This document discusses recipes for GDPR-compliant data science. It covers topics like data privacy, risks, ethics, compliance, and governance. On data privacy, it explains information privacy and regulations like GDPR and CCPA. On risks, it discusses risks in data like improper analytics and low data quality. On ethics, it discusses issues around automated decision-making, non-discrimination, and the right to explanation. On compliance, it advocates for monitoring and automated reporting. On governance, it notes challenges of constraints and advocates a bottom-up approach through monitoring data activities.


![www.kensu.io
A. DATA PRIVACY
Information privacy, also known as data privacy or data protection, is the
relationship between the collection and dissemination of
a. data,
b. technology,
c. the public expectation of privacy,
d. legal
and political issues surrounding them.[1]
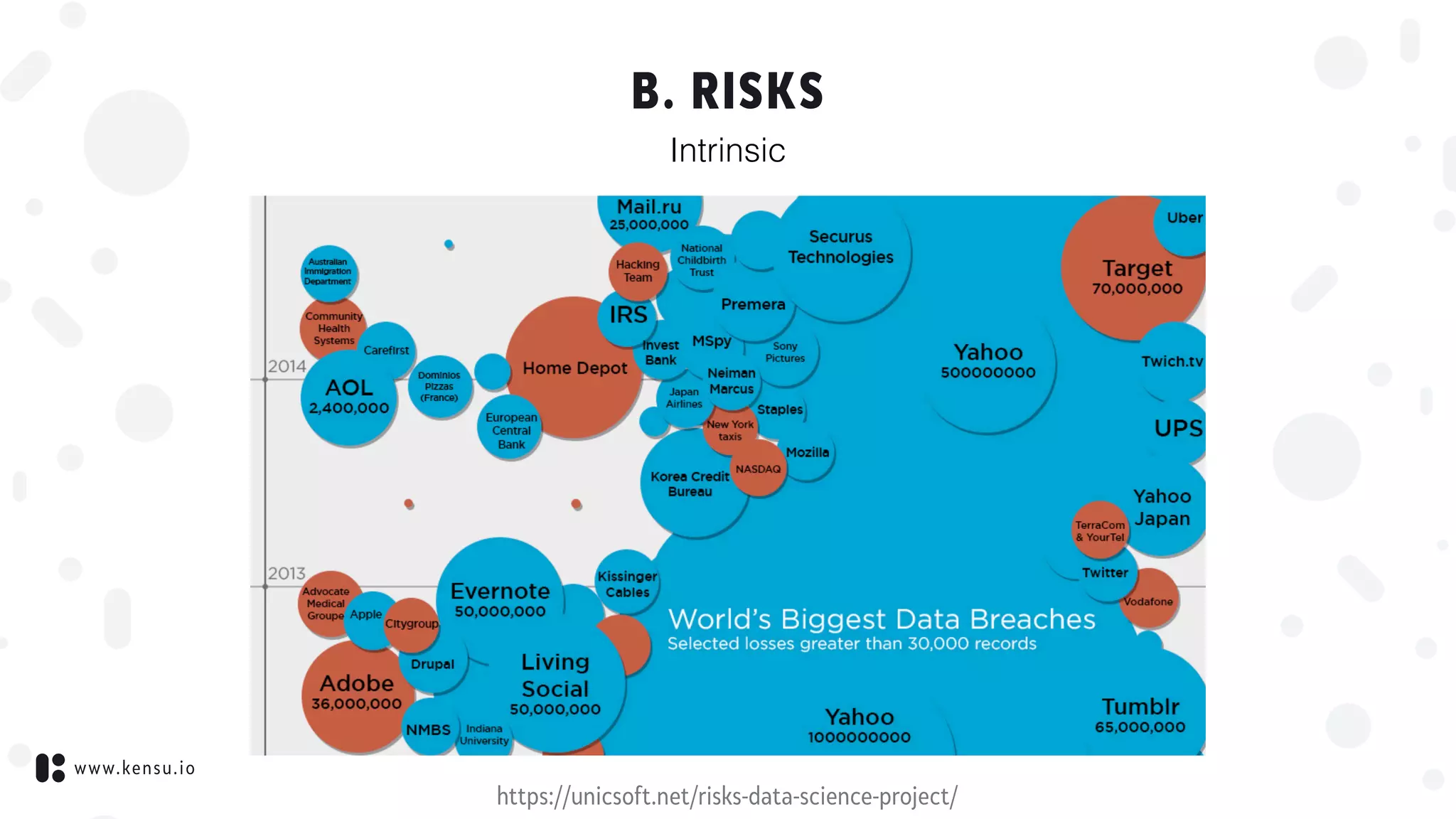
Privacy concerns exist wherever personally identifiable information or
other sensitive information is collected, stored, used, and finally
destroyed or deleted – in digital form or otherwise.
Improper or non-existent disclosure control can be the root cause for
privacy issues.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_privacy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/governance-compliance-190222153833/75/Governance-compliance-4-2048.jpg)















![www.kensu.io
C. ETHIC
Automated decision-making
https://www.miamiherald.com/news/nation-world/national/article89562297.html
Discrimination… can be unintended
“Ingress players, like the database volunteers, appeared to
skew male, young and English-speaking, […].
Though the surveys did not gather data on race or income
levels, the average player spent almost $80 on the Ingress
game […] suggesting access to disposable income.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/governance-compliance-190222153833/75/Governance-compliance-22-2048.jpg)