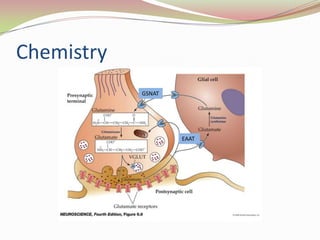
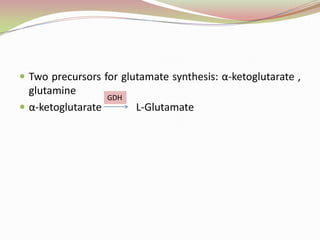
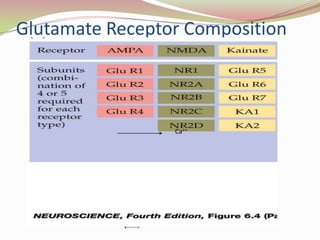
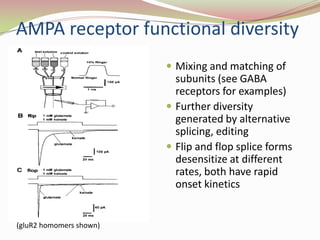
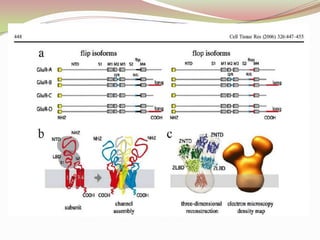
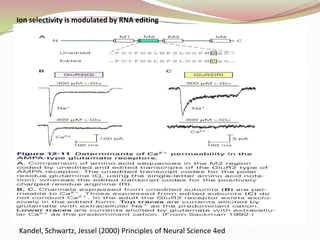
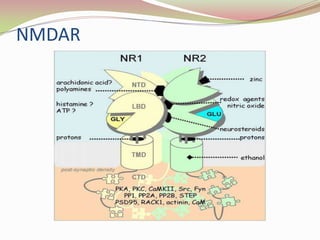
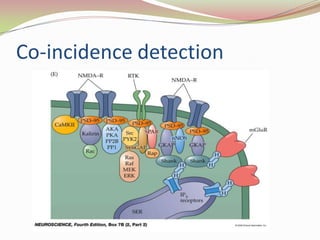
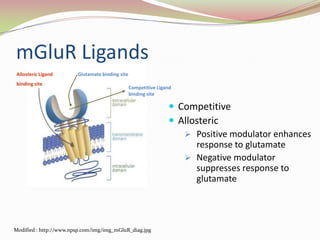
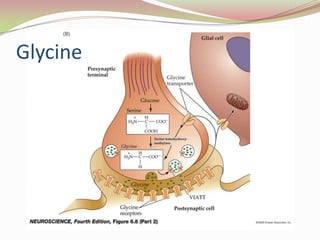
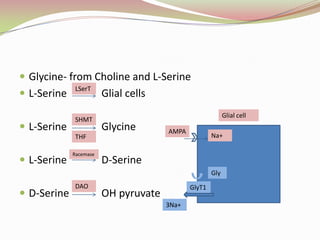
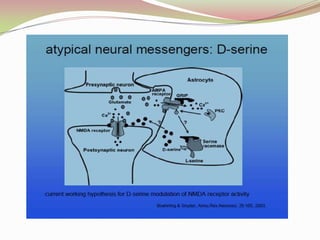
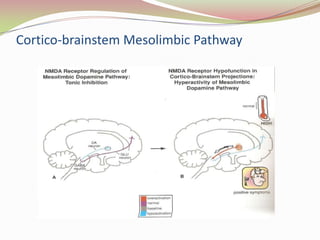
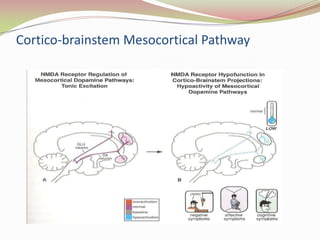
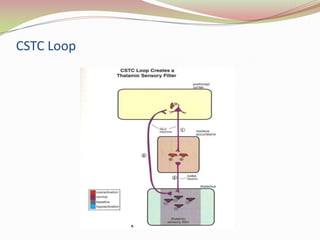
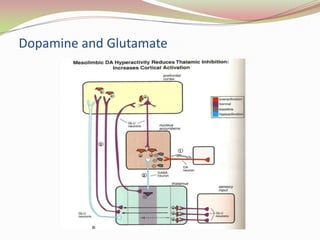
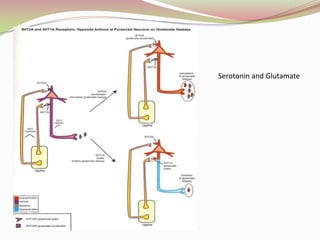
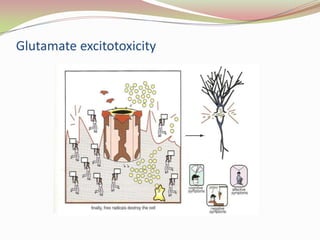
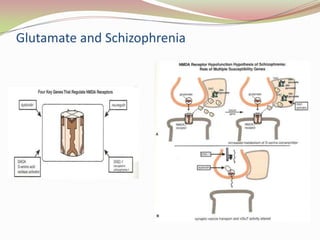
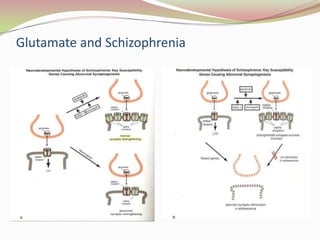
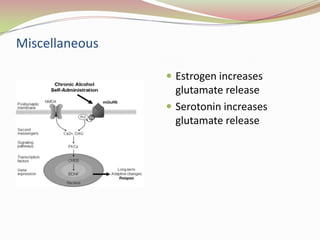
Glutamatergic neurotransmission involves glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. There are two pathways for glutamate synthesis from precursors and multiple receptor types including NMDA, AMPA, KA, and metabotropic receptors. The different receptor subunits provide diversity in function. Glutamate signaling is involved in many brain pathways and clinical implications include roles in schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, and drug mechanisms of action.