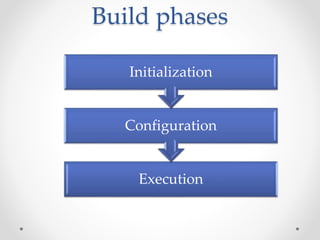
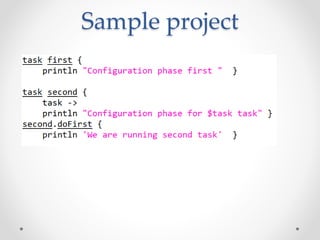
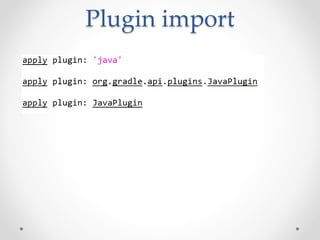
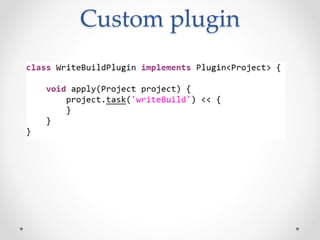
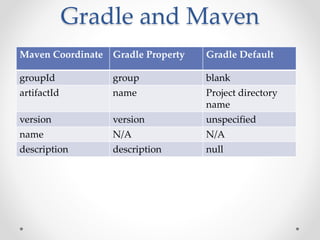
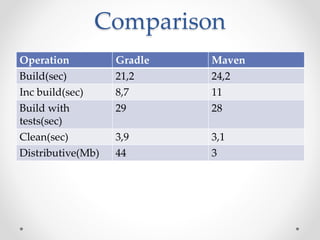
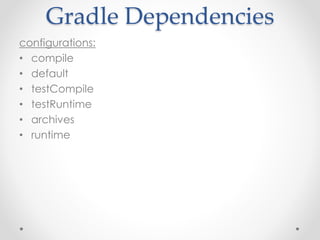
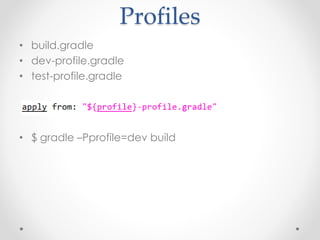
Gradle is a flexible, general-purpose build automation tool that improves upon existing build tools like Ant, Maven, and Ivy. It uses Groovy as its configuration language, allowing builds to be written more clearly and concisely compared to XML formats. Gradle aims to provide the flexibility of Ant, the dependency management and conventions of Maven, and the speed of Git. It handles tasks, dependencies, plugins, and multiproject builds. Gradle configurations map closely to Maven scopes and it has good support for plugins, testing, caching, and integration with tools like Ant and Maven.