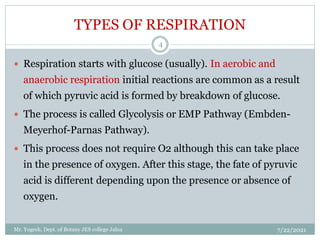
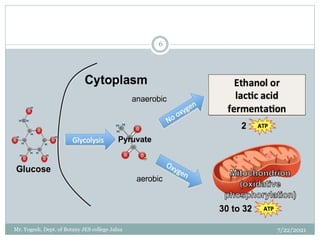
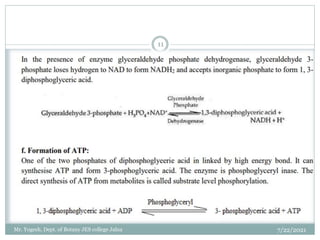
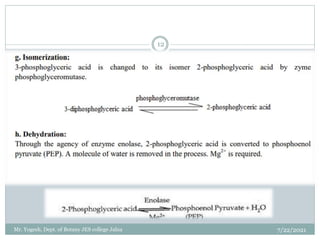
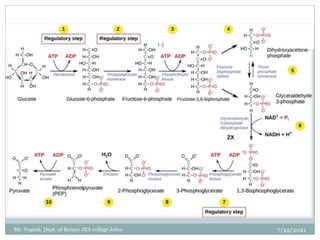
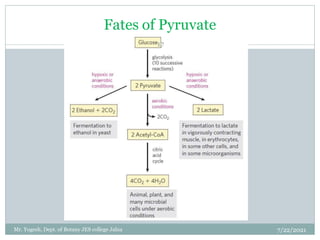
The document discusses aerobic respiration and its three main steps - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and terminal oxidation. Glycolysis involves the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid, occurring in the cytoplasm. It releases some energy in the form of ATP and reducing power as NADH. In aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid is further oxidized through the Krebs cycle in the mitochondria, fully oxidizing the organic molecules into carbon dioxide and water. Oxygen acts as the terminal electron acceptor in this process.