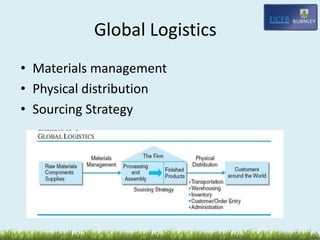
This document discusses global marketing management and international distribution. It defines international distribution as designing and managing material flows across borders to achieve corporate objectives at minimum cost. Key topics covered include:
- The complexity of international physical distribution due to factors like distance, exchange rate fluctuations, and regulations.
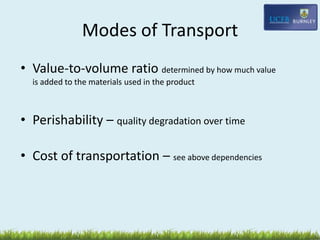
- Modes of transport like ocean shipping, air freight, and how value and perishability determine optimal modes.
- Issues in global distribution like hedging inflation/currency risks and tax differentials between countries.
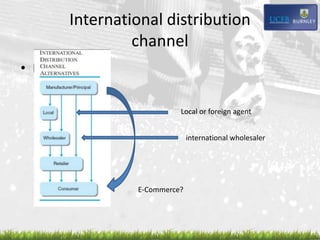
- The role of e-commerce and how online retailers operate internationally.
- Sourcing strategies and managing international distribution channels.