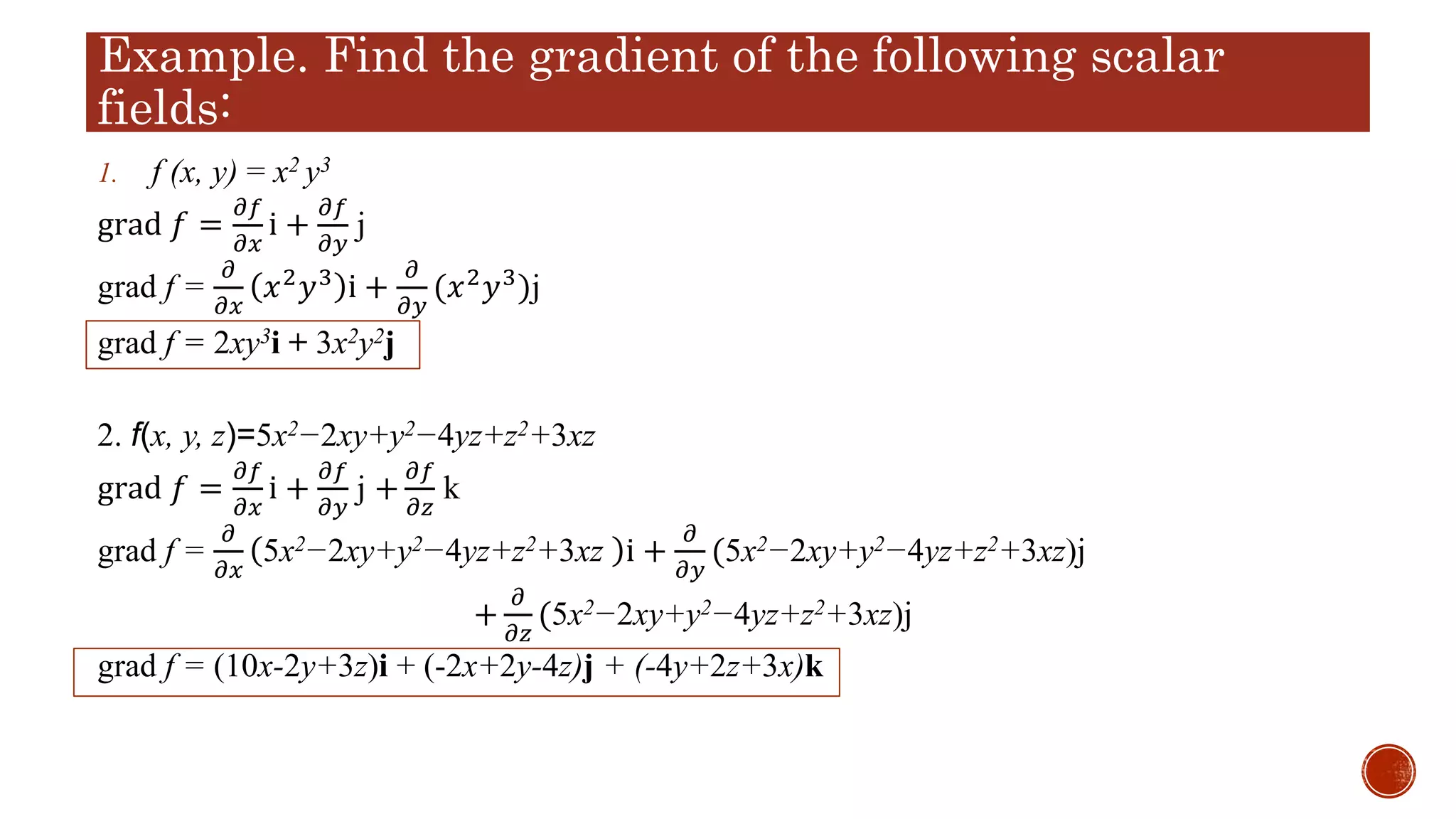
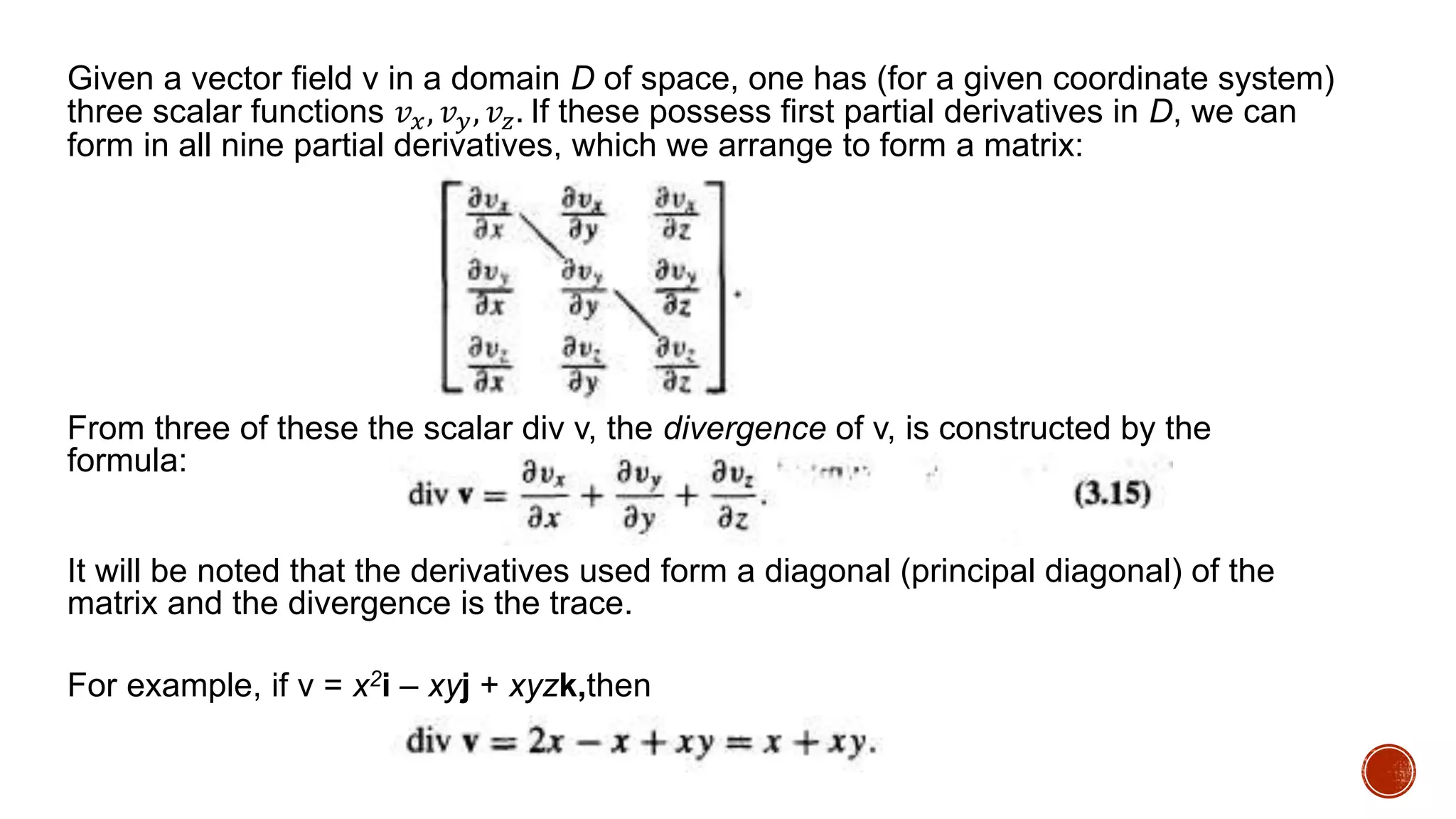
The document discusses gradients and divergence of scalar and vector fields. It defines the gradient of a scalar field f as the vector of its partial derivatives, representing the maximum rate of change of f in a given direction. The divergence of a vector field v is defined as the trace of its partial derivative matrix. Examples are given of computing the gradient of scalar fields like f(x,y,z)=5x^2-2xy+y^2-4yz+z^2+3xz and the divergence of vector fields like F=x^2yi-(z^3-3x)j+4y^2k. Basic properties of the gradient and divergence operators are also outlined.