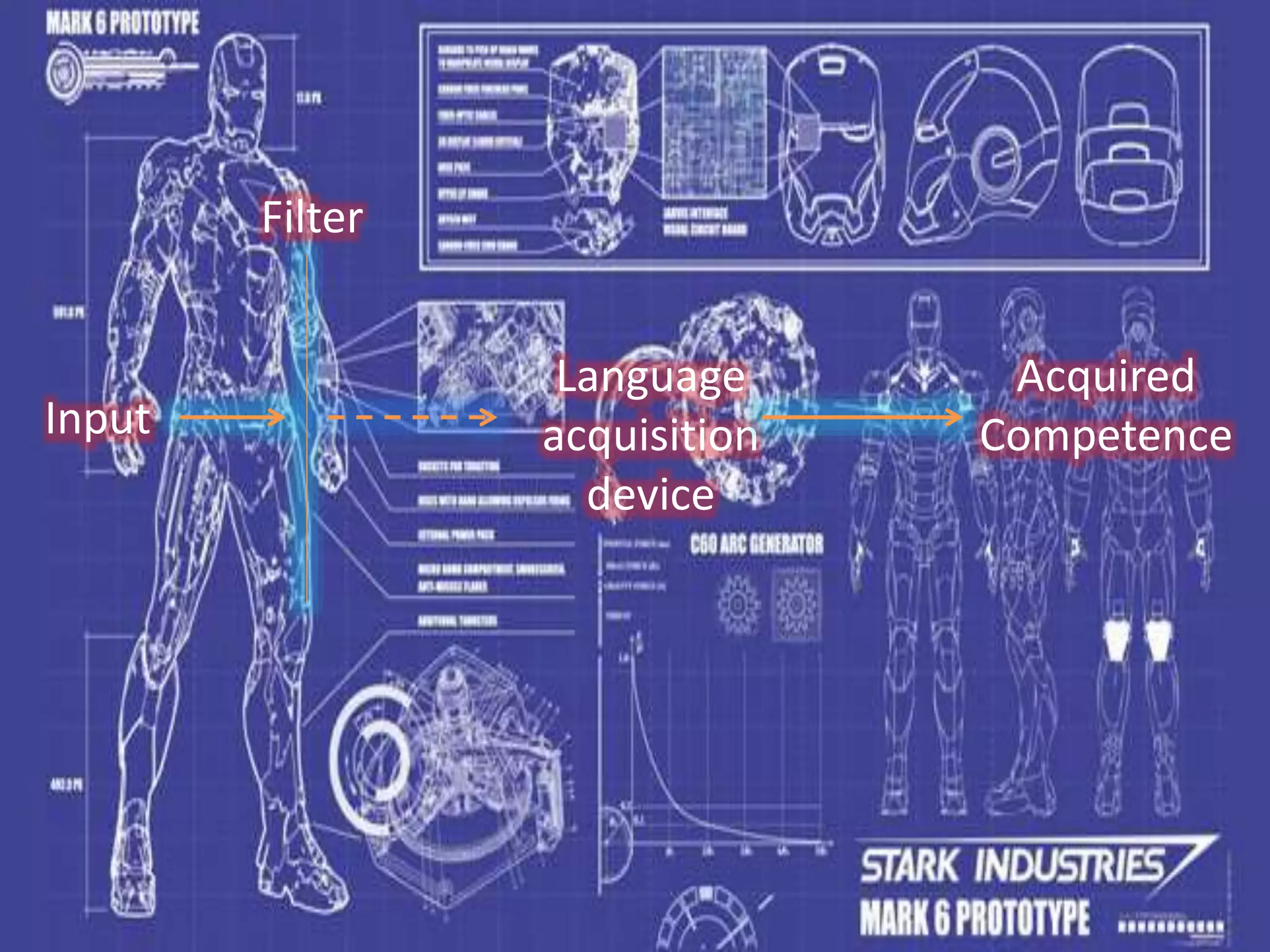
The document discusses Stephen Krashen's theories of language acquisition, including:
1. The acquisition-learning distinction, which separates implicit language acquisition from explicit language learning.
2. The natural order hypothesis, stating that grammar structures are acquired in a predictable order.
3. The monitor hypothesis, that acquisition produces fluency while learning edits forms after production.
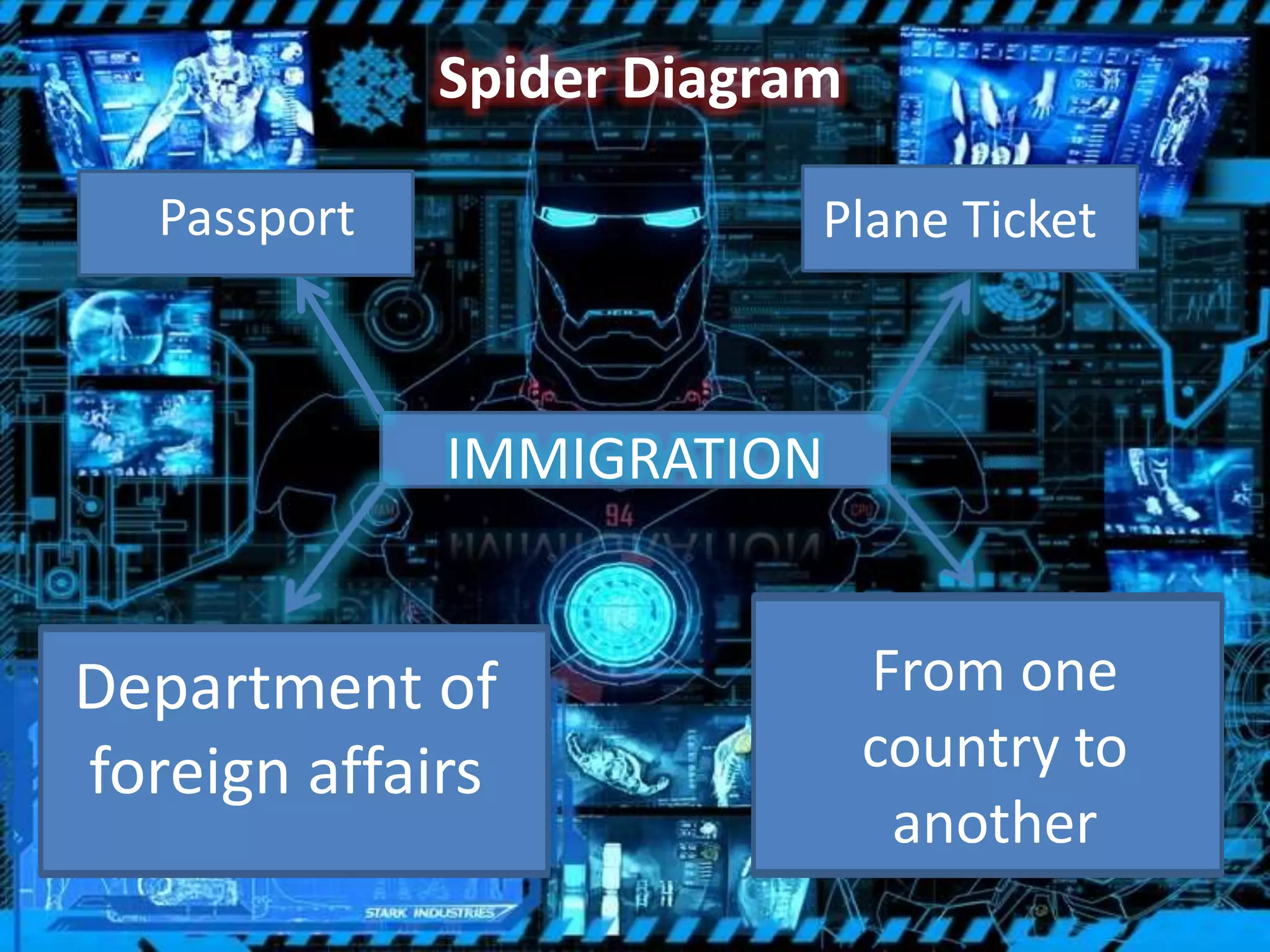
It also discusses methods for effective study skills and comprehension, including the PQRST method, spider diagrams, SQ4R method, and PQ4R method. These involve previewing material, generating questions, reading, reflecting, reciting answers, and reviewing.