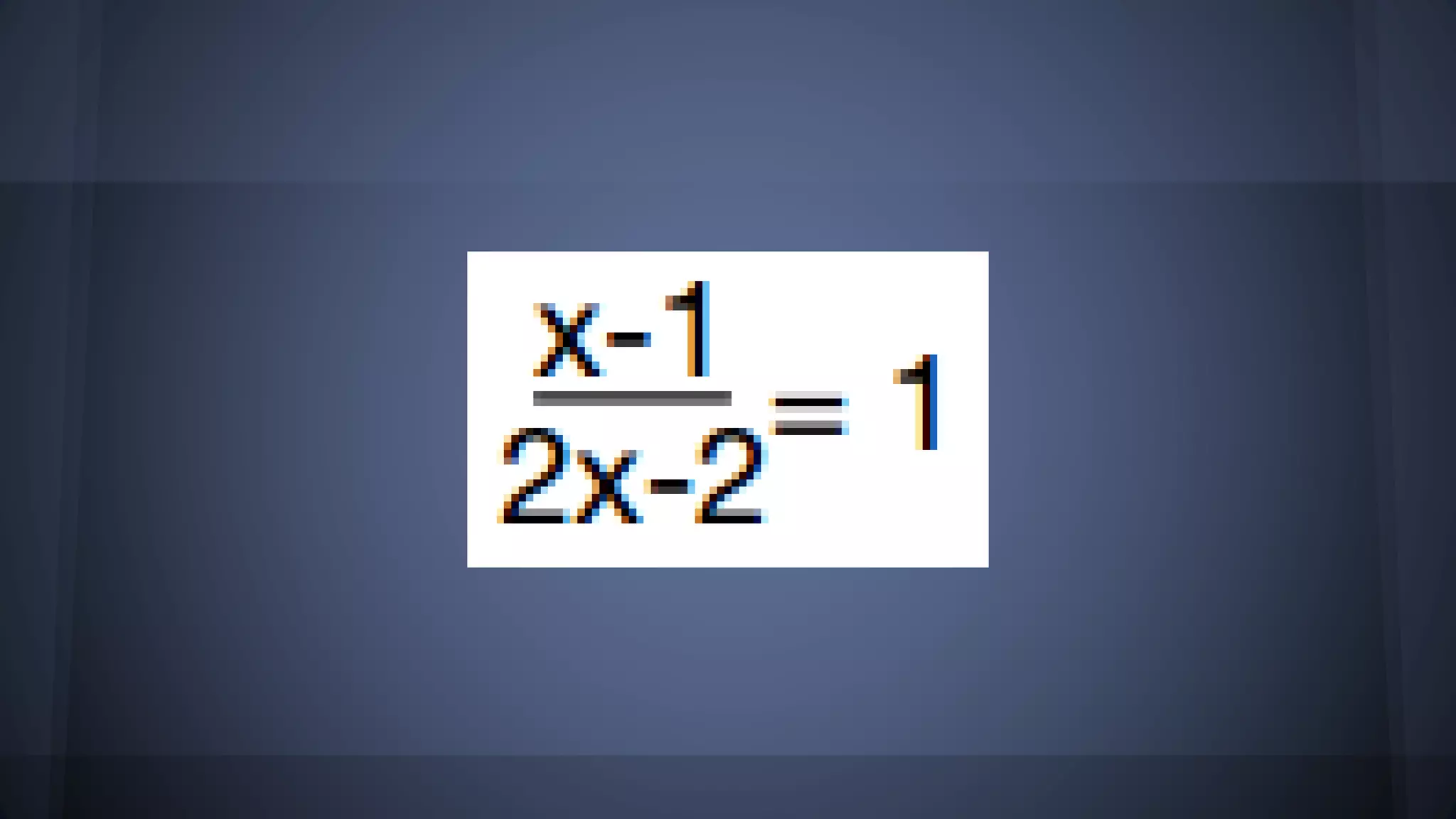Embed presentation
Download to read offline

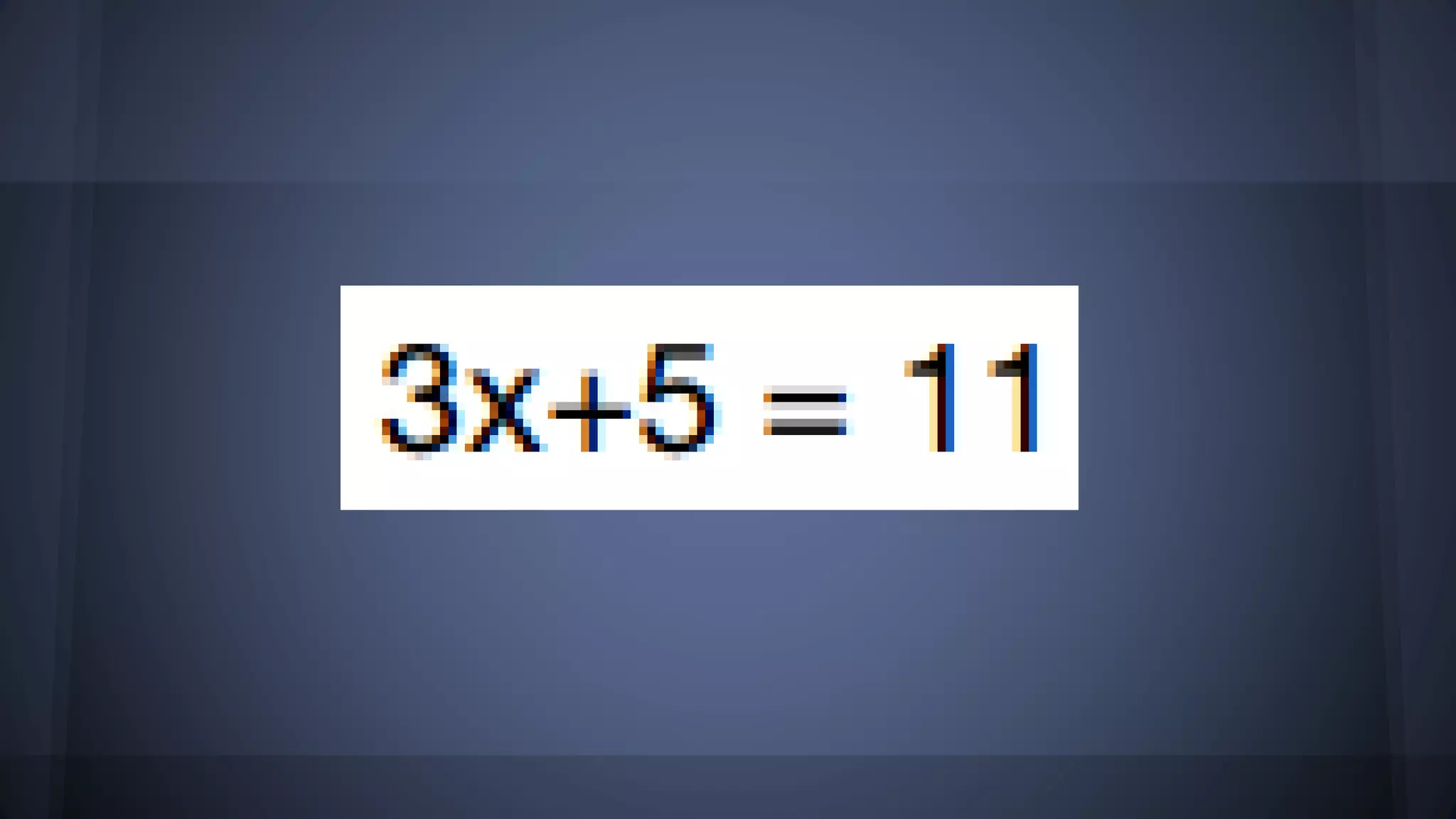

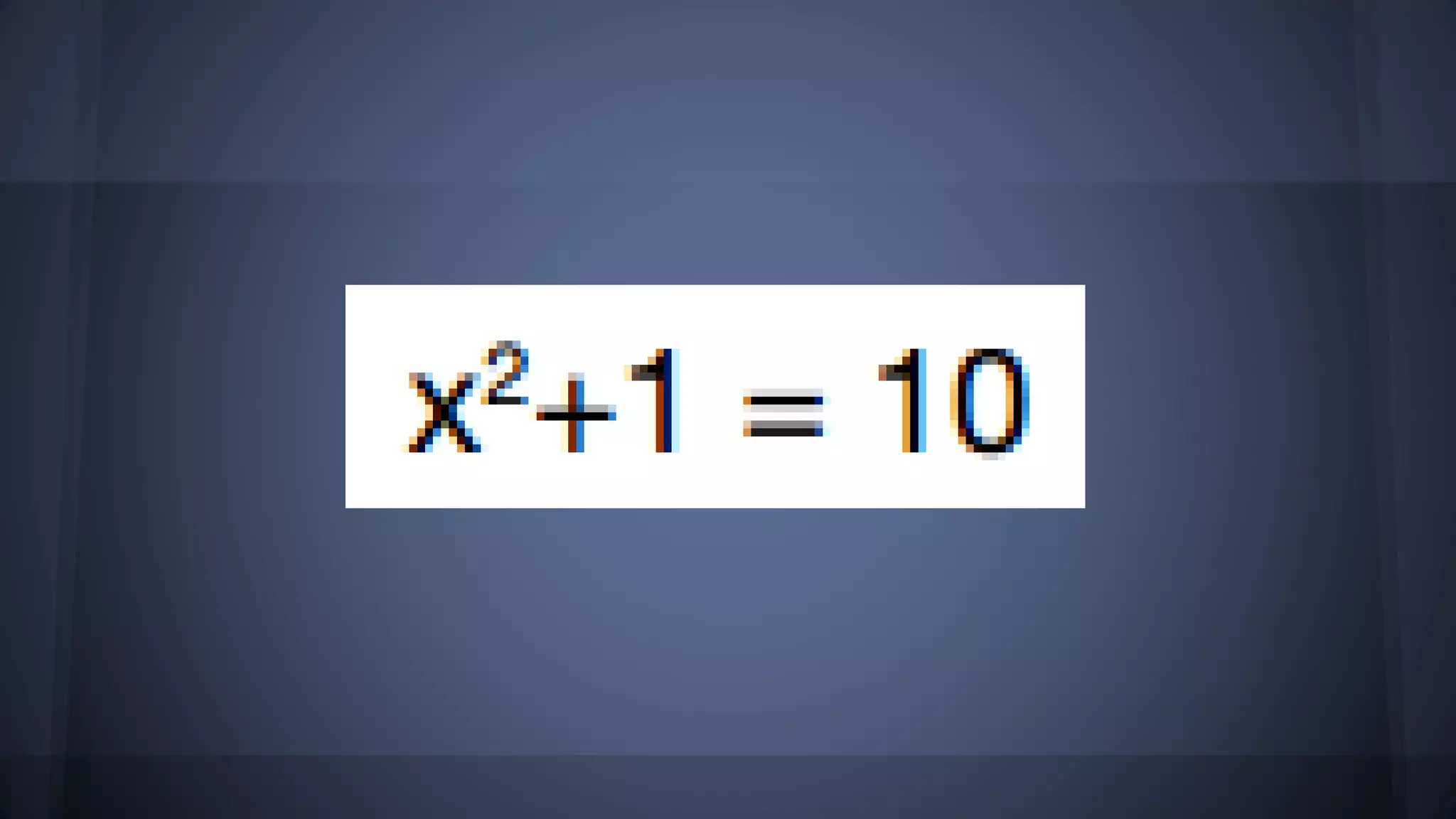

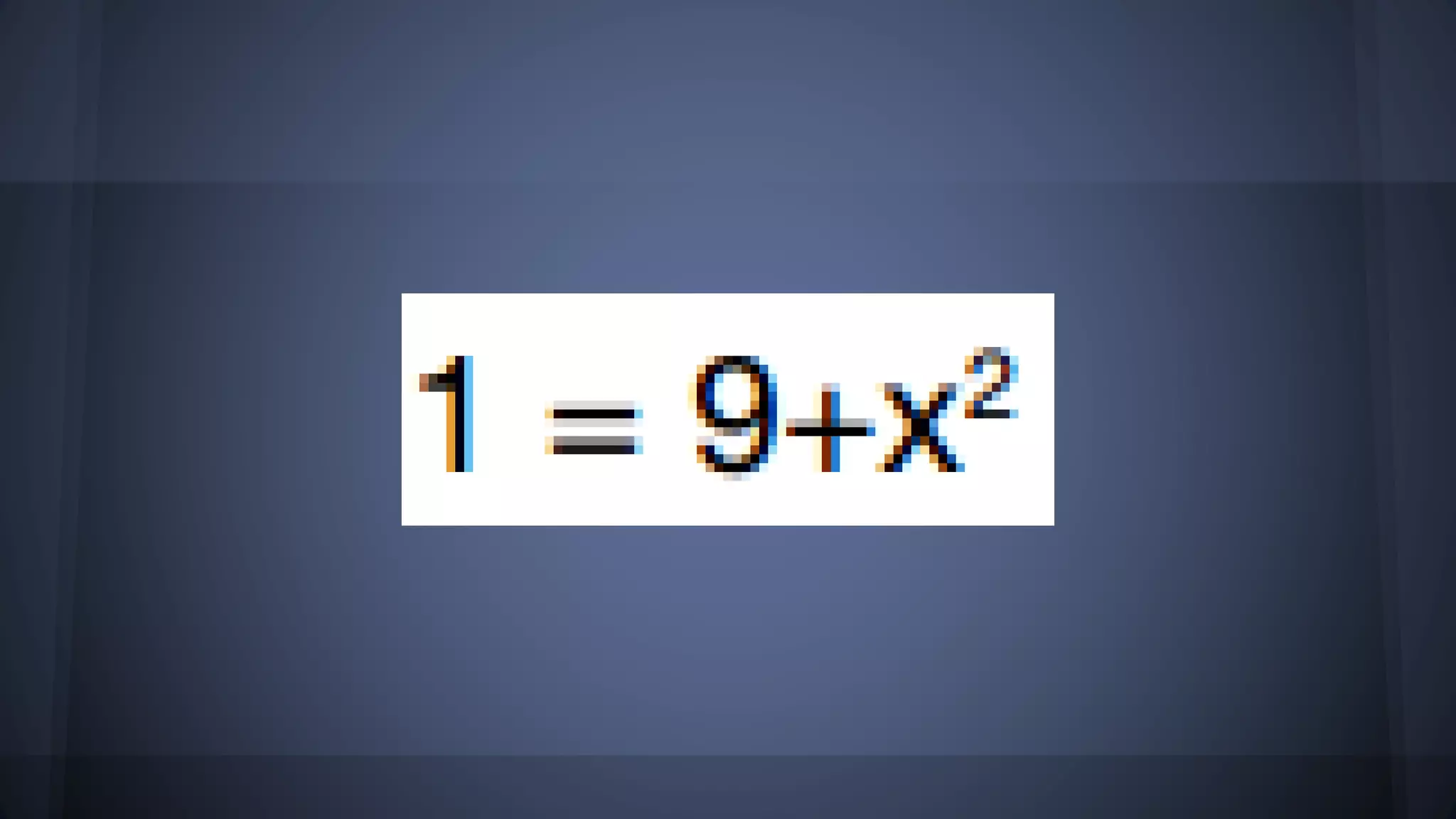

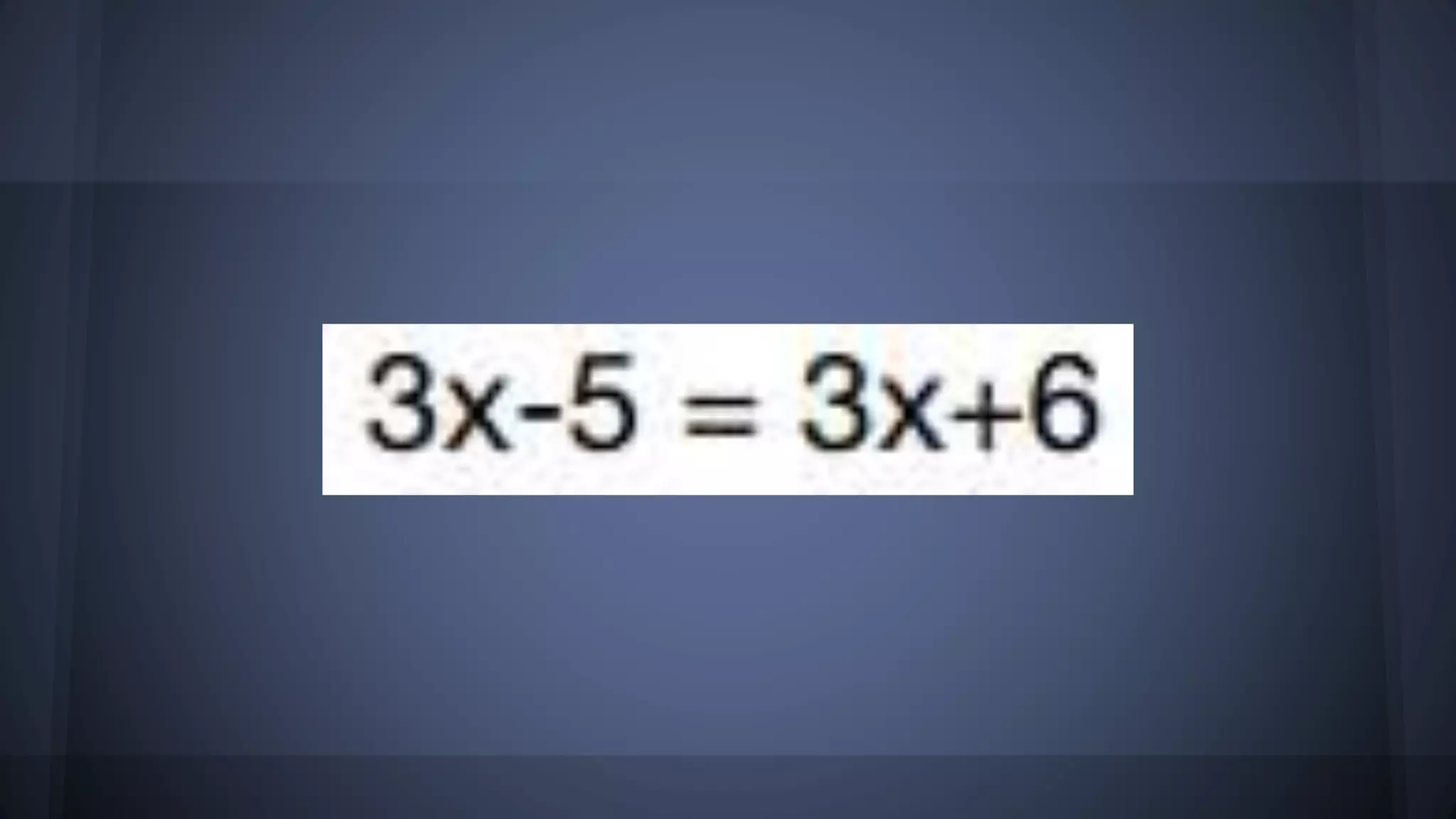

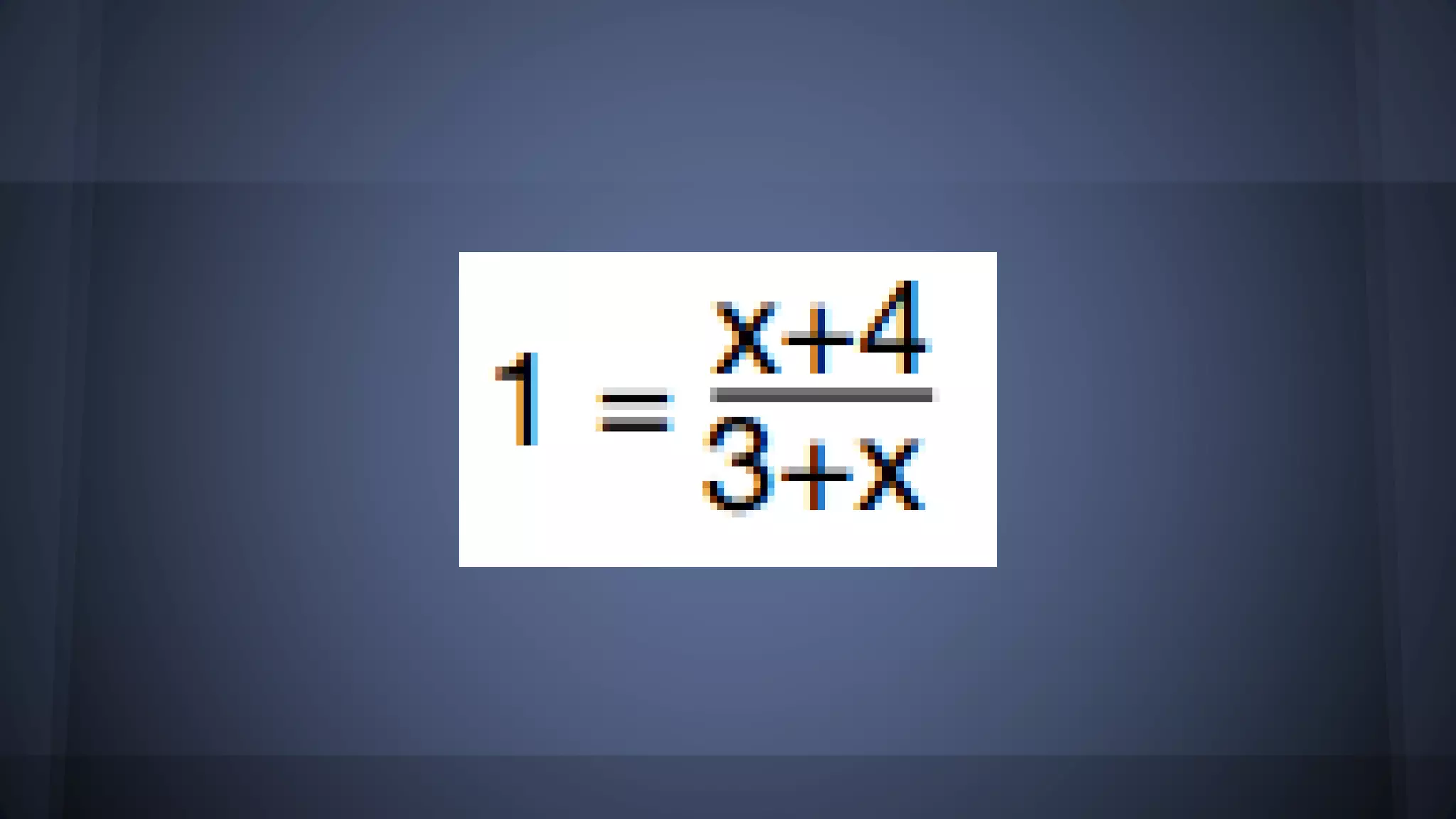

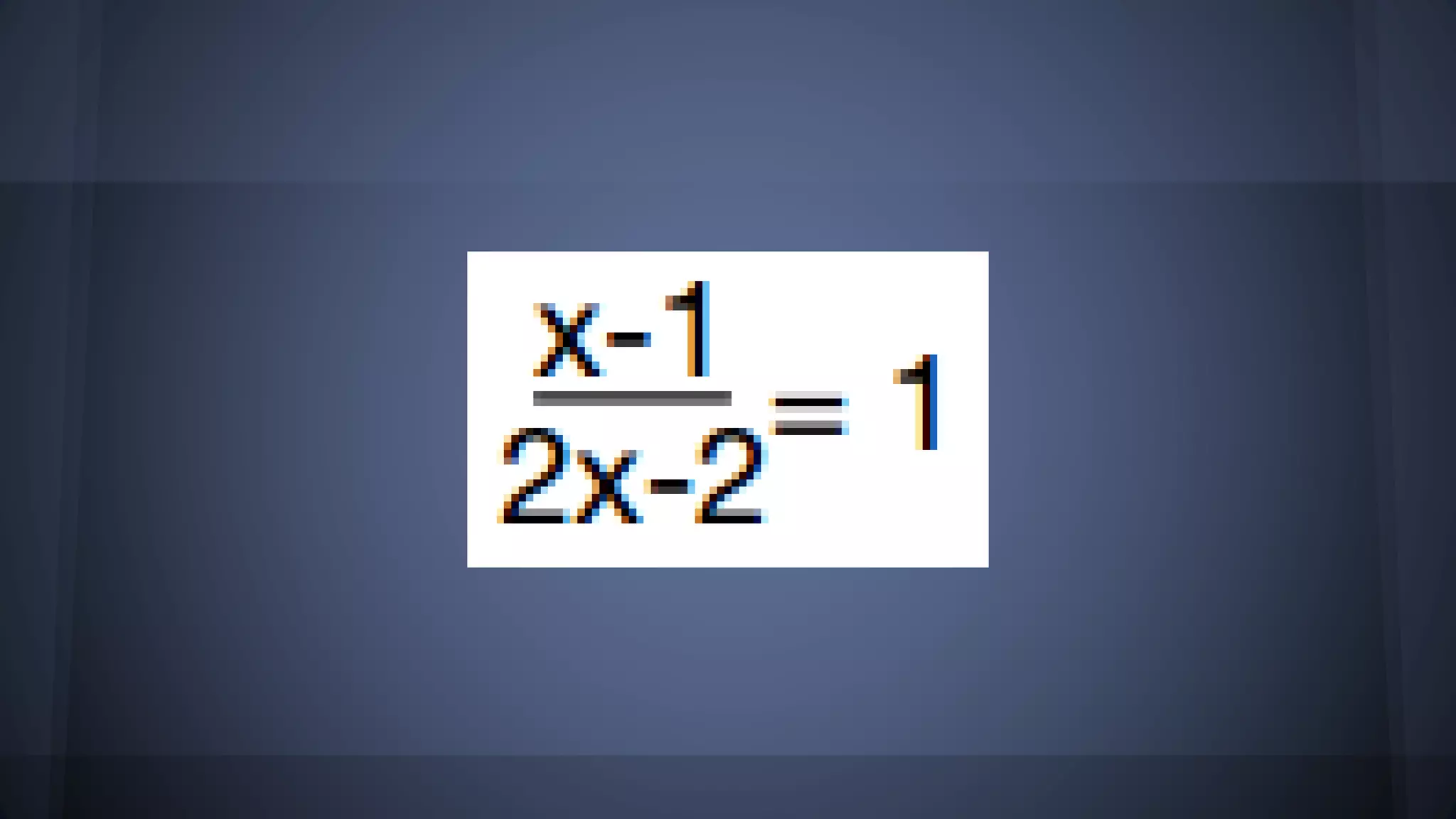

The document discusses whether solutions exist for various equations. In three sentences: It asks if solutions exist for different equations and provides explanations for each. For the equations 3x = 6, x^2 = 9, and x^2 >= 0 + 9, solutions do exist as you can find values of x that satisfy the equations. However, for the equations 3x - 5 = 3x + 6, x+4 = x+3, and the fraction equation given, no solutions exist as the equations cannot be satisfied no matter the value of x.