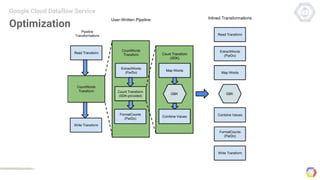
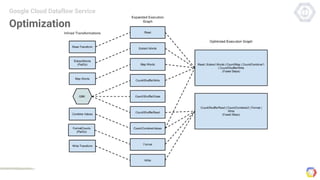
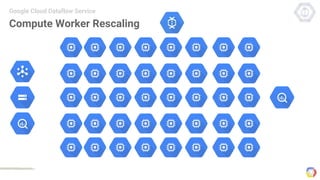
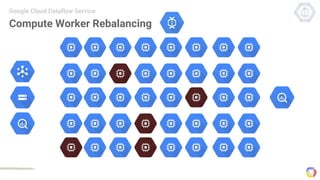
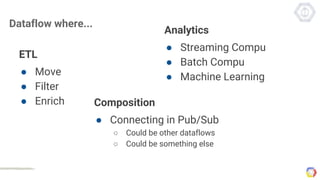
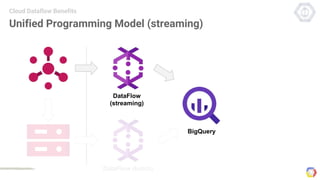
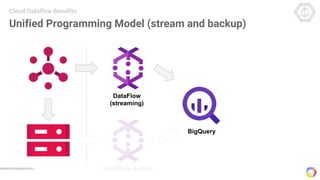
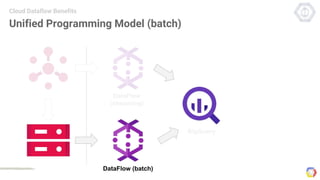
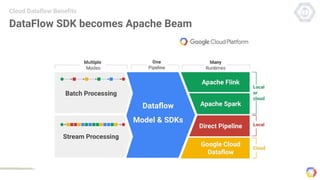
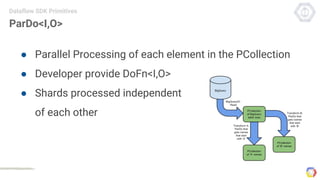
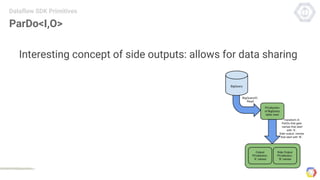
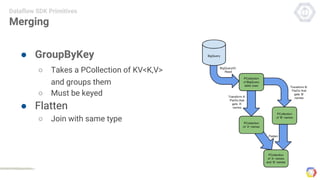
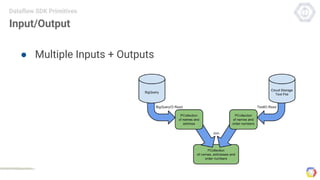
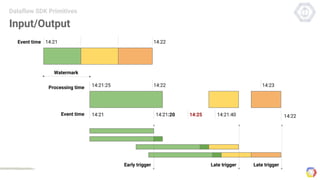
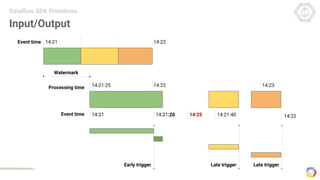
Cloud Dataflow is a fully managed service and SDK from Google that allows users to define and run data processing pipelines. The Dataflow SDK defines the programming model used to build streaming and batch processing pipelines. Google Cloud Dataflow is the managed service that will run and optimize pipelines defined using the SDK. The SDK provides primitives like PCollections, ParDo, GroupByKey, and windows that allow users to build unified streaming and batch pipelines.





















![How it work
Google Cloud Dataflow Service
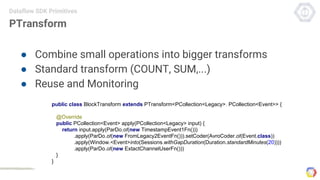
Pipeline p = Pipeline.create(options);
p.apply(TextIO.Read.from("gs://dataflow-samples/shakespeare/*"))
.apply(FlatMapElements.via((String word) -> Arrays.asList(word.split("[^a-zA-Z']+")))
.withOutputType(new TypeDescriptor<String>() {}))
.apply(Filter.byPredicate((String word) -> !word.isEmpty()))
.apply(Count.<String>perElement())
.apply(MapElements
.via((KV<String, Long> wordCount) -> wordCount.getKey() + ": " + wordCount.getValue())
.withOutputType(new TypeDescriptor<String>() {}))
.apply(TextIO.Write.to("gs://YOUR_OUTPUT_BUCKET/AND_OUTPUT_PREFIX"));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p20160218-googleclouddataflow-160220144832/85/Google-Cloud-Dataflow-34-320.jpg)