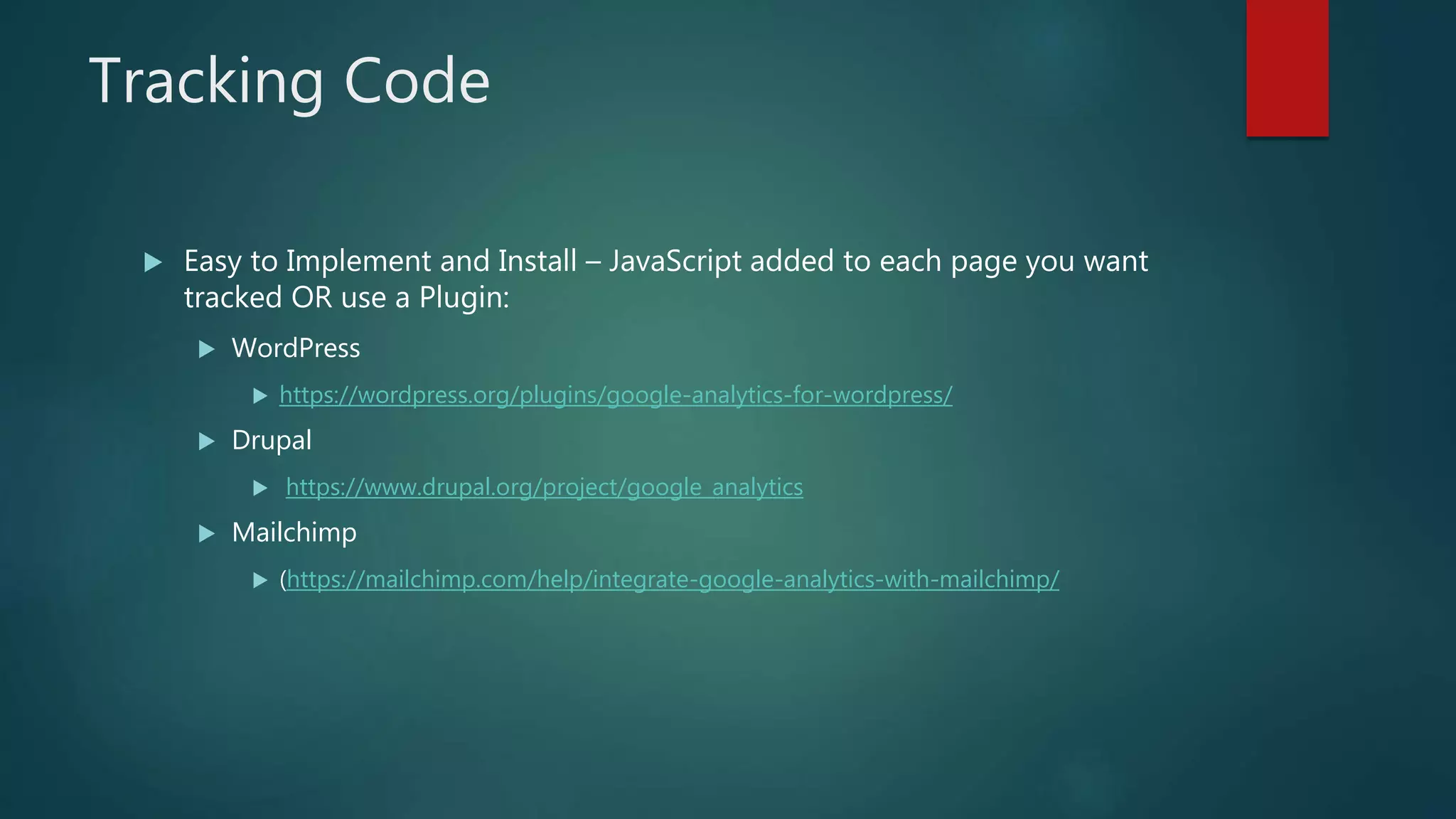
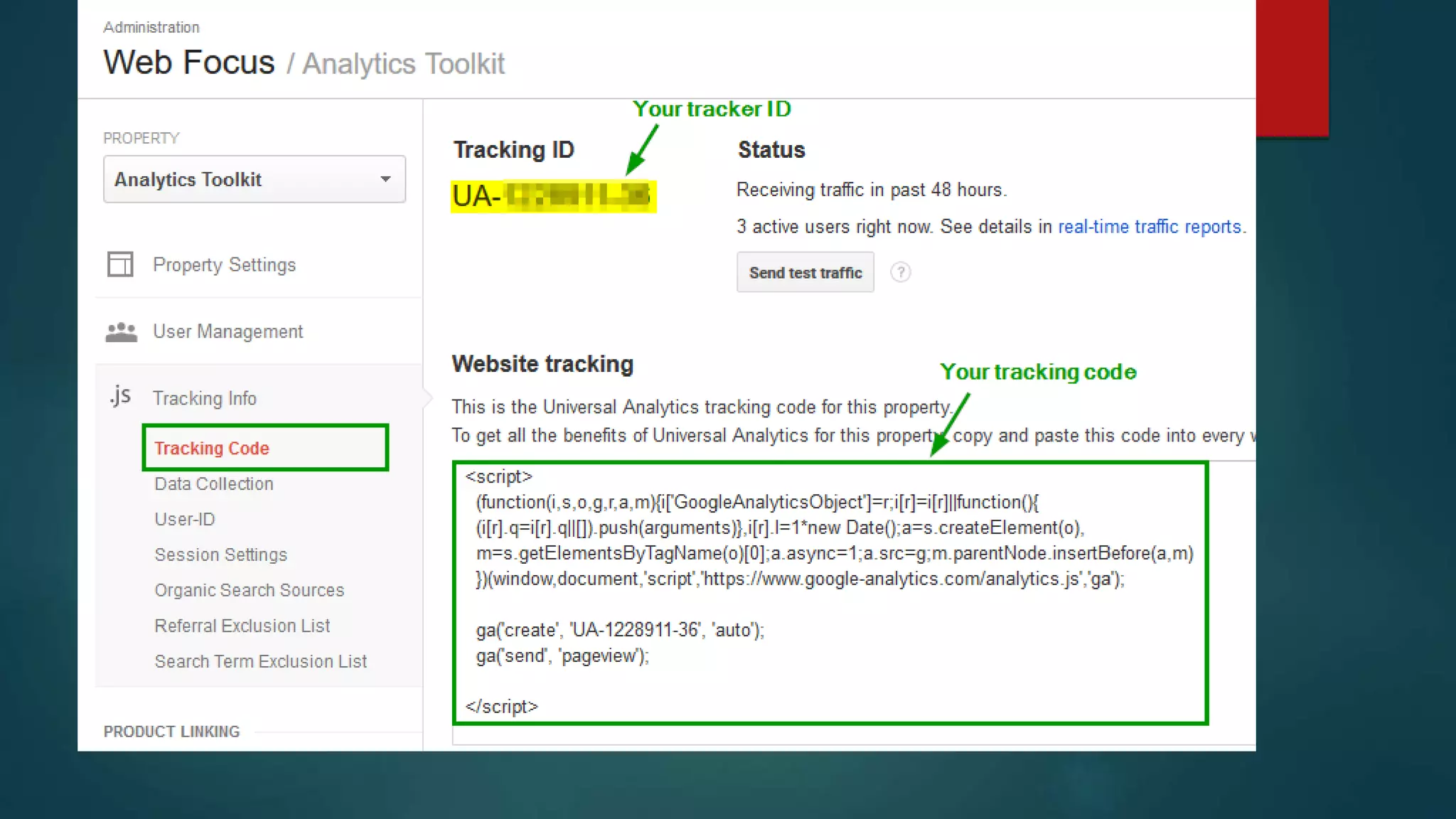
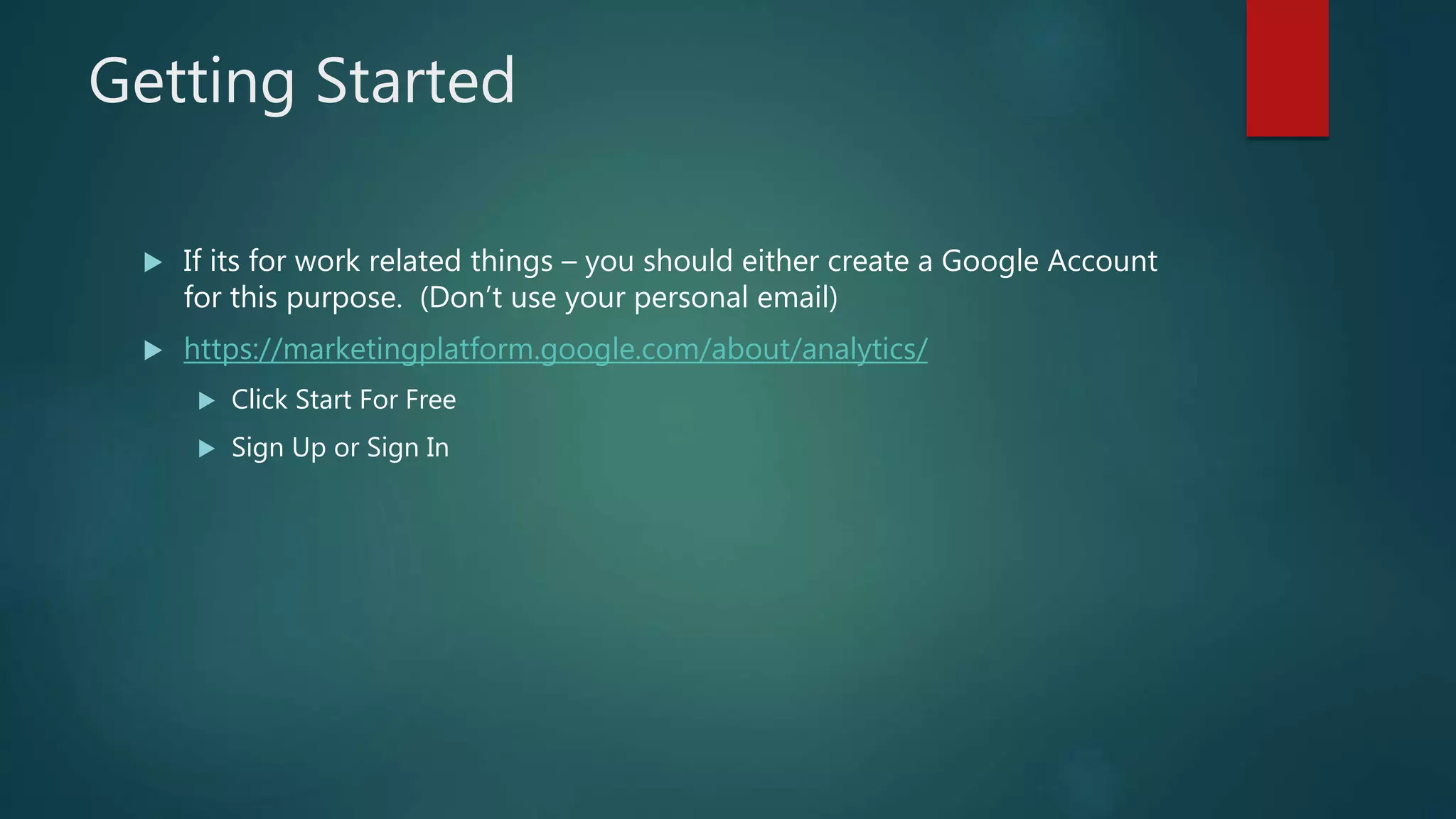
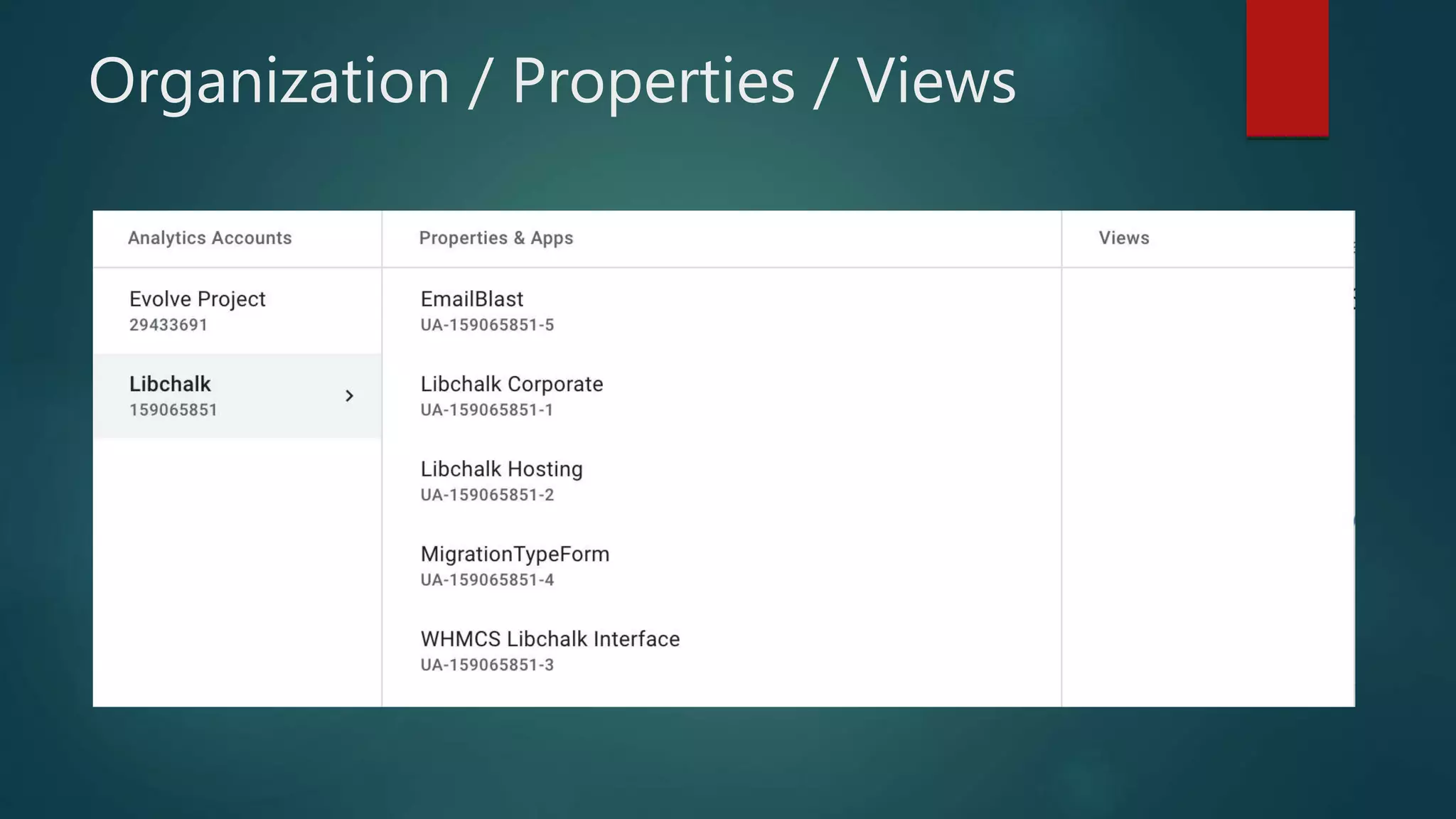
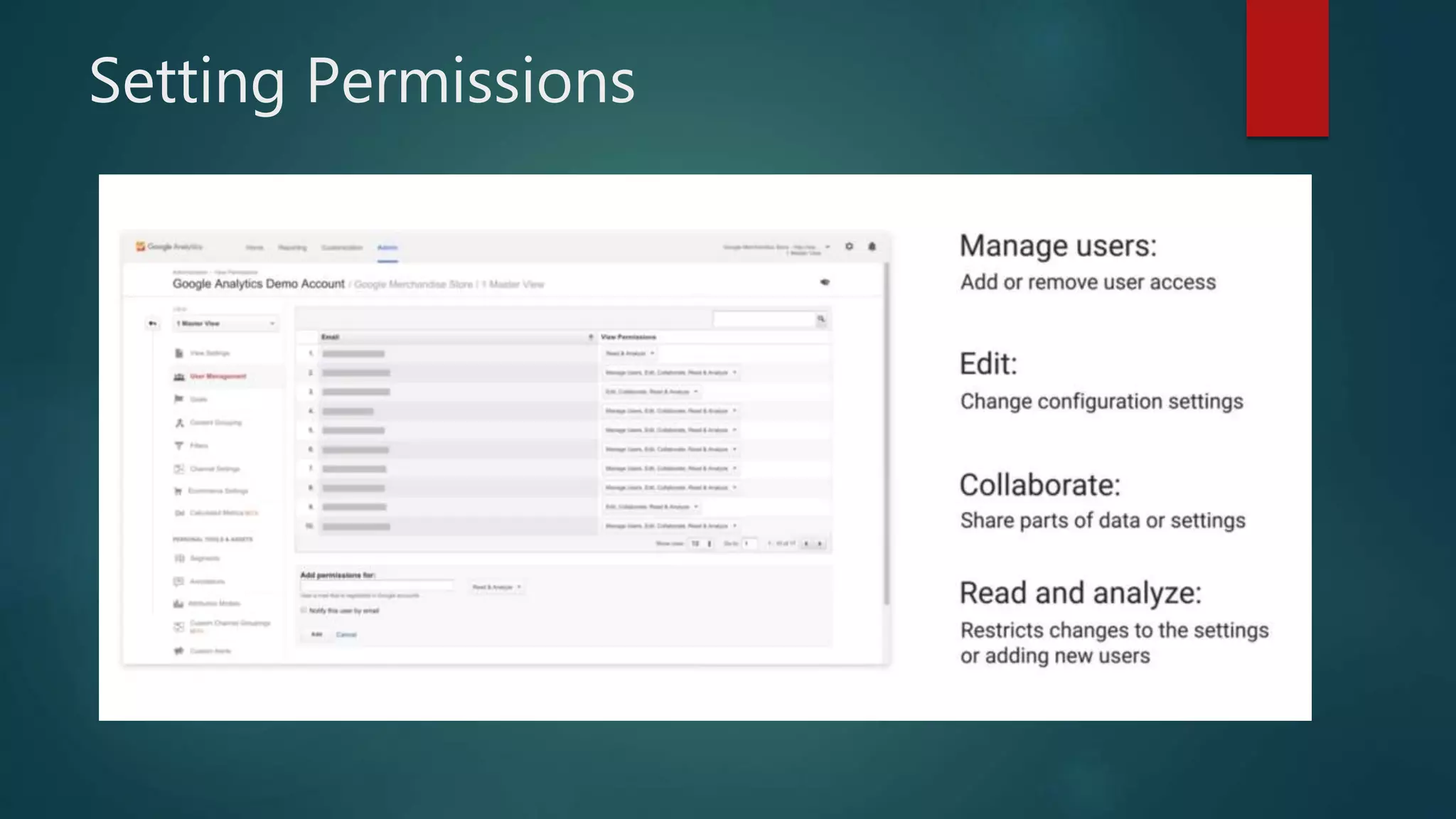
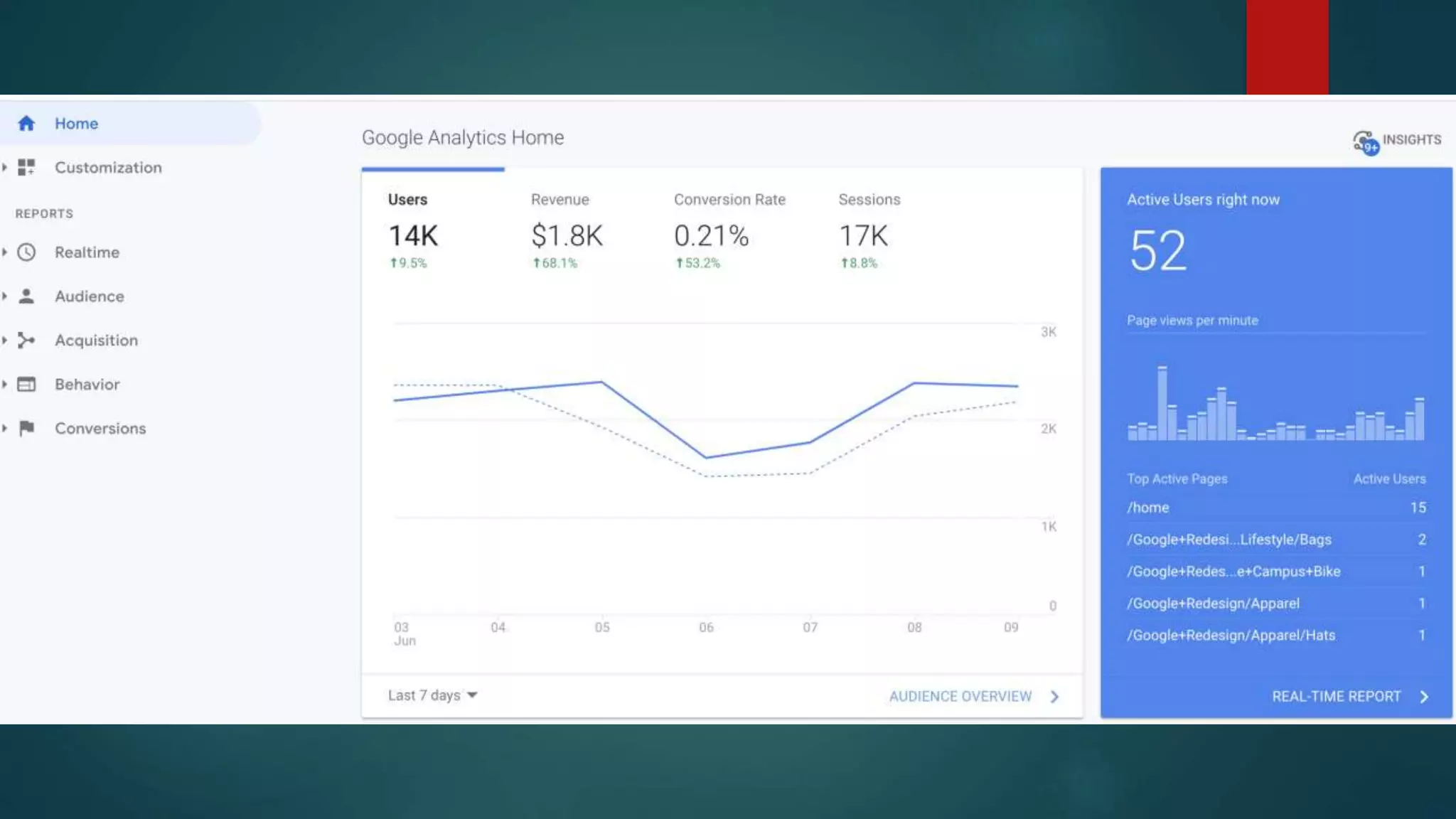
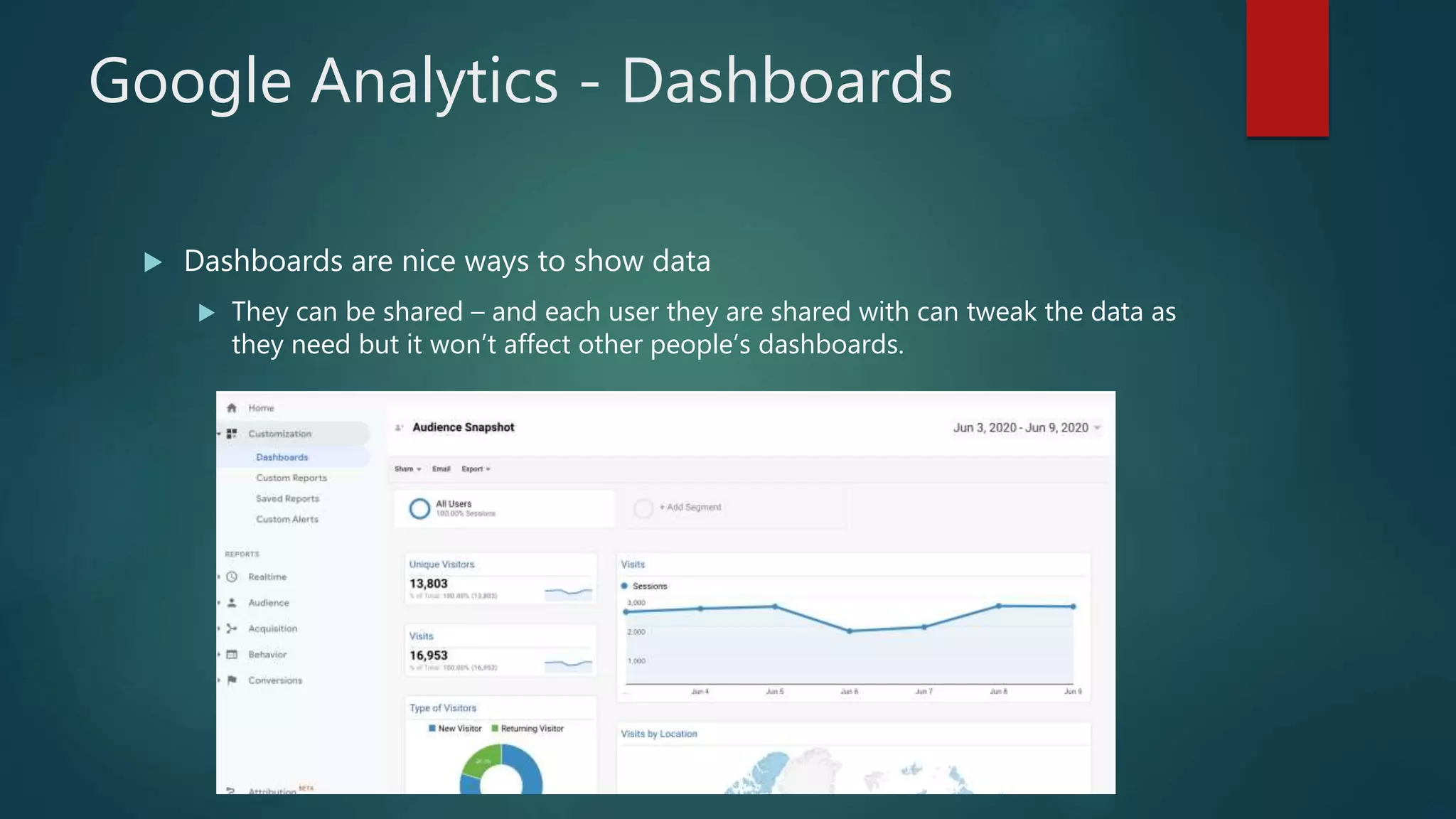
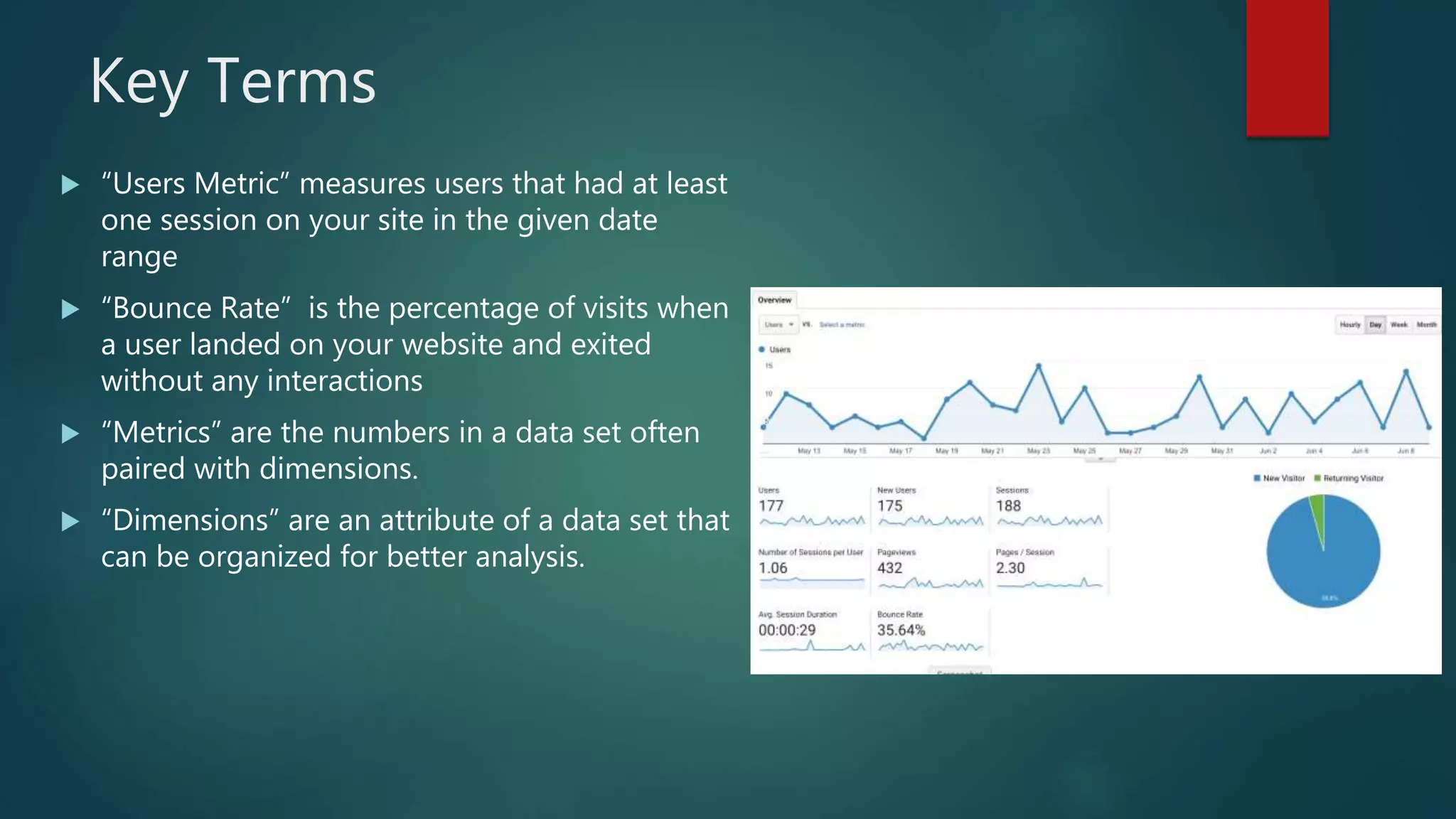
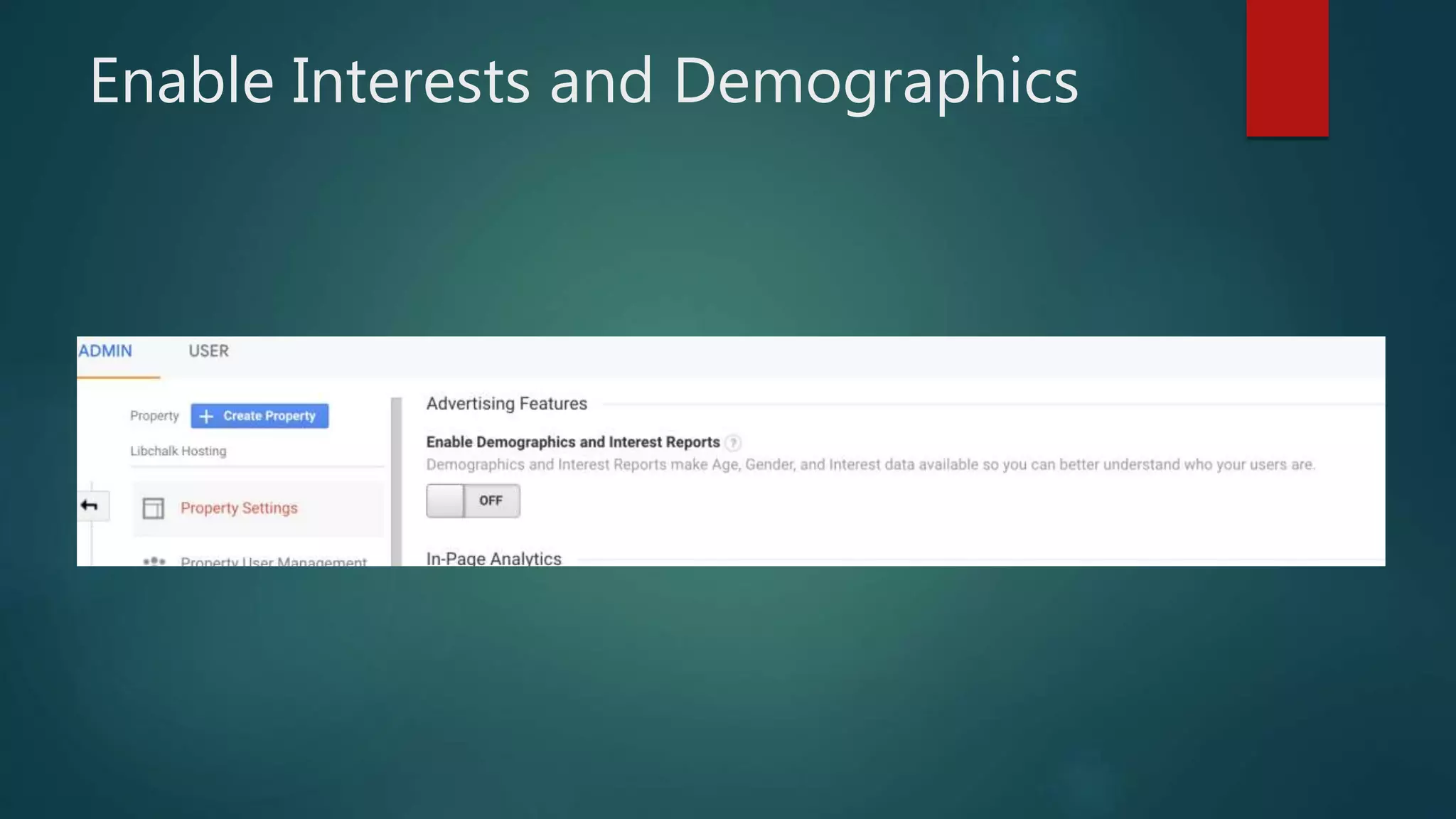
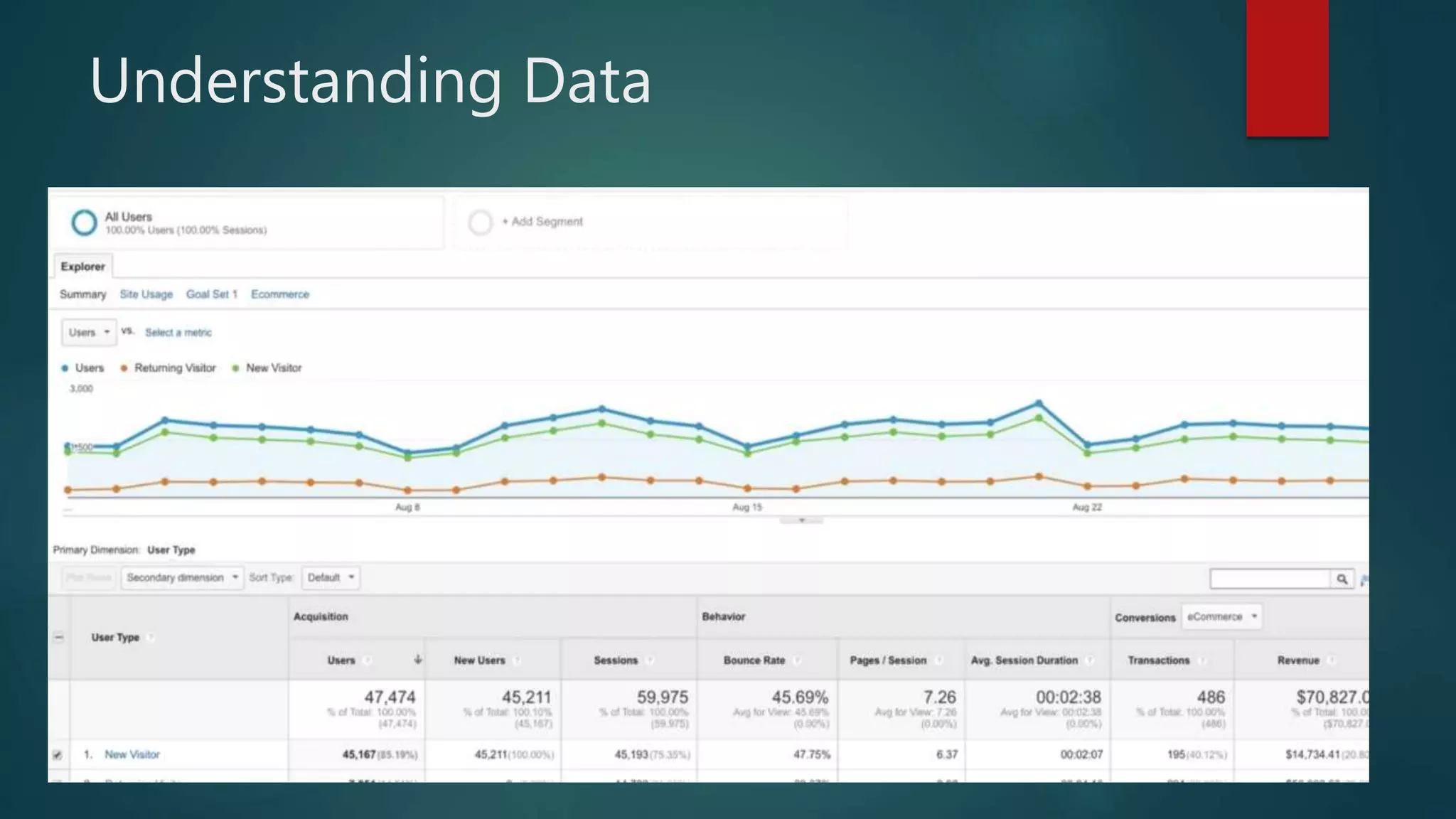
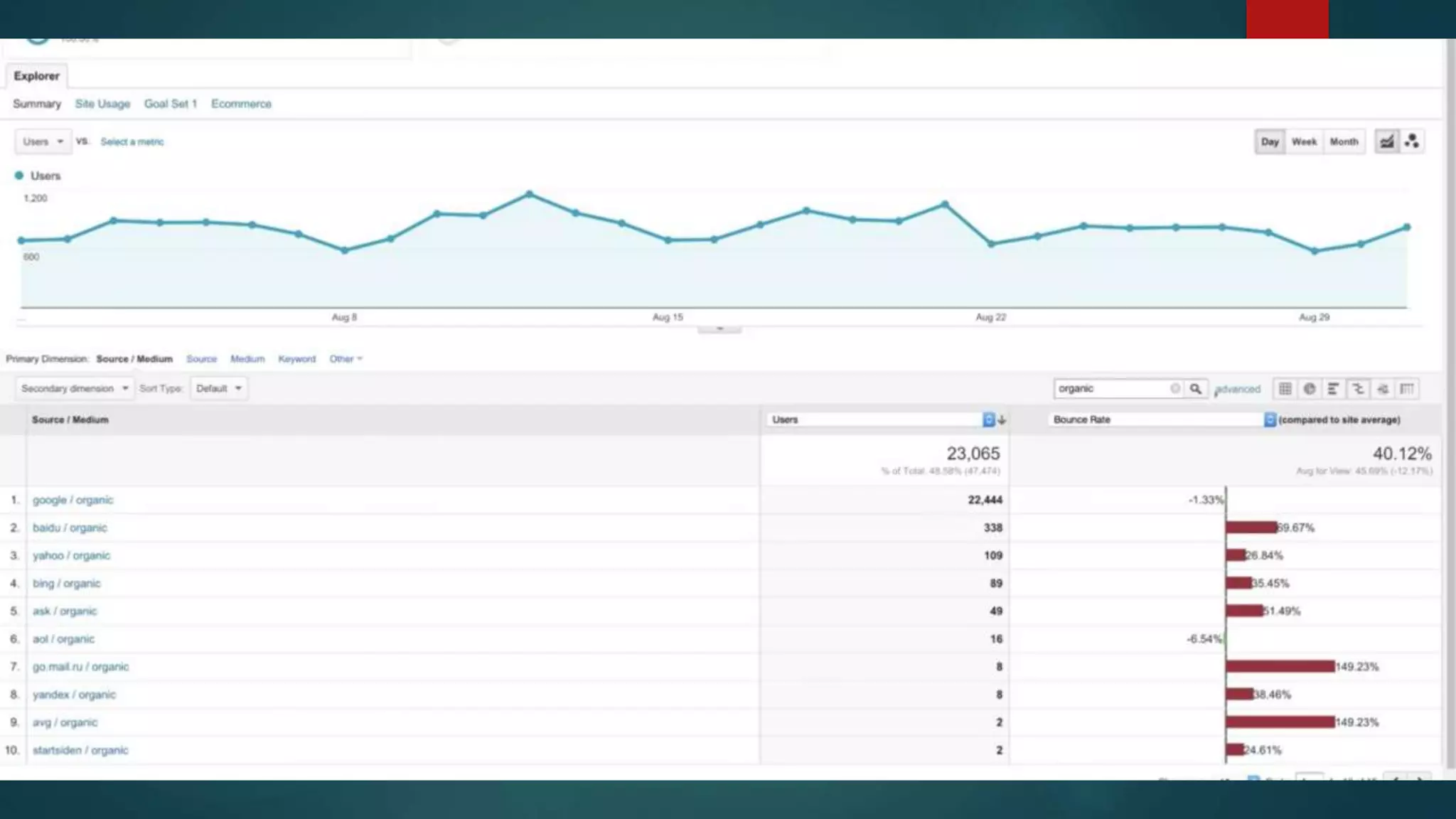
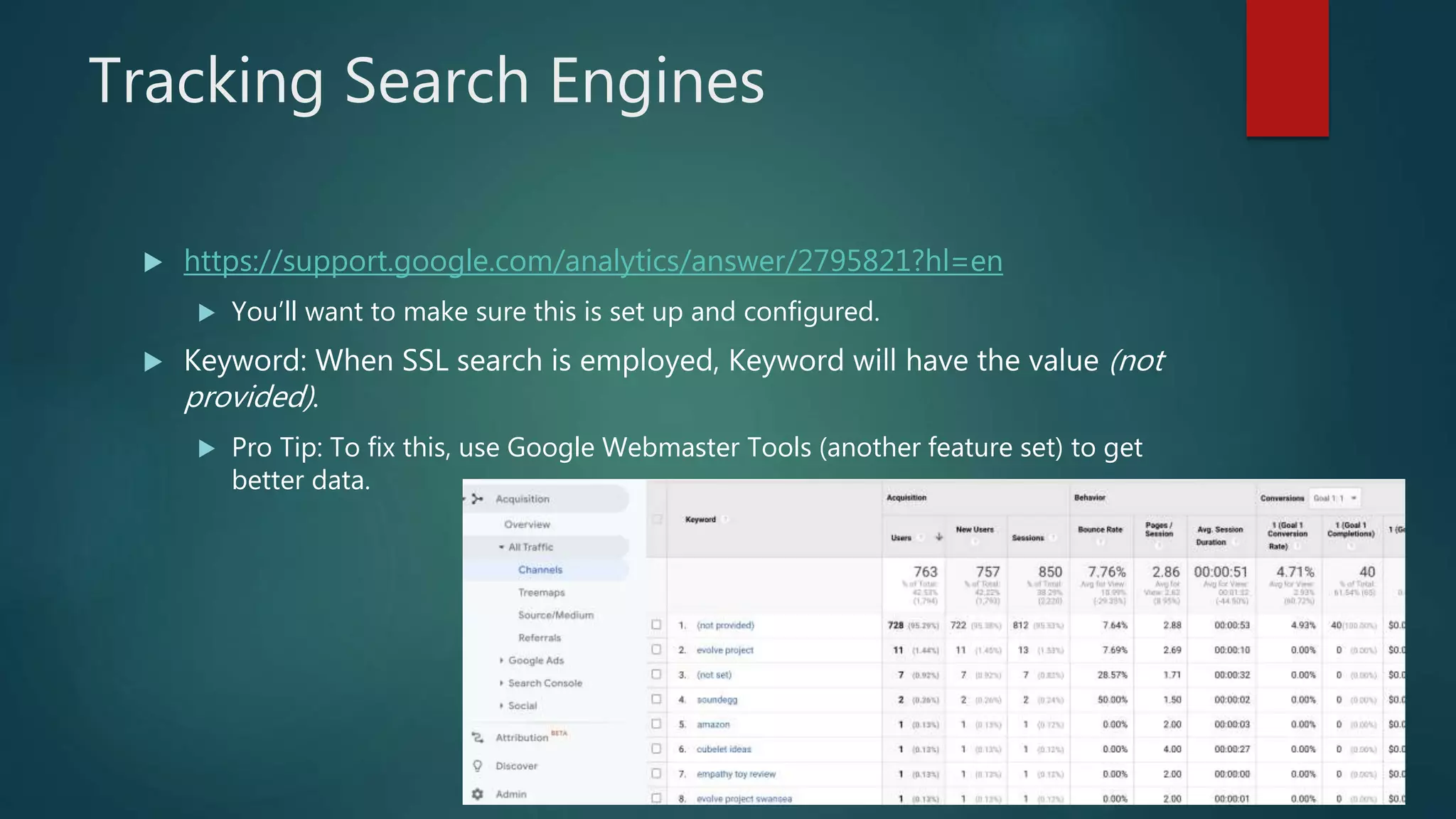
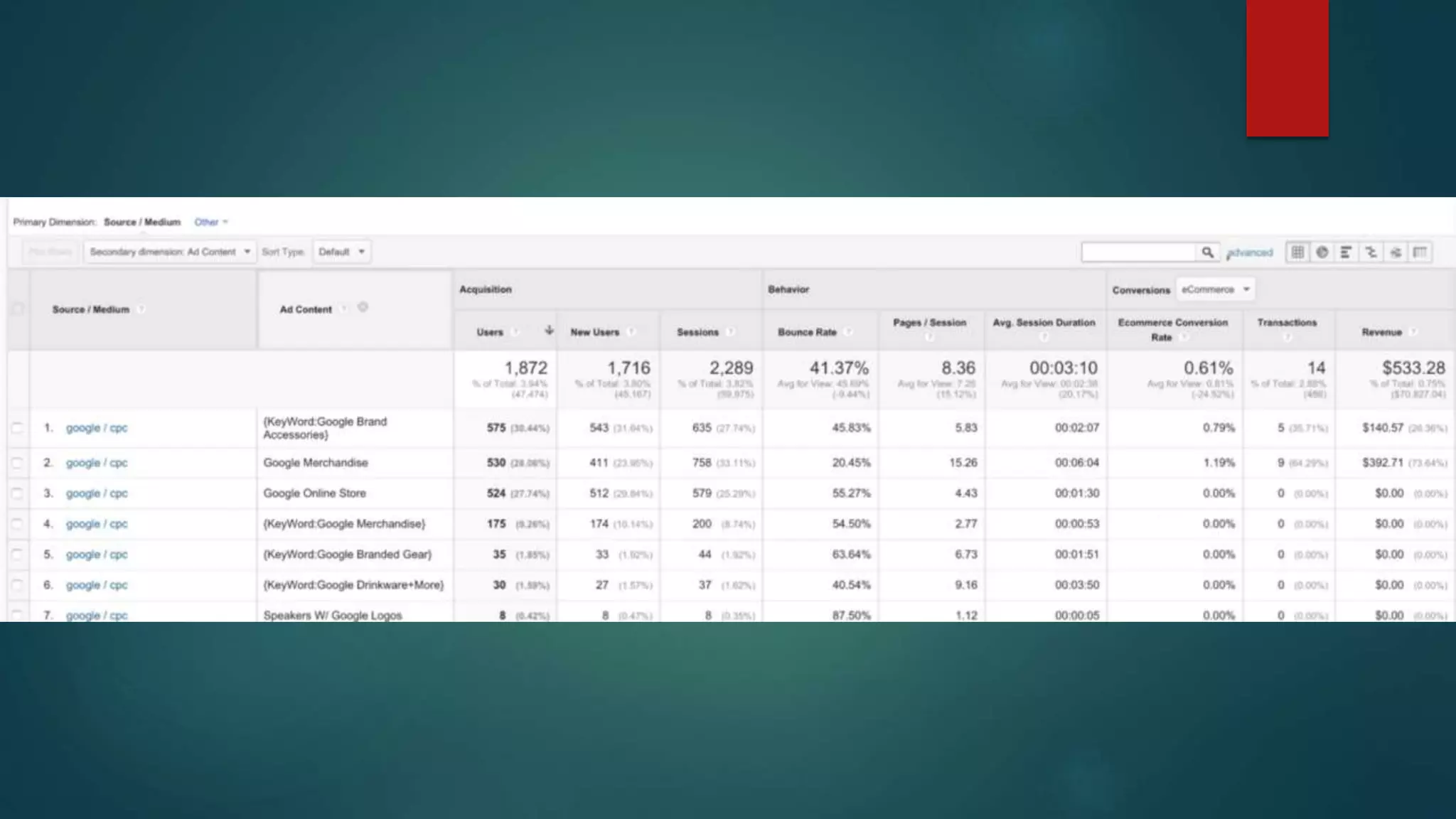
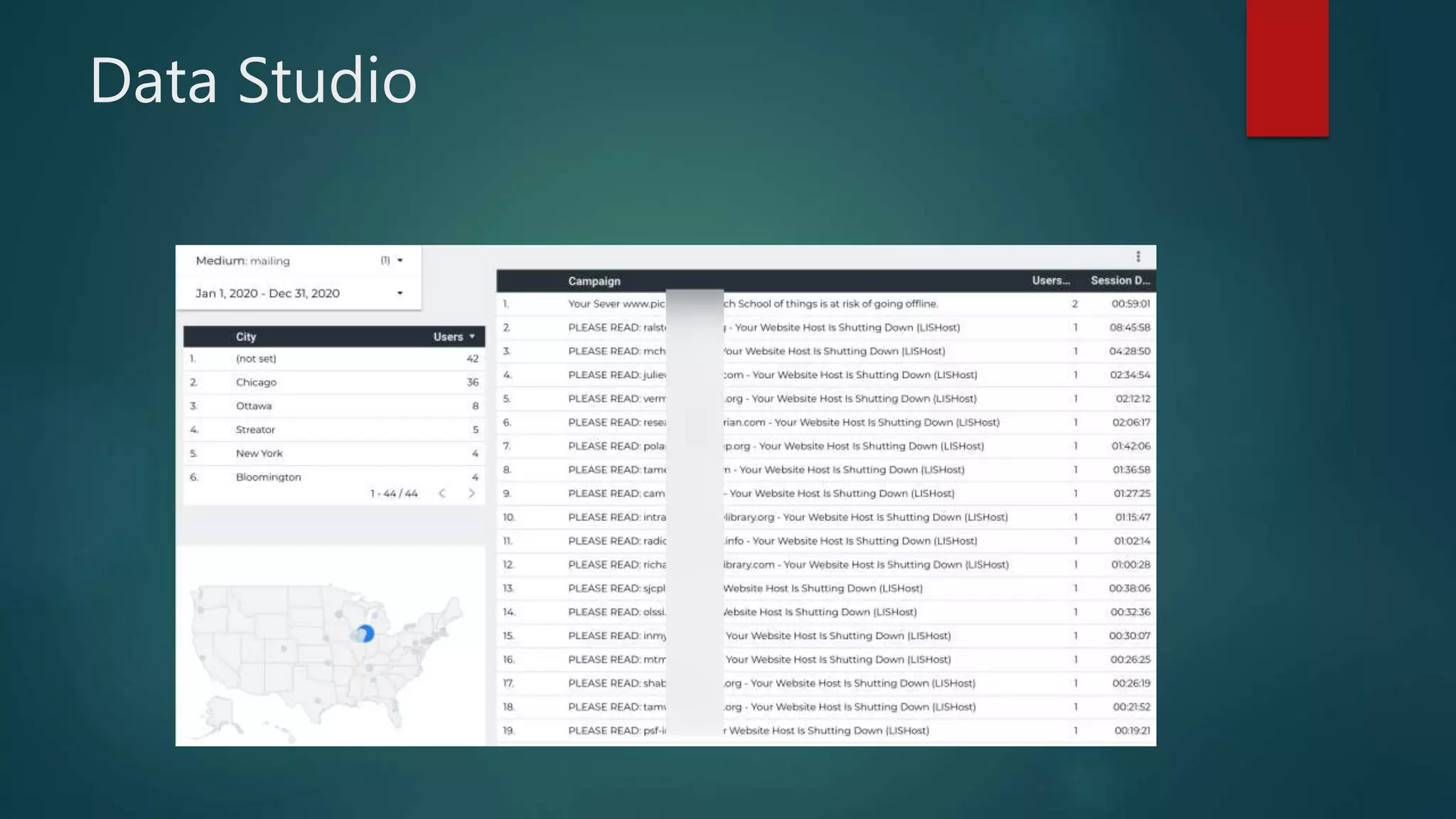
This document outlines a webinar by Brian Pichman introducing Google Analytics and Google Data Studio, focusing on their significance in tracking website performance and enhancing digital experiences. It covers topics such as setting up analytics, tracking visitor activity, understanding key metrics, and using Google Data Studio for reporting. Resources, tips for implementation, and guidance on data tracking for marketing campaigns are also provided.