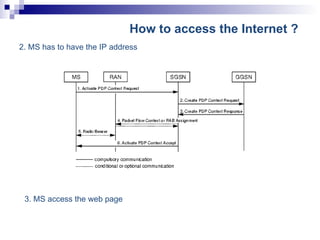
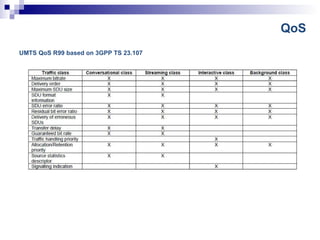
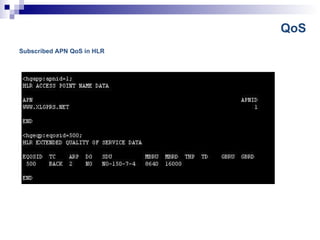
The document discusses GPRS and UMTS networks in the core network. It covers topics like GPRS system overview, mobility management, session management, quality of service, and roaming implementation in the core network. It describes the functions of core network elements like the SGSN and GGSN, including mobility management, session management, payload handling, charging, quality of service, and security. It also discusses access point names (APNs) and how quality of service is implemented in GPRS and UMTS networks.