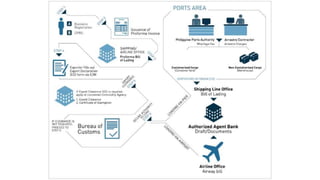
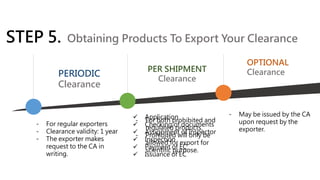
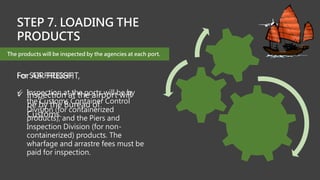
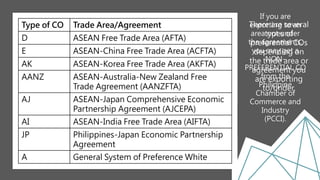
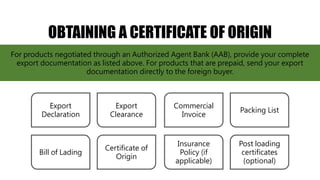
The Philippine Export Guidebook 2015 outlines the comprehensive procedures and documentation necessary for successful exports, emphasizing the importance of organizational and product readiness. It details sequential steps for business registration, order confirmation, product declaration, and acquiring required export clearances and certificates, culminating in payment methods for foreign buyers. Exporters must comply with various regulations and documentation requirements depending on the nature and destination of the goods.