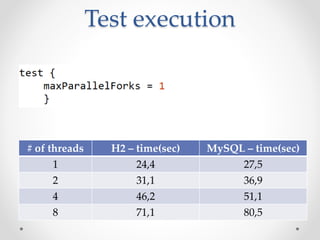
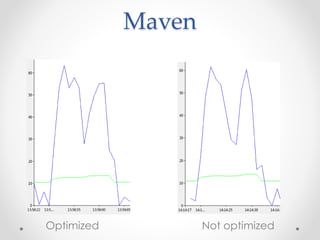
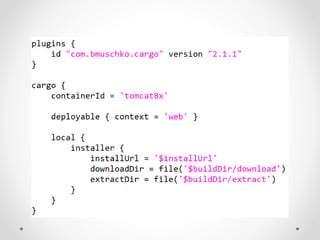
This document summarizes the key points about Gradle build automation tool. It discusses some limitations of Ant and Maven, how Gradle addresses them using Groovy as its configuration language. Gradle provides features like caching, daemon, plugins, and integration with Maven. It offers better performance than Maven for multi-project builds. The document compares Gradle and Maven build times on sample projects and outlines some pros and cons of Gradle.