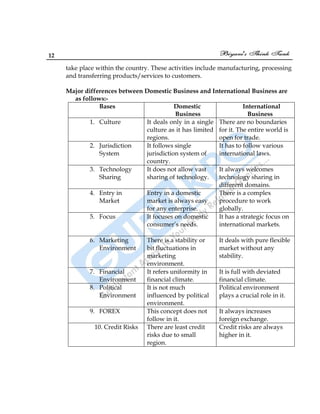
This document provides information about an international business textbook. It includes the preface, which thanks various people for their contributions. It also outlines the scope and importance of international business, including how it differs from domestic business. Specifically, it notes that international business involves cross-border trade, the exchange of goods and services between countries, and can include exports, imports and foreign direct investment. Domestic business only operates within one country.