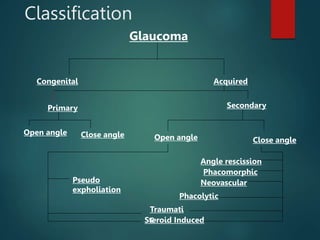
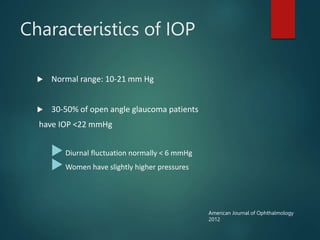
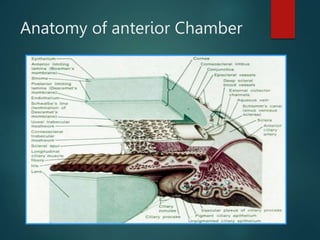
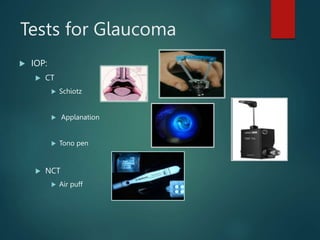
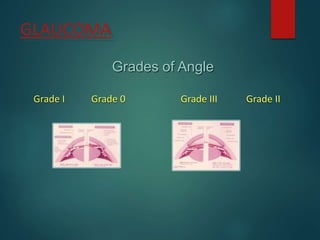
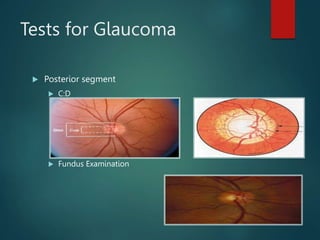
The document provides an overview of glaucoma, including its definition as a group of diseases causing progressive optic neuropathy that can lead to blindness if untreated. It discusses the classification of glaucoma, characteristics of intraocular pressure (IOP), testing methods, symptoms, and management options, including low vision rehabilitation. Additional details are provided on the definitions of low vision, impacts of ocular diseases, and devices used for rehabilitation.