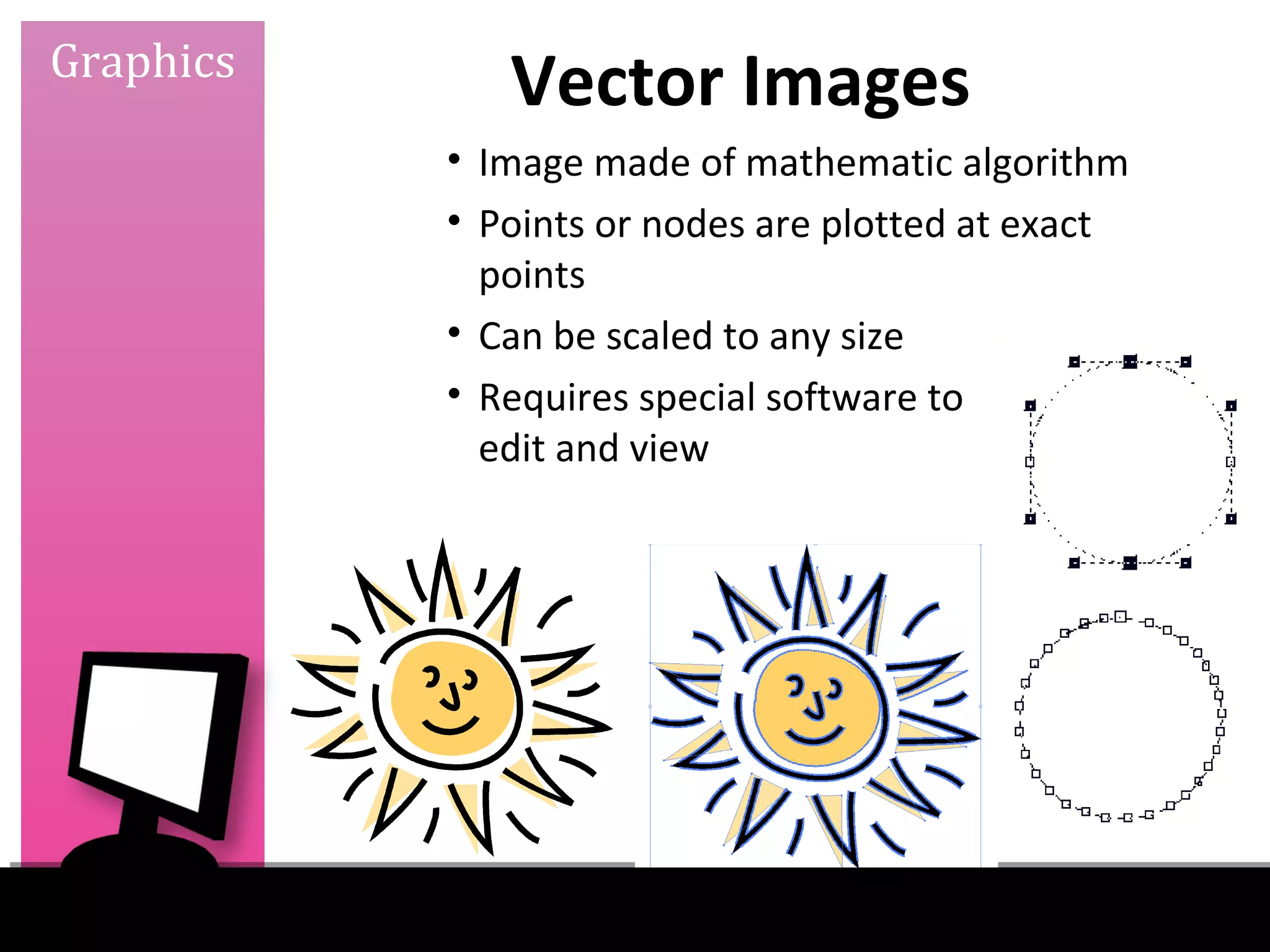
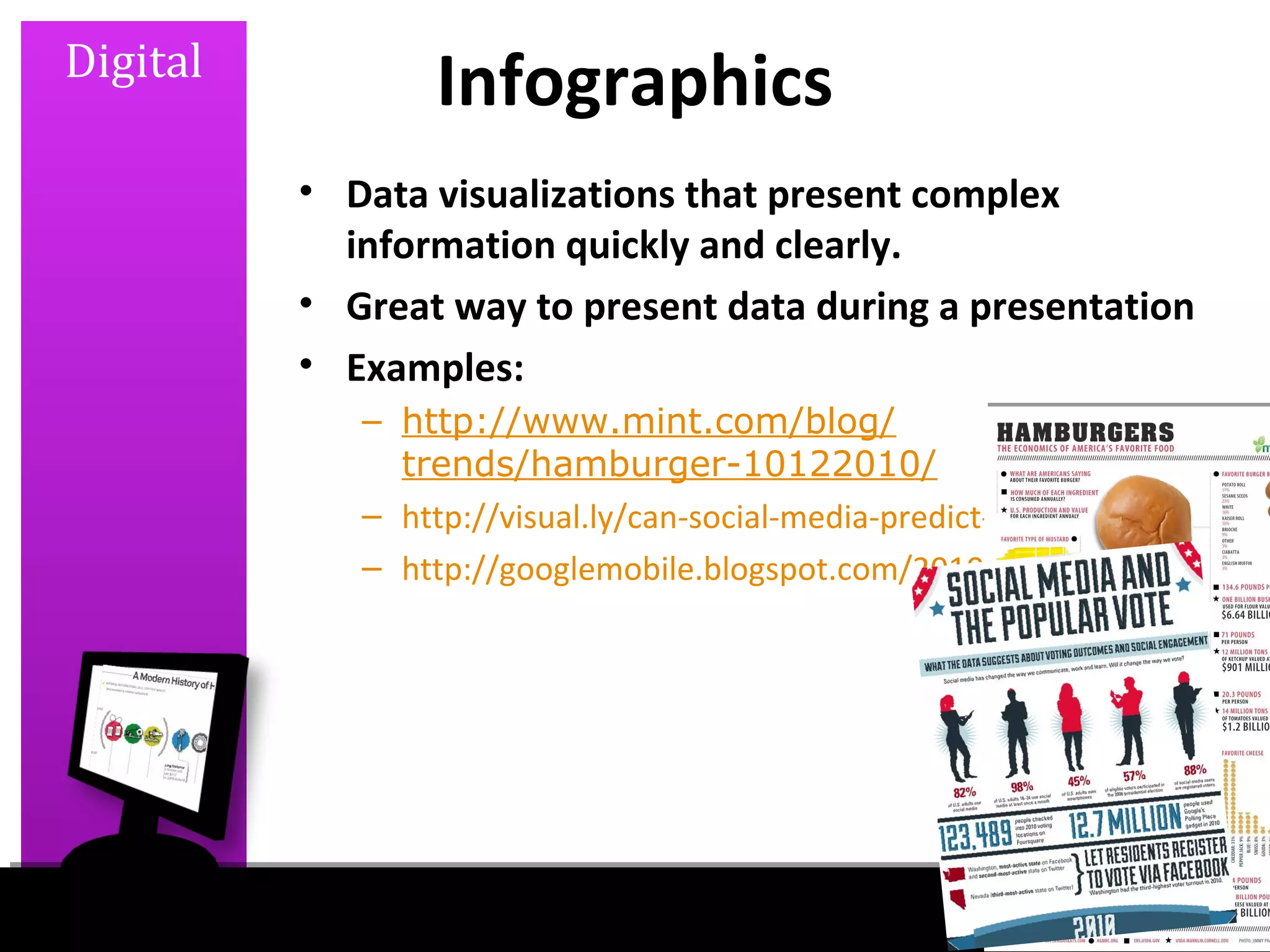
This document discusses graphics, design, color, copyright, and digital concepts for educational purposes. It provides information on visual learning, types of graphics like photos and diagrams, criteria for good graphics, raster and vector images, scaling graphics, elements of design, color models and printing basics, fair use and copyright guidelines, finding open resources, and common file formats. Examples and sources for finding infographics are also included. The document aims to teach best practices for using visual elements in an educational context.