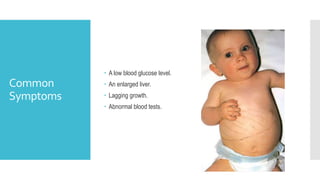
Glycogen storage disease is a rare inherited condition that affects the body's ability to metabolize glycogen, a complex sugar. There are several types that affect different organs like the liver, muscles, or blood cells. Symptoms vary by type but can include an enlarged liver, low blood sugar, muscle weakness, and developmental delays. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam, blood and urine tests, and sometimes biopsies or imaging tests. Treatment focuses on dietary changes and medications to manage symptoms.