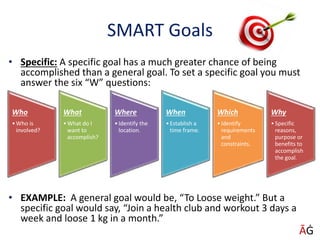
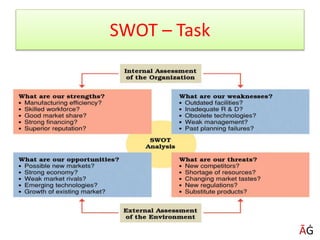
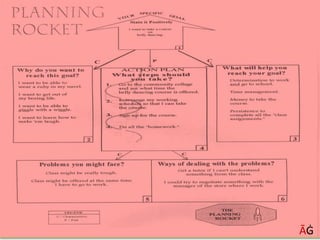
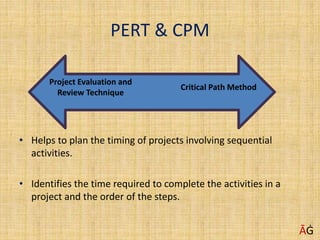
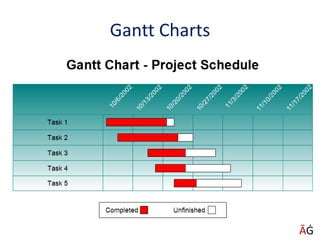
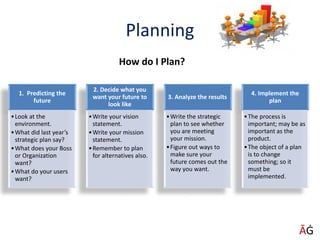
The document discusses various techniques for achieving goals such as PERT, CPM, Gantt charts, balanced scorecards, and delegation, planning, and scheduling. It emphasizes the importance of setting SMART goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-based. Various examples are provided to illustrate concepts like critical paths, Gantt charts, delegation steps, and time management matrices.