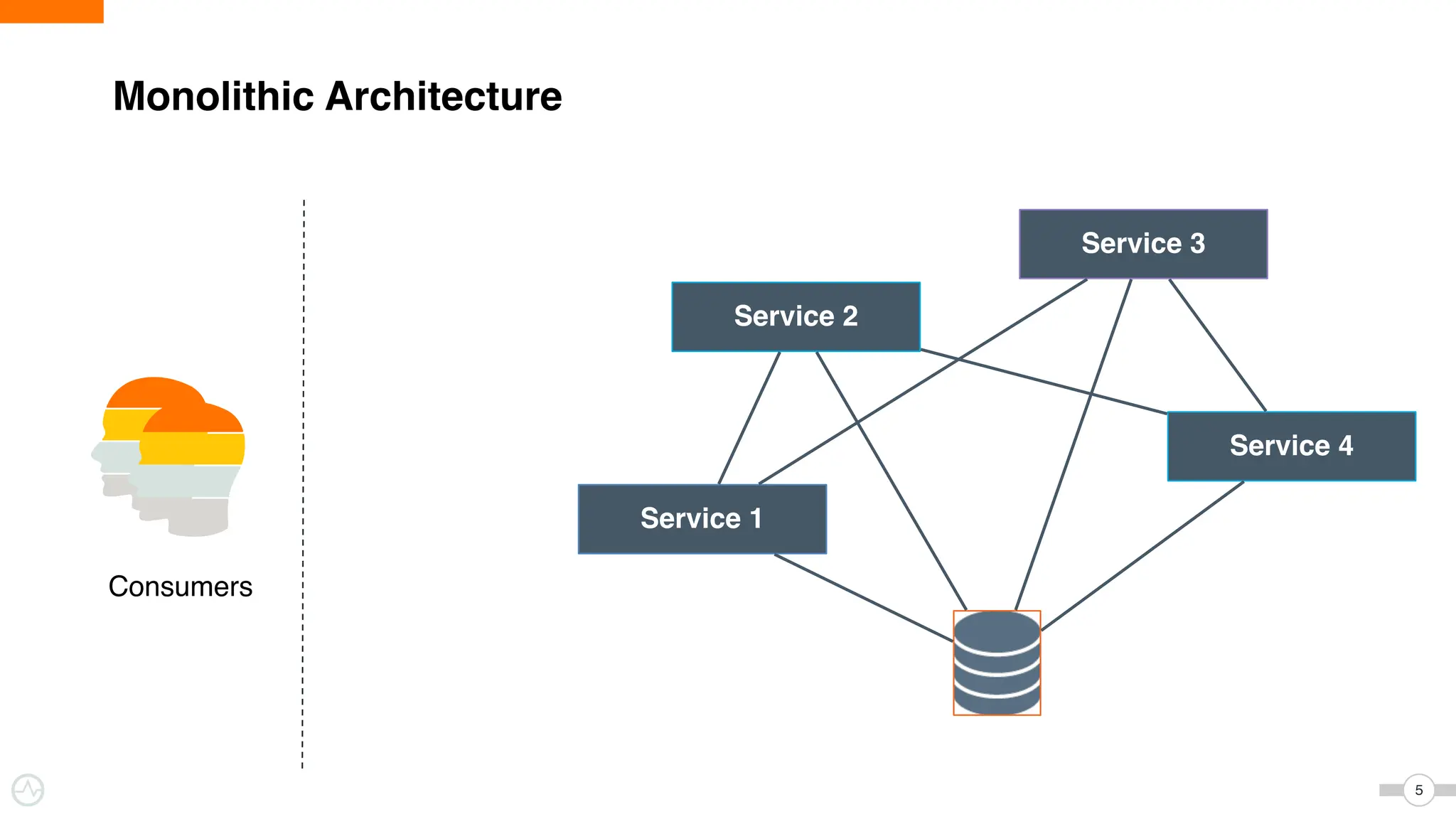
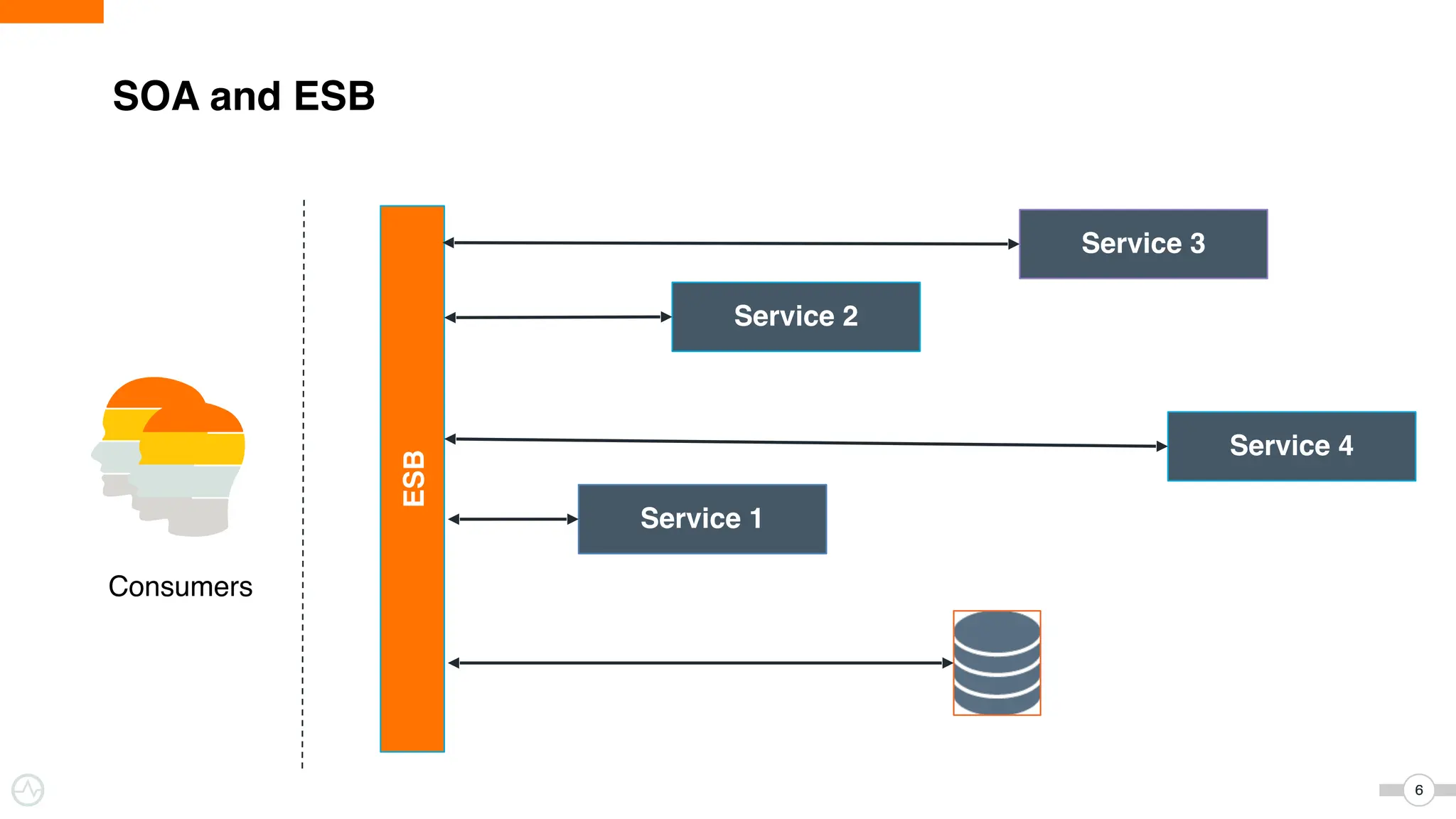
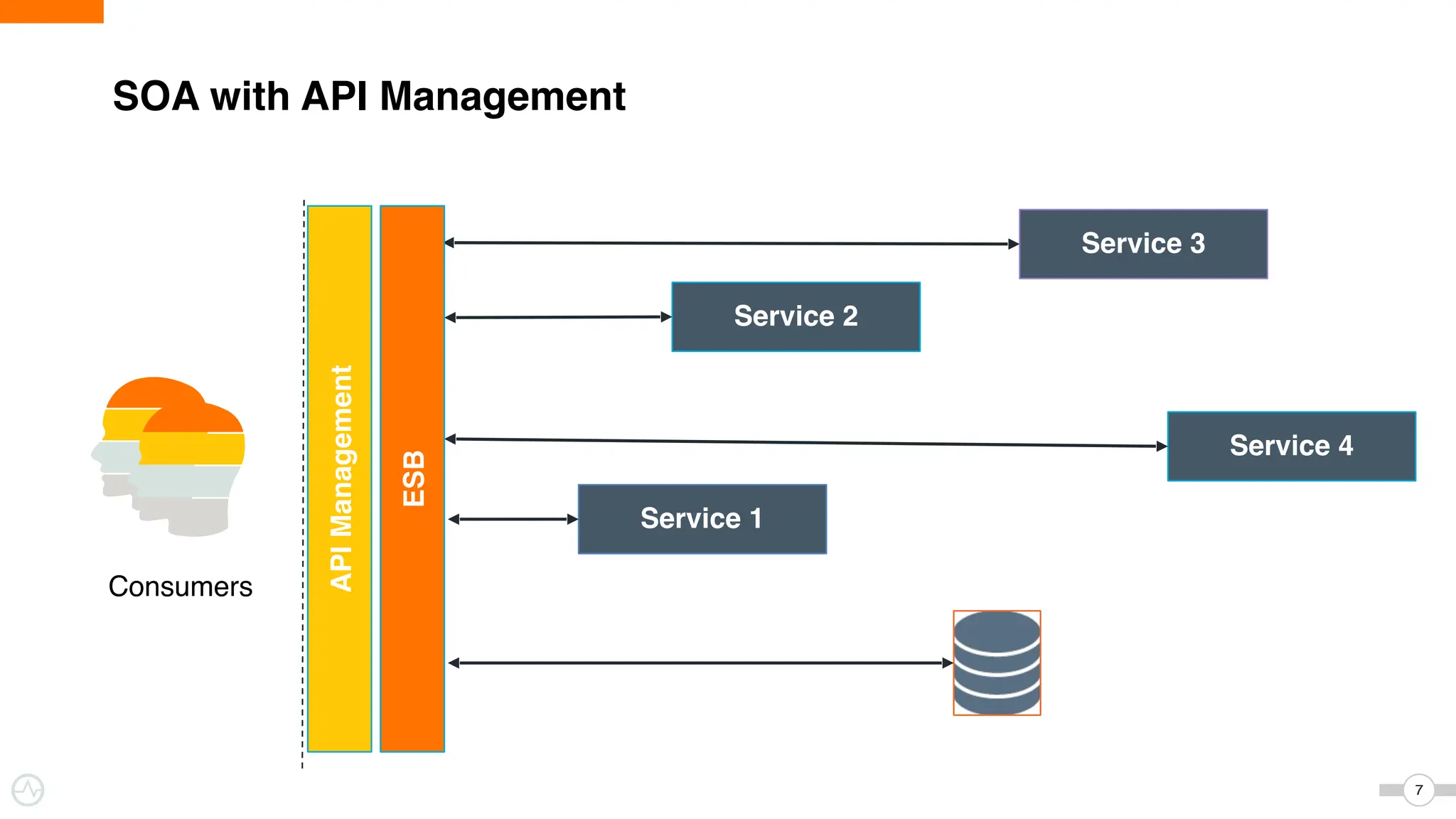
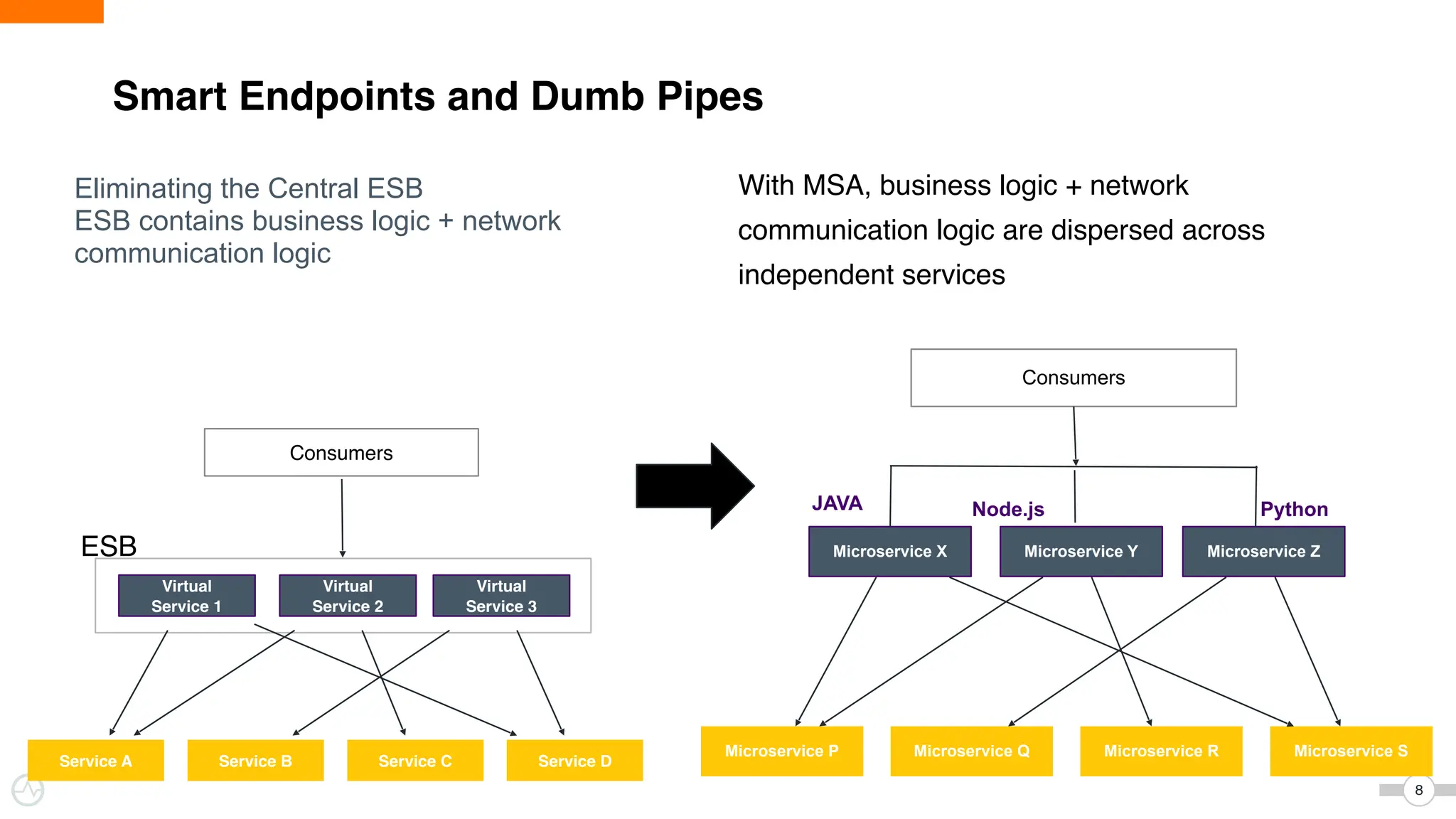
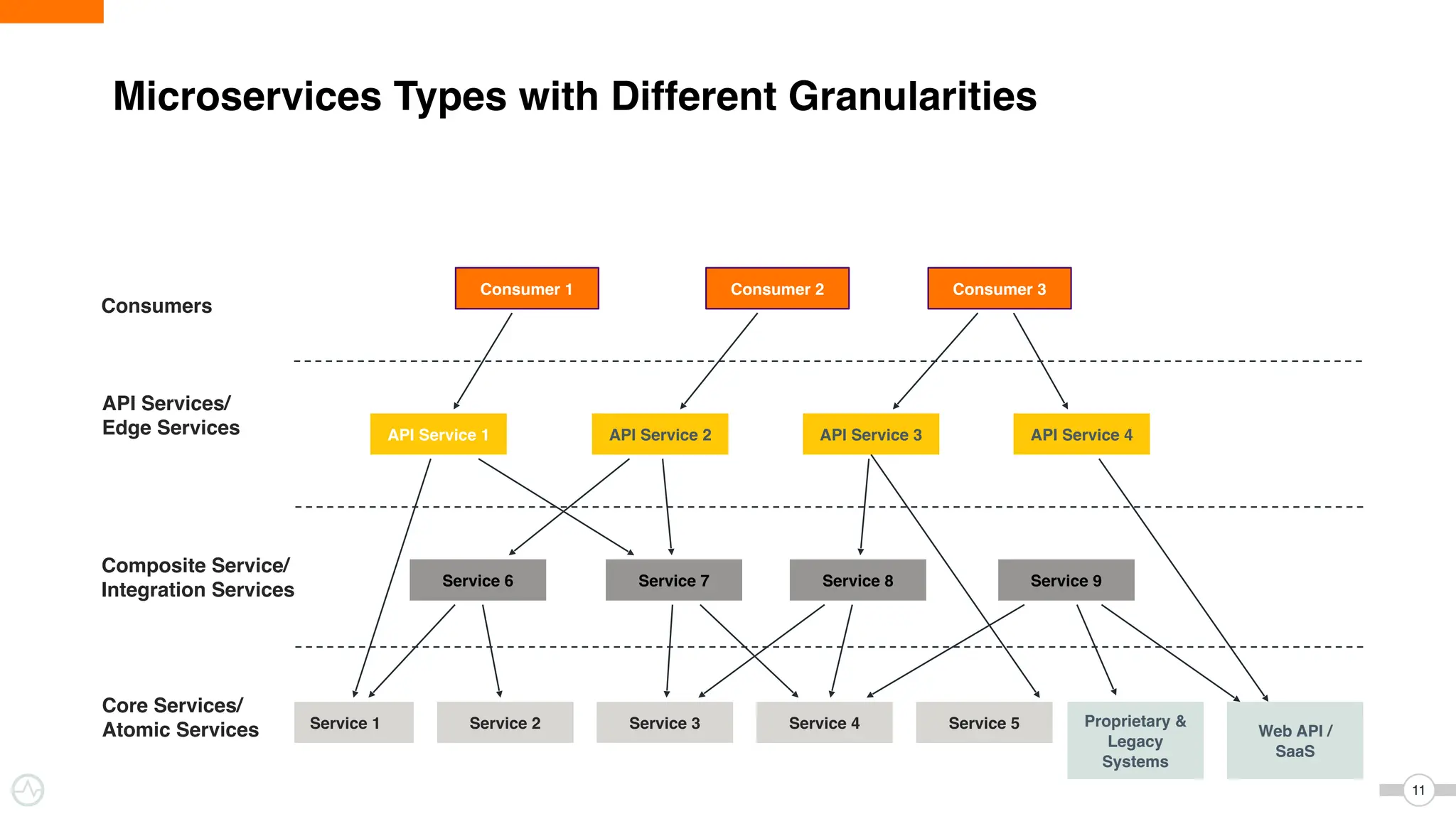
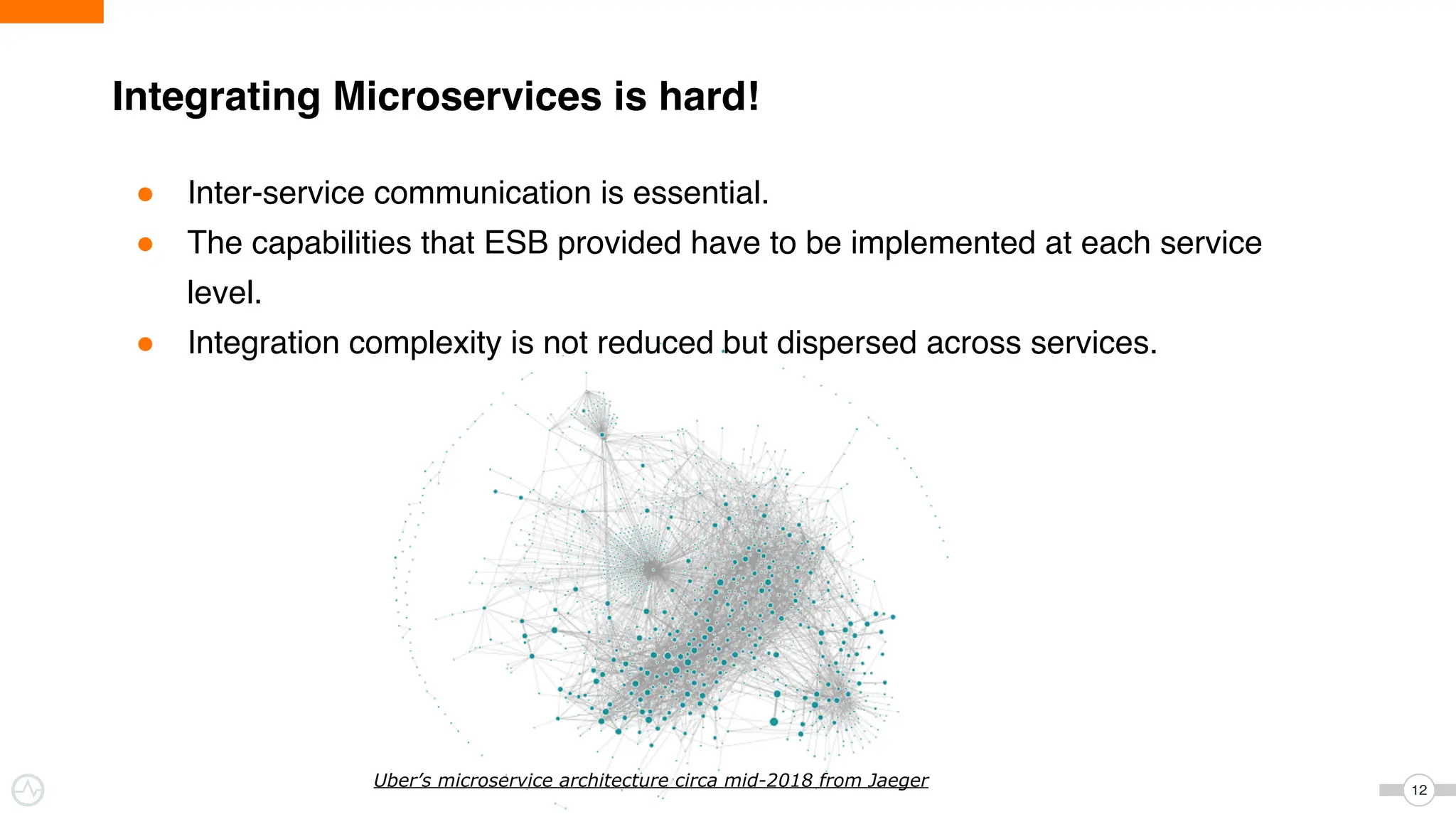
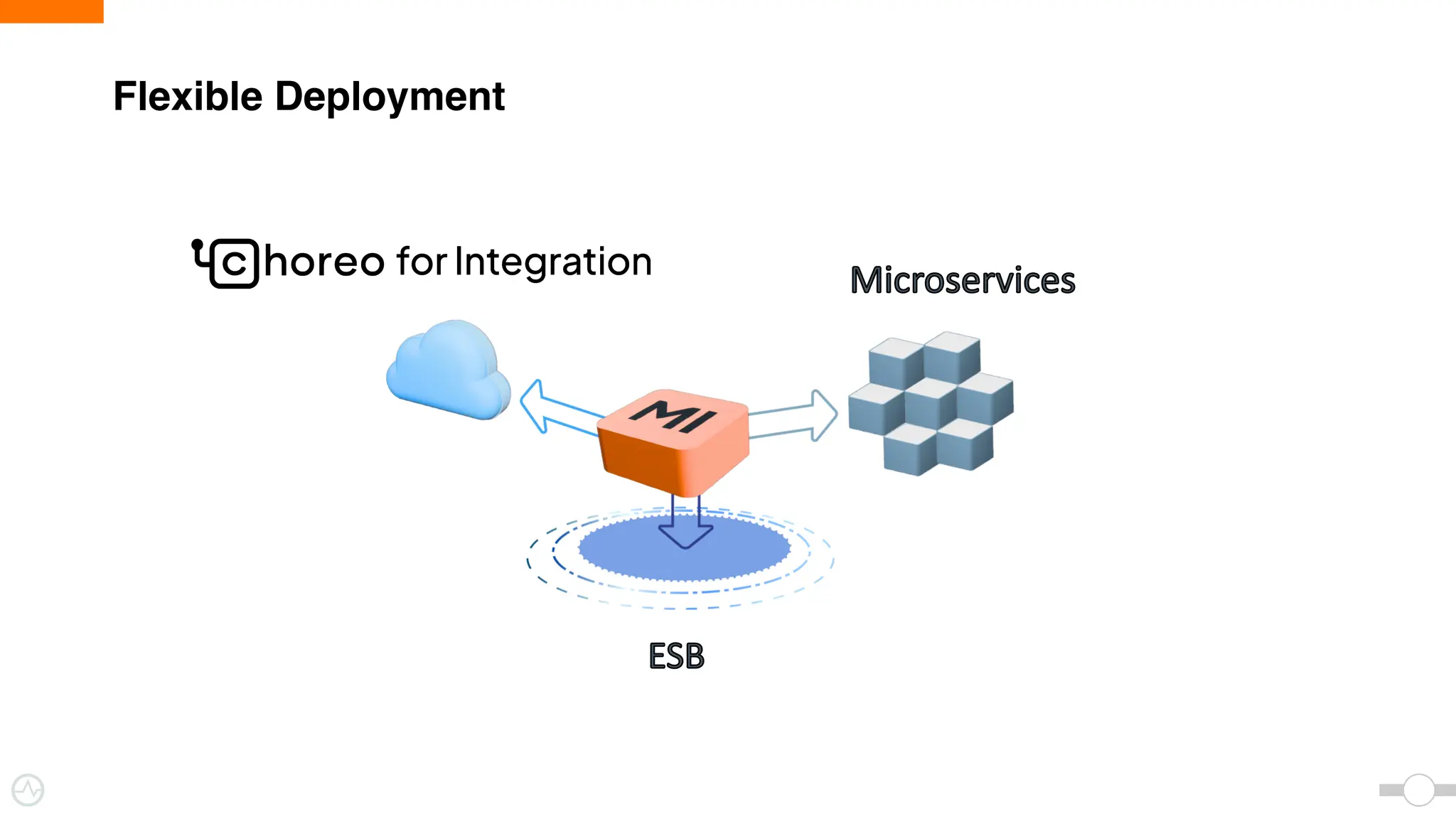
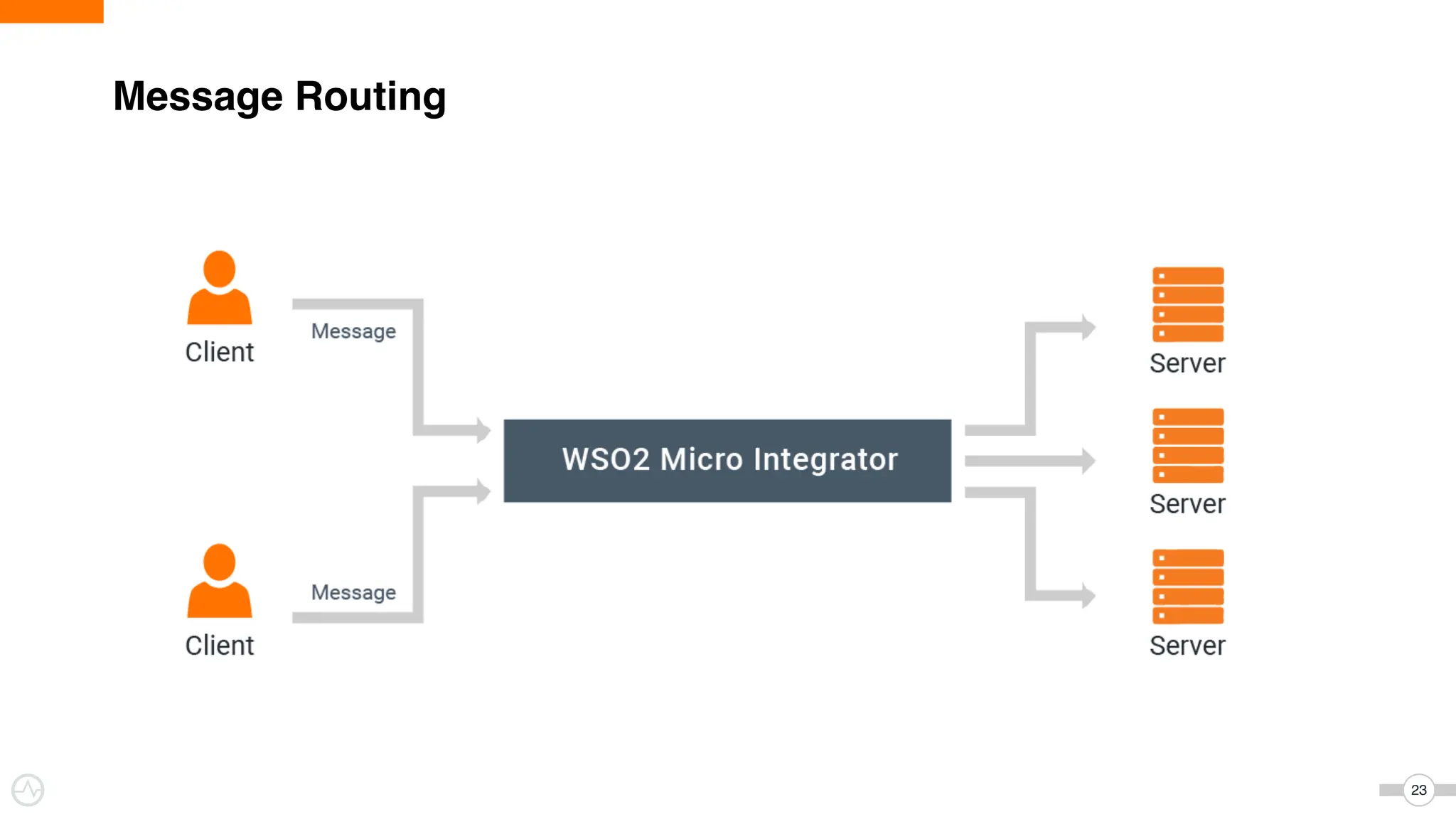
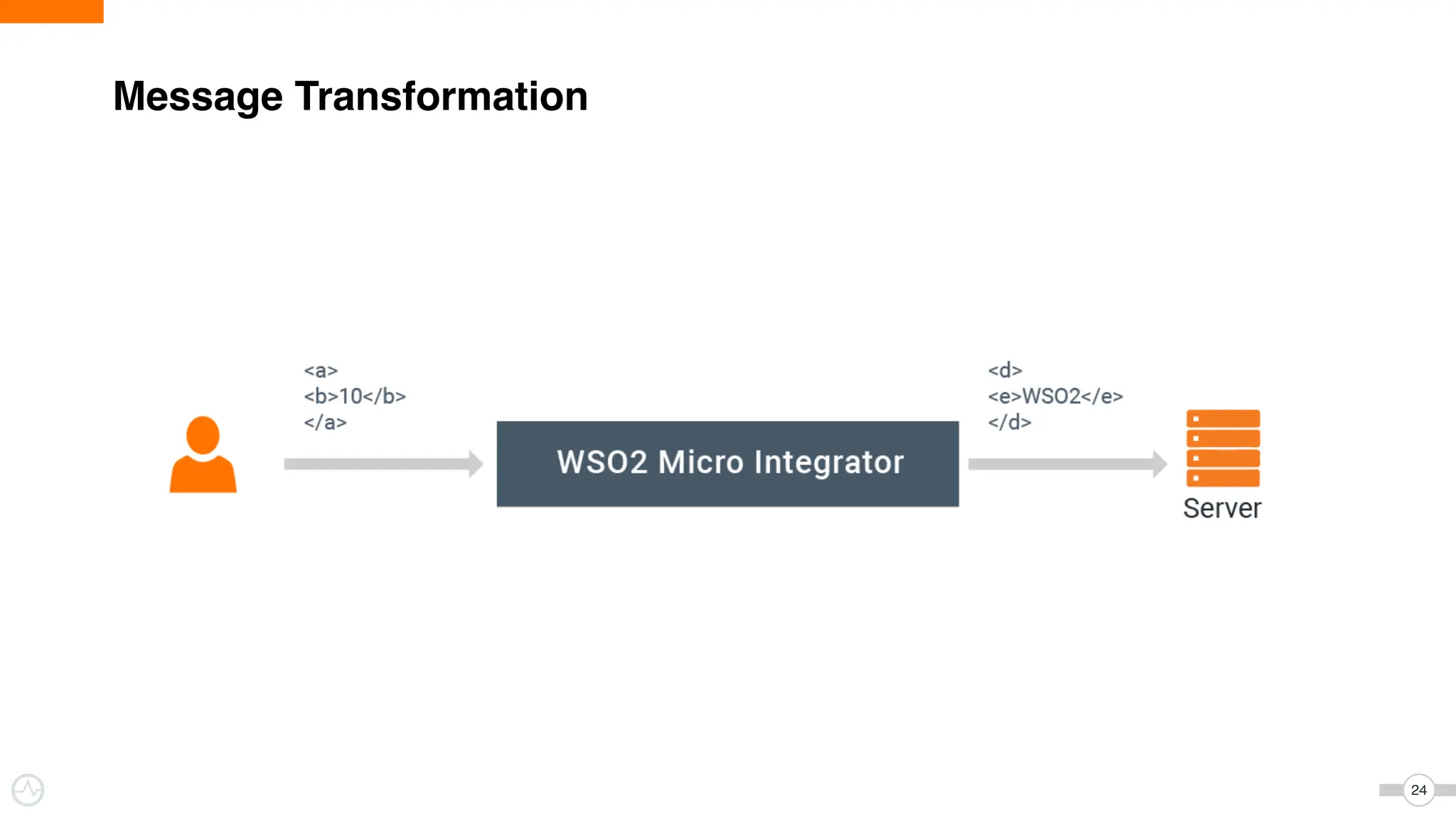
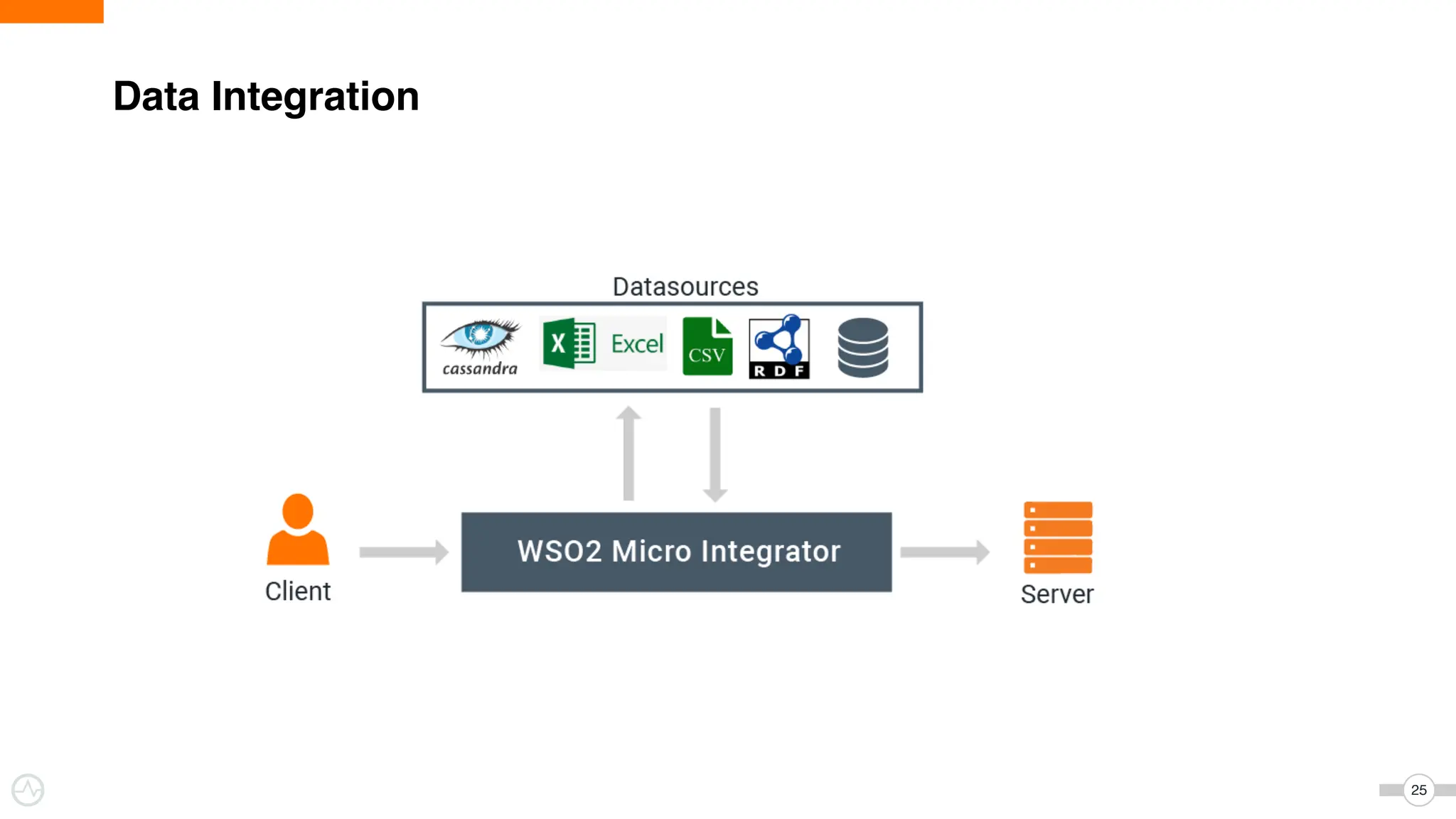
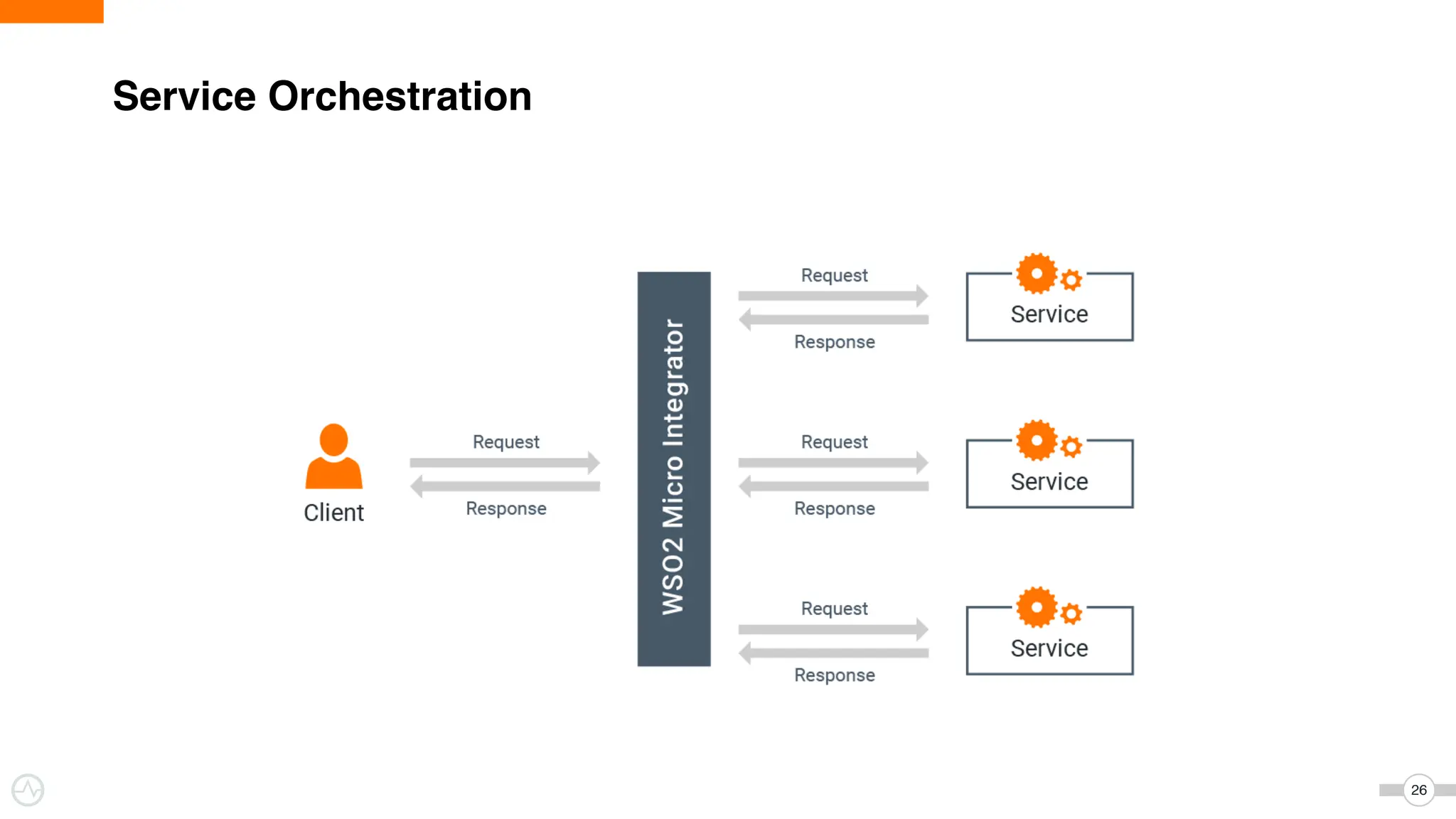
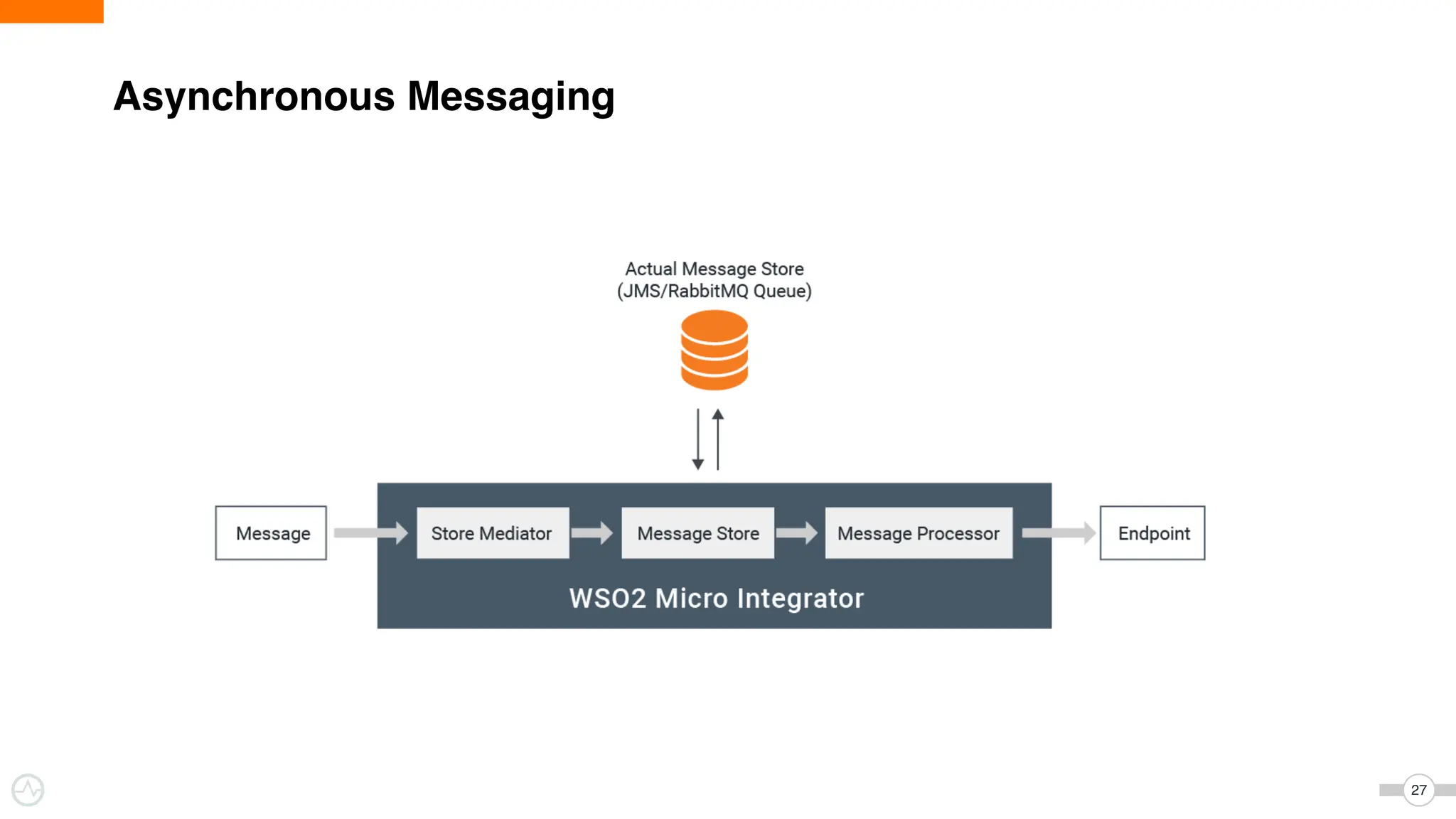
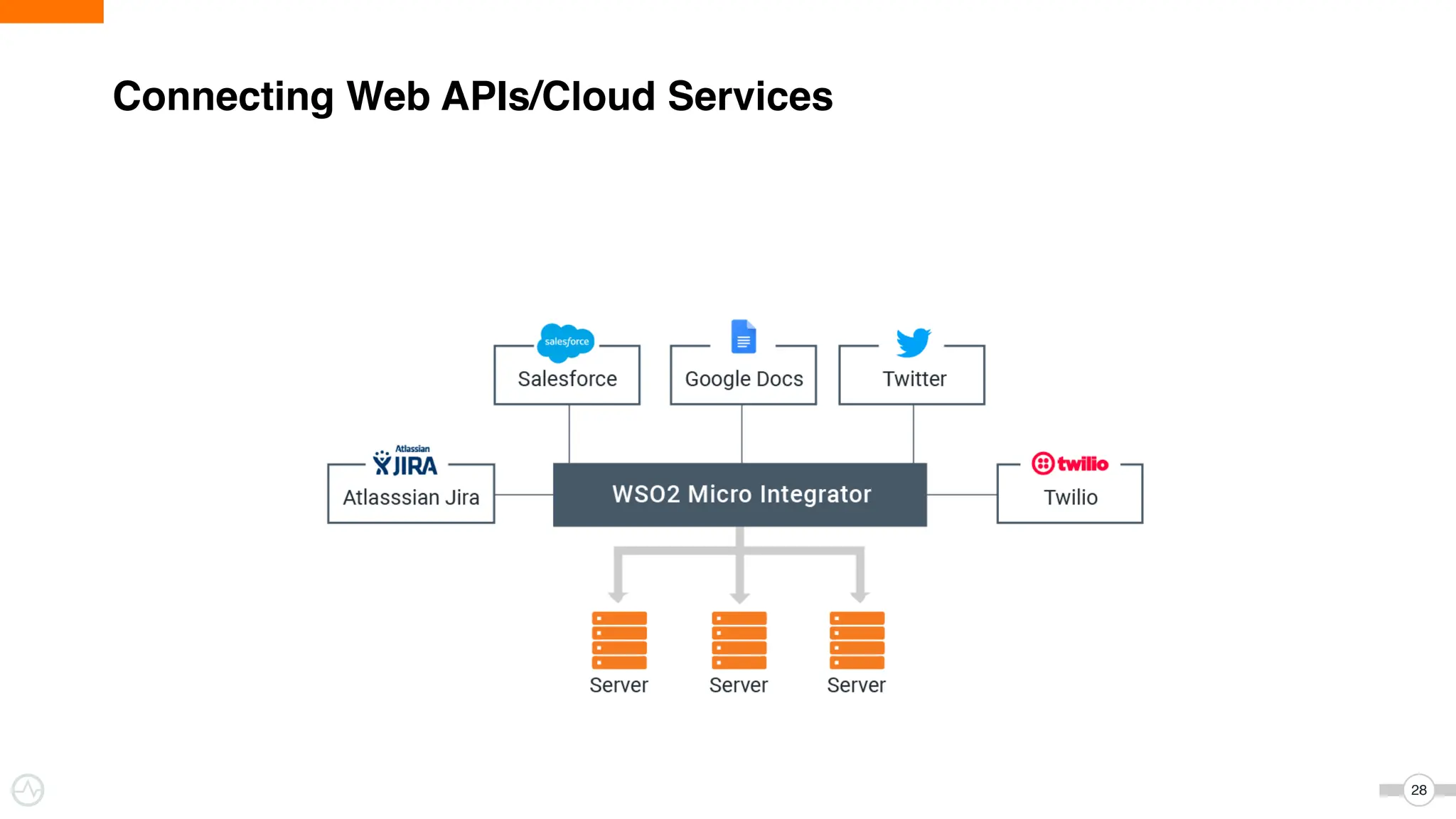
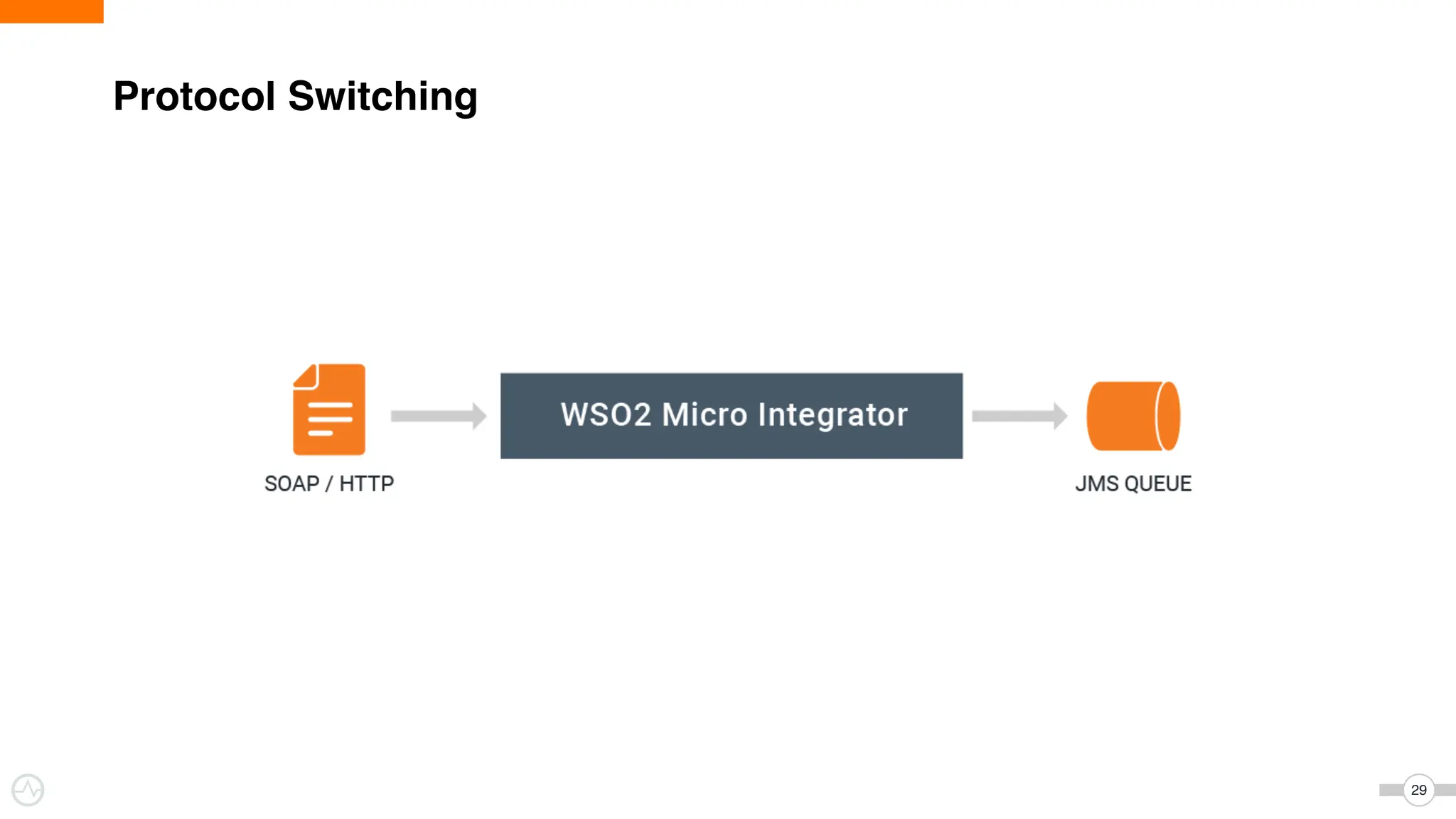
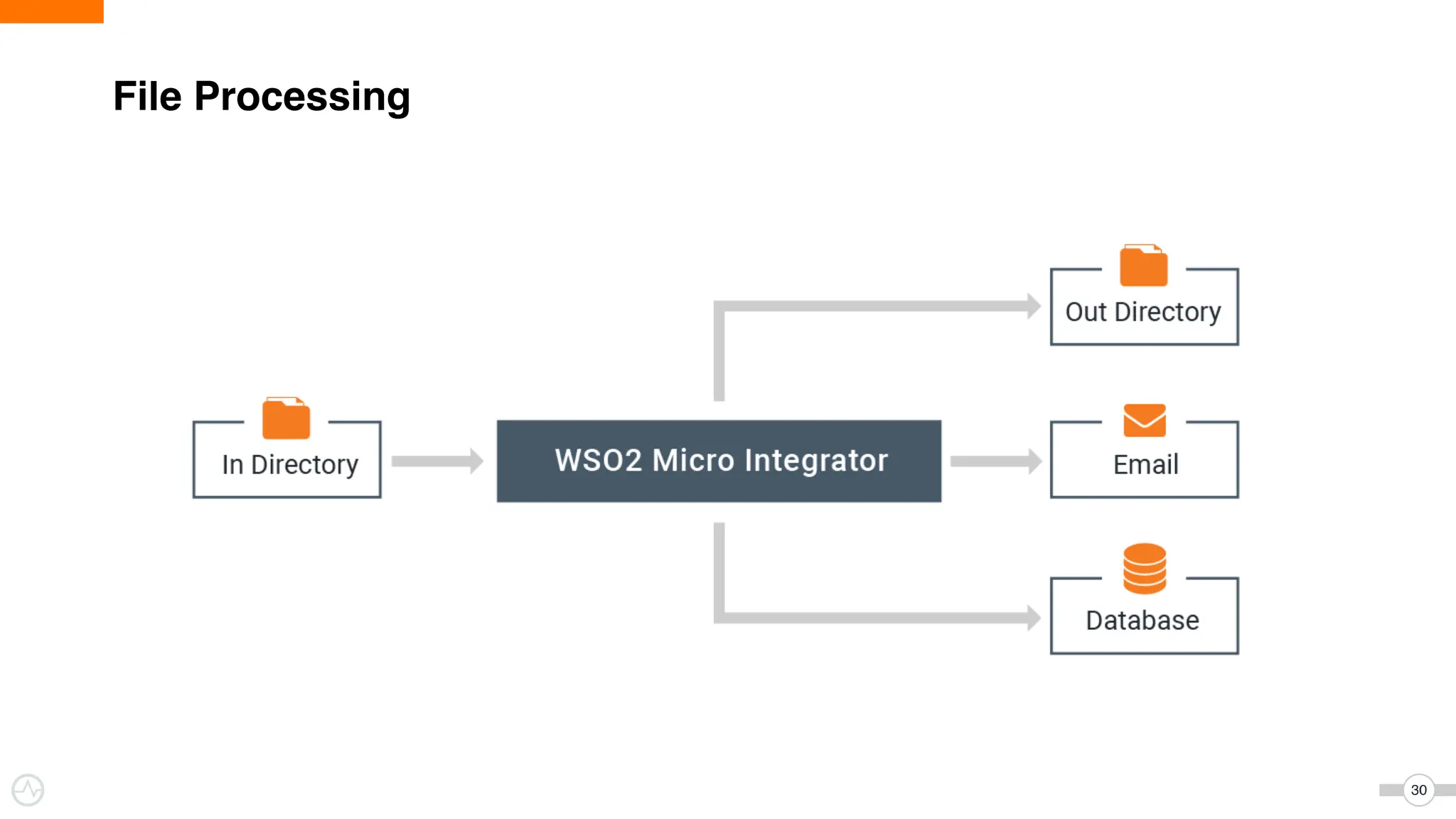
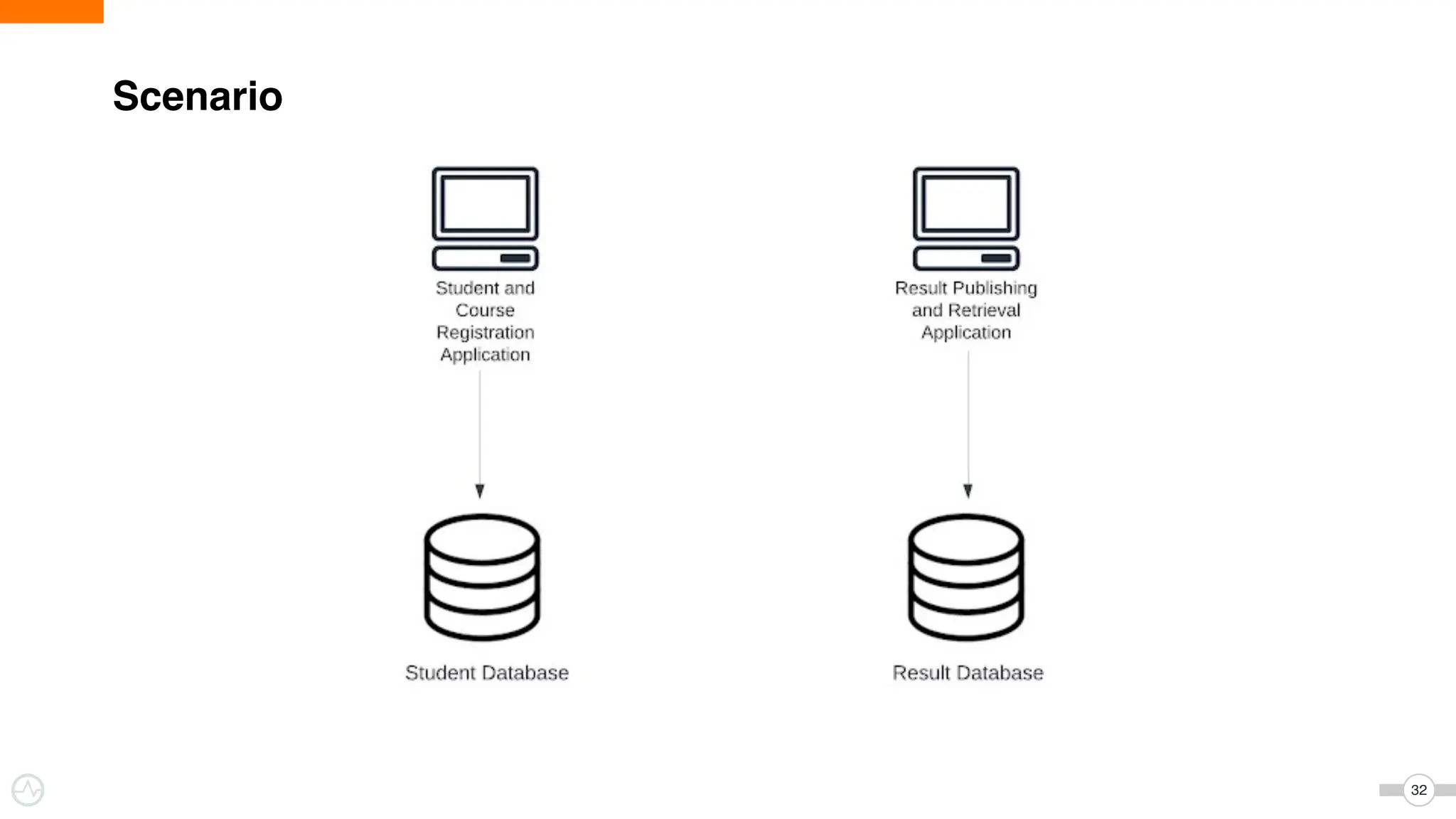
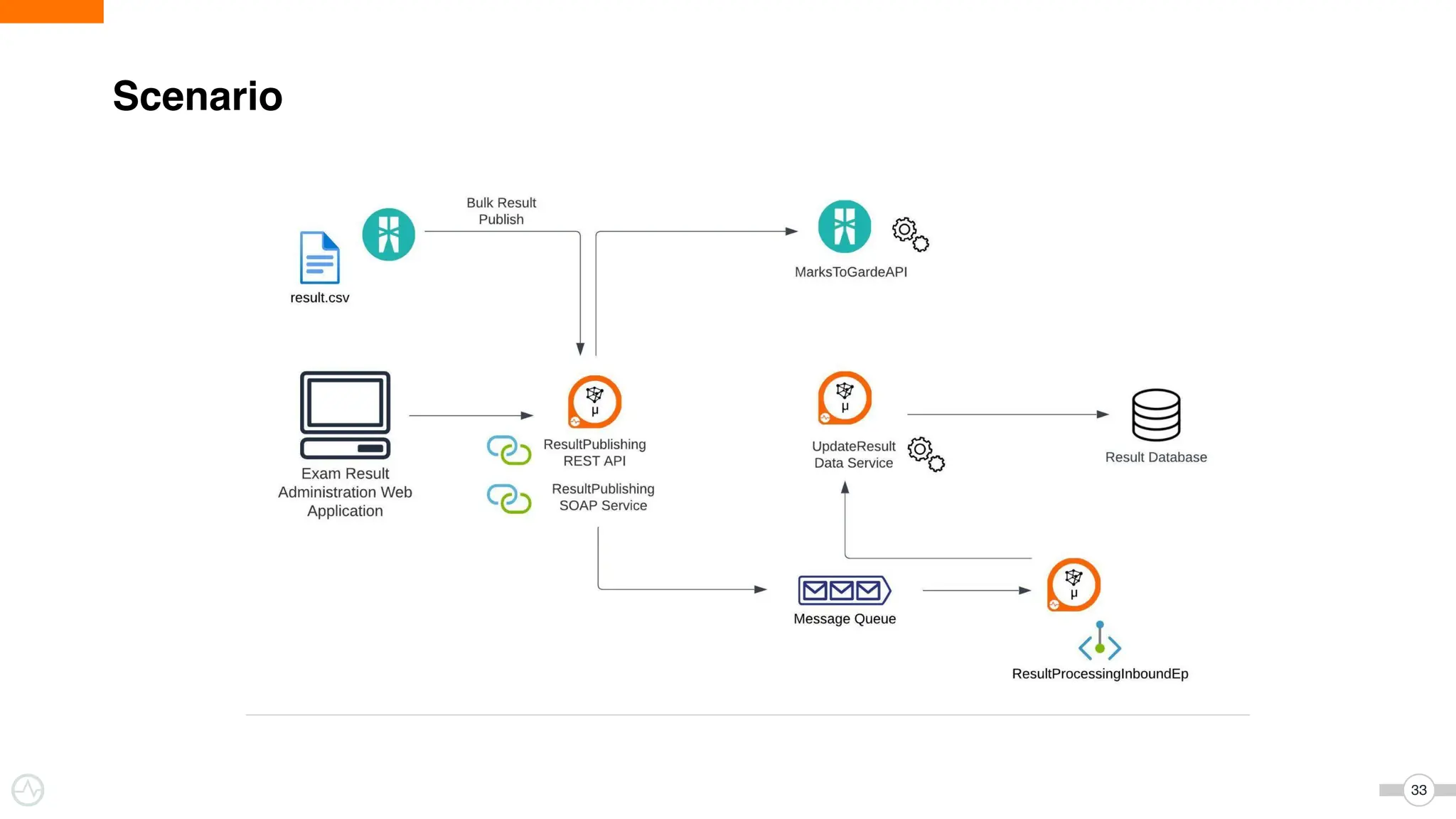
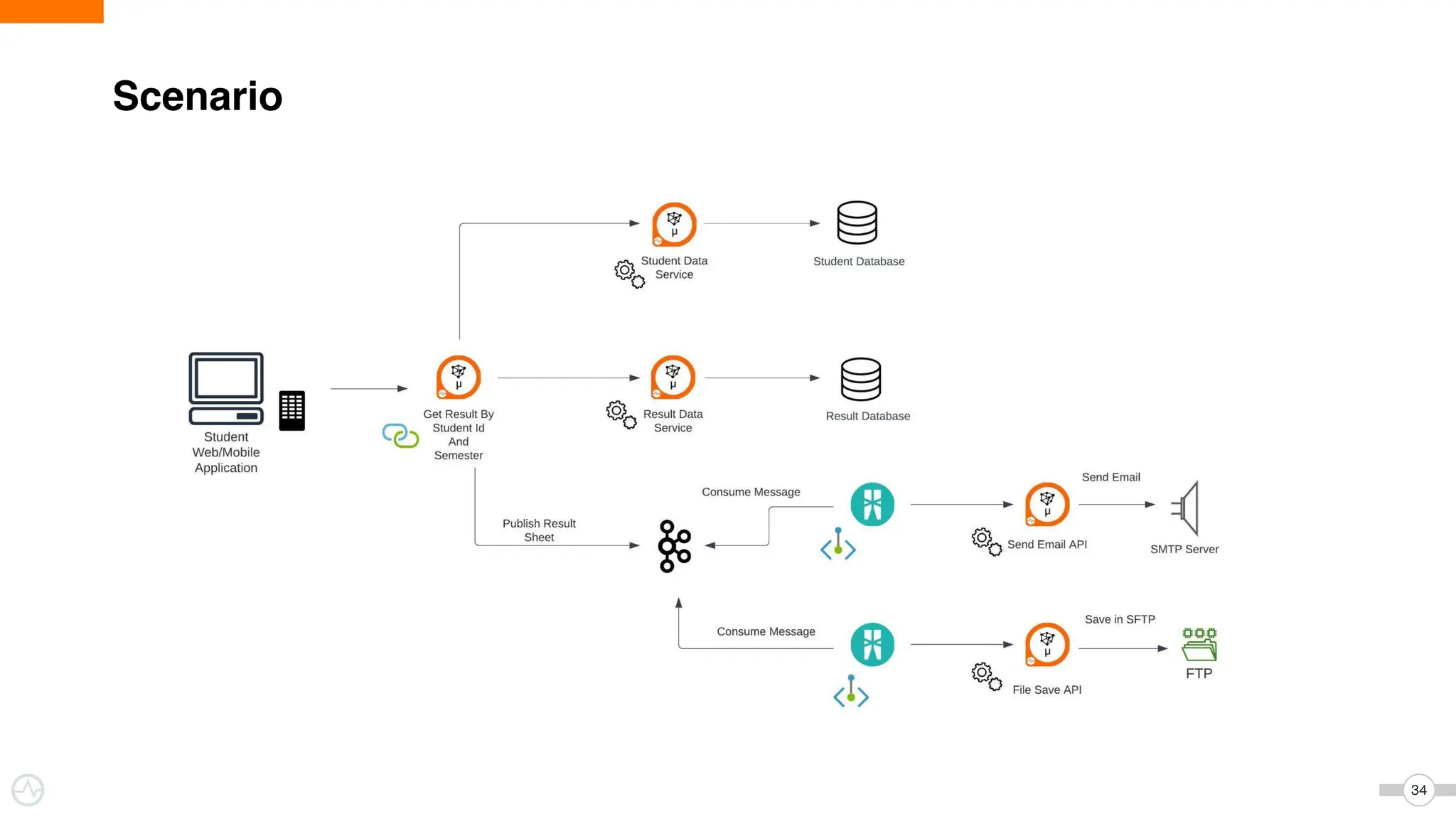
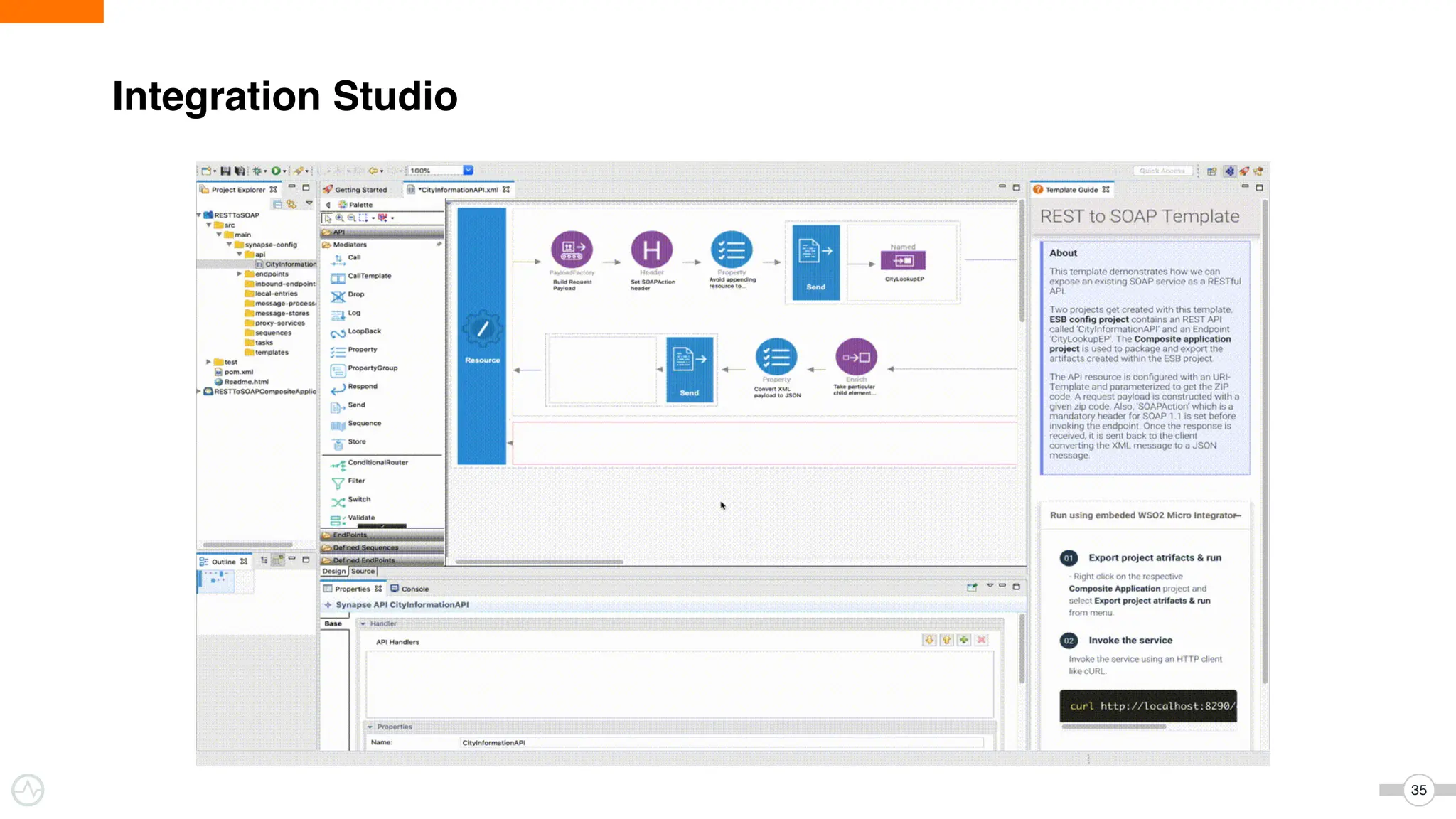
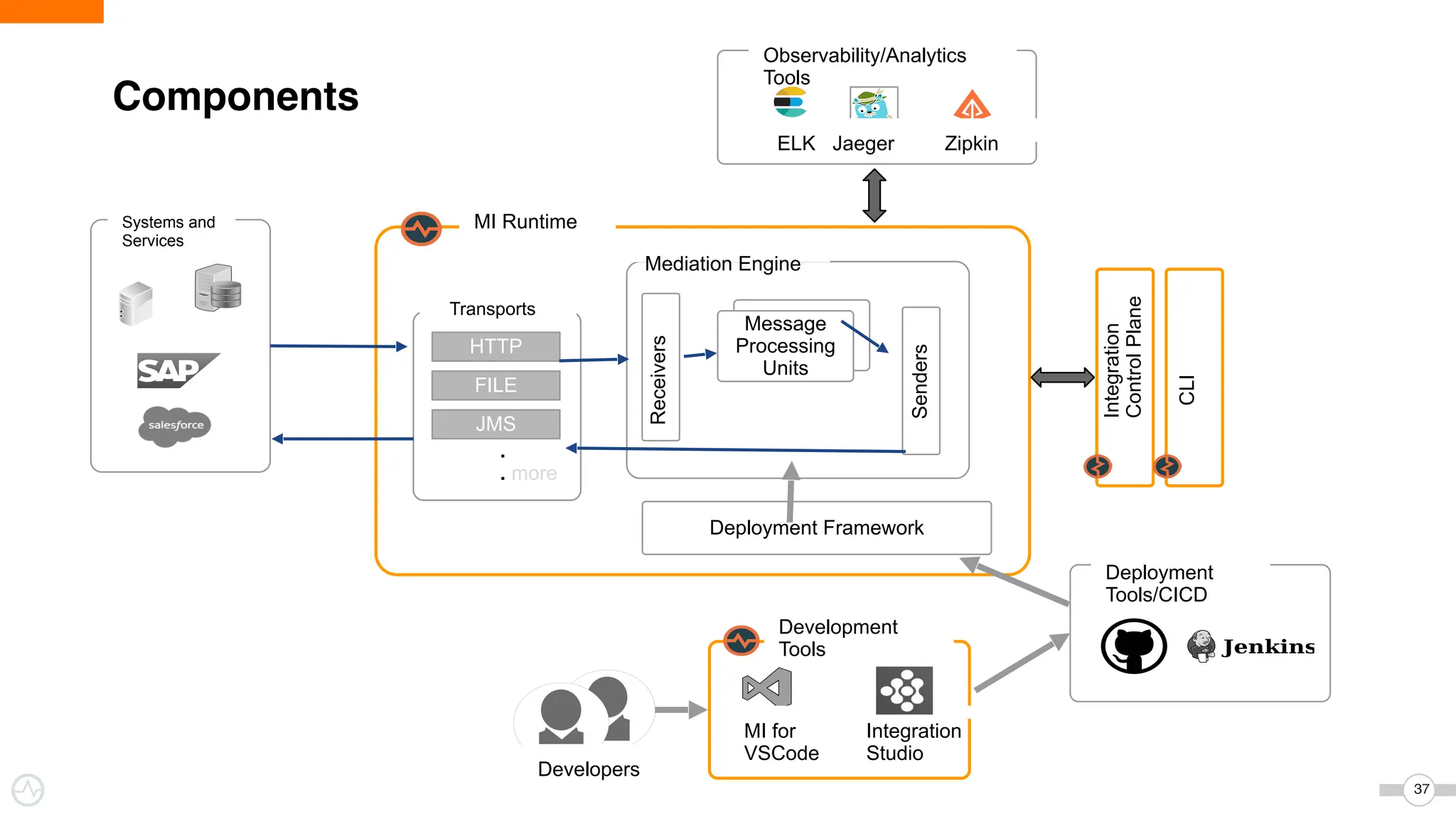
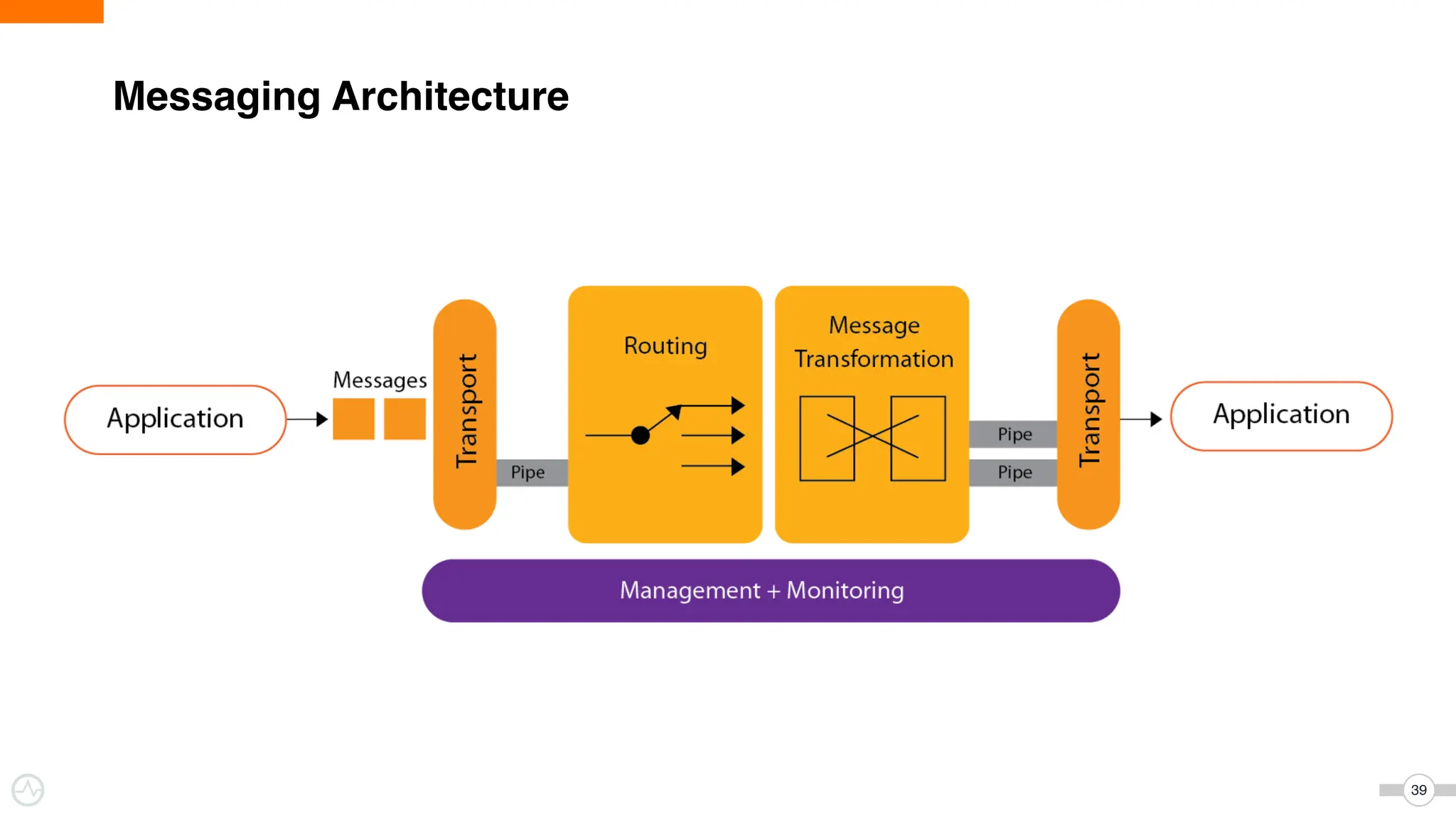
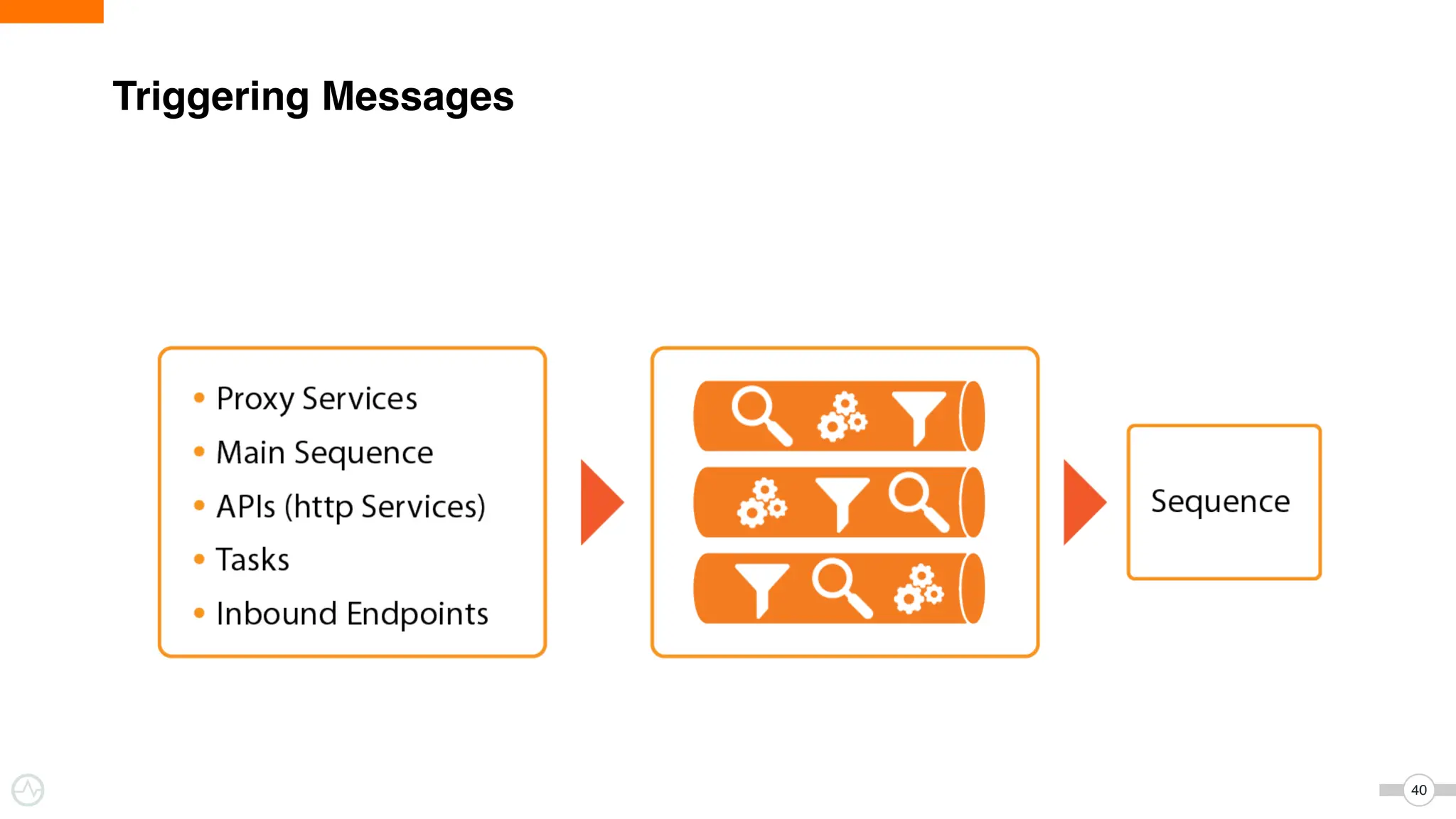
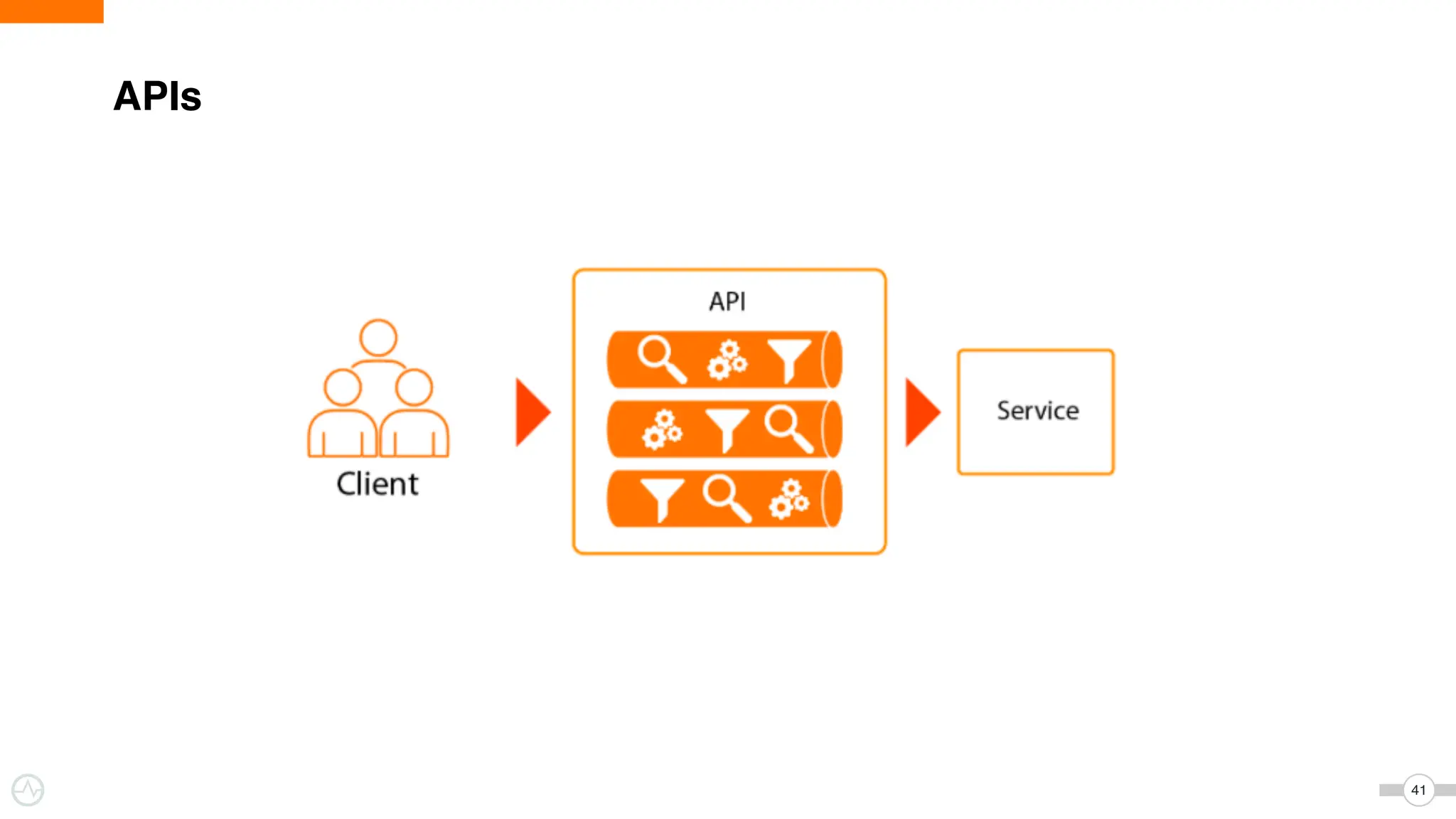
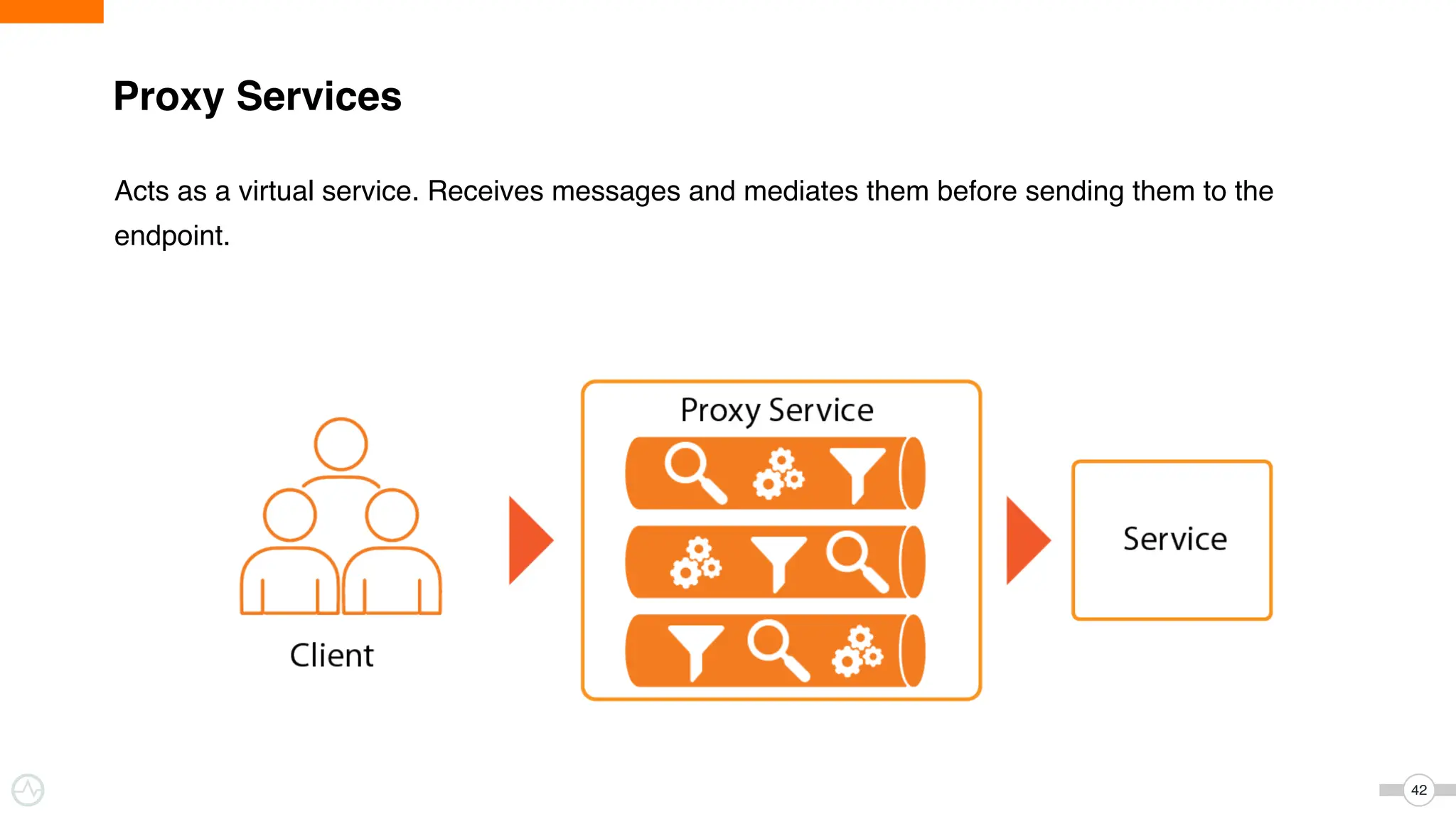
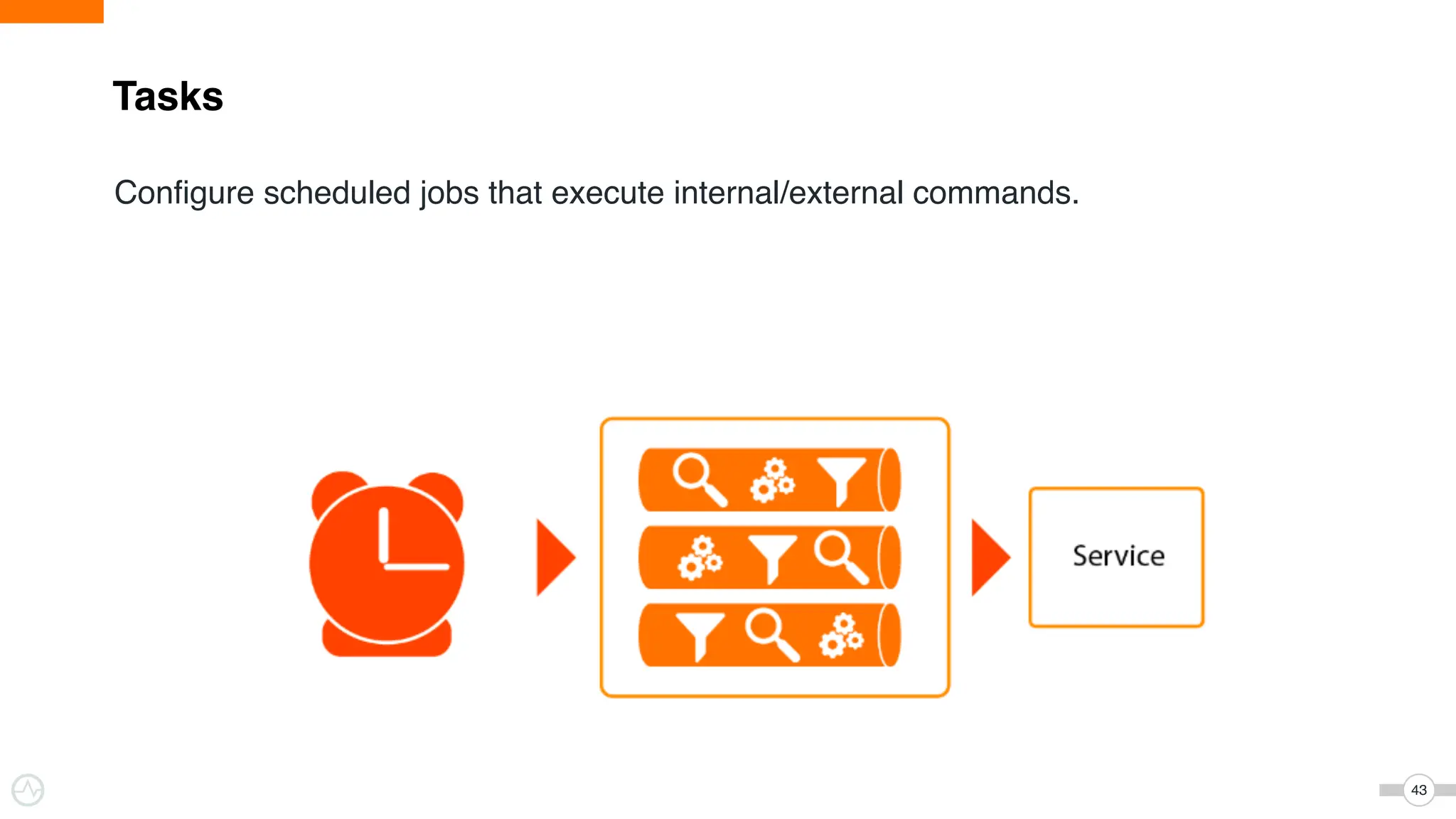
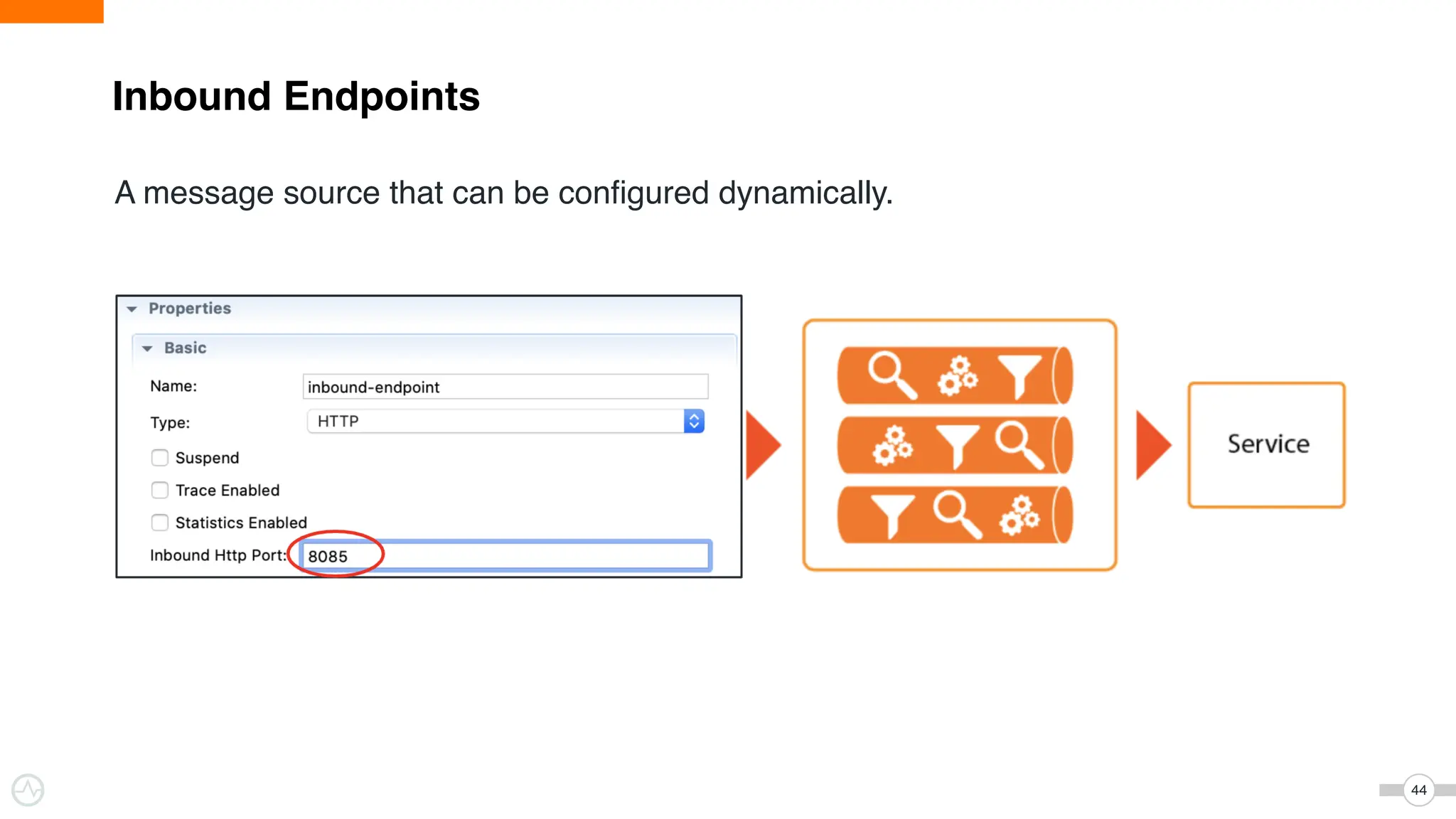
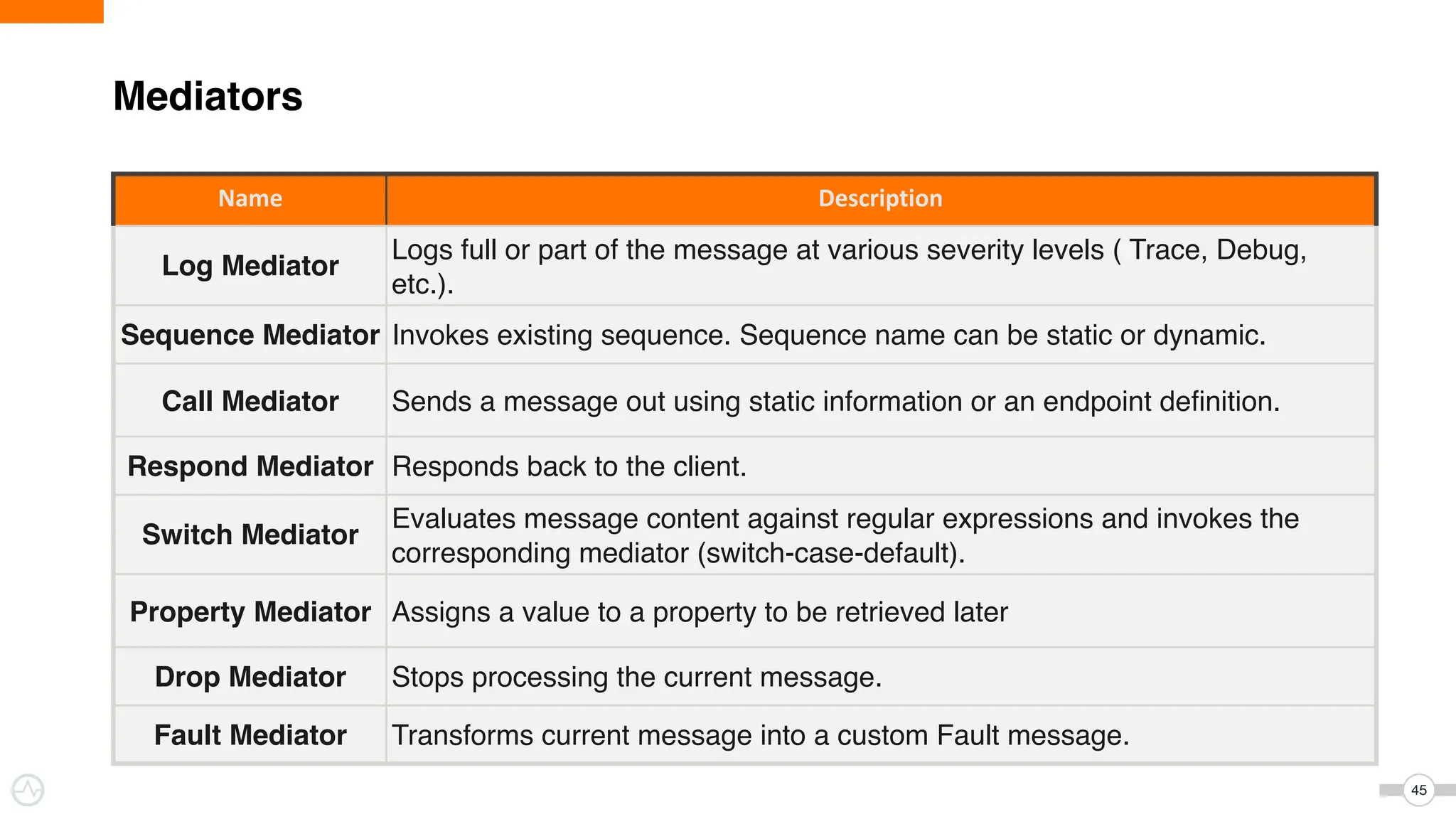
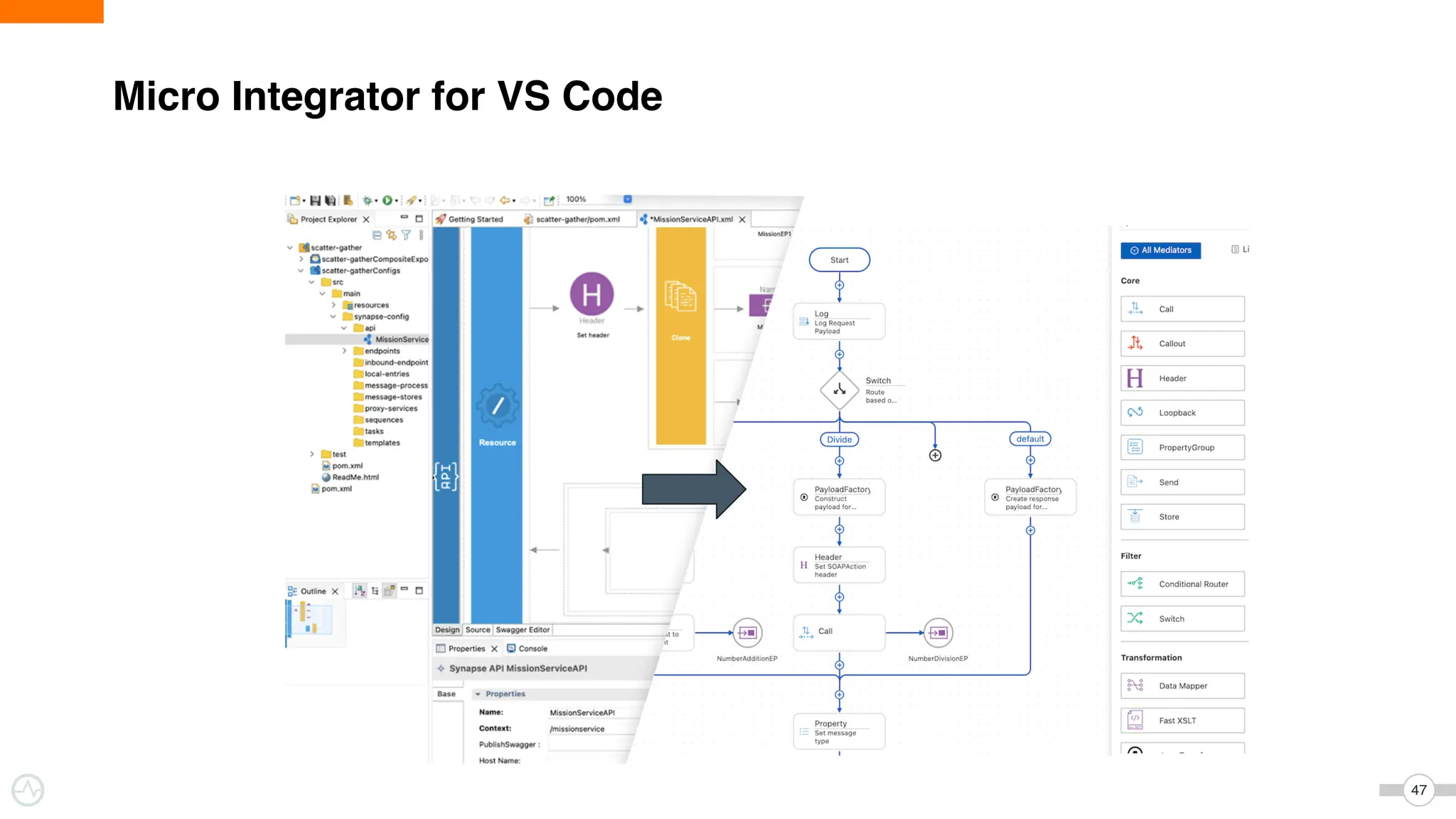
The document discusses WSO2 Micro Integrator's role in integrating microservices within decentralized architectures, emphasizing the shift from monolithic to microservices architecture. It highlights key aspects such as inter-service communication, message routing, and various types of microservices and their complexities. Additionally, it presents the features and functionalities of WSO2 Micro Integrator that facilitate effective integration across different technologies and systems.