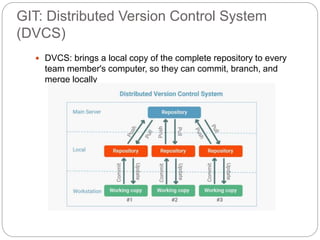
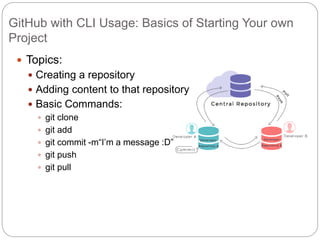
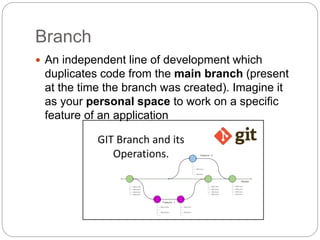
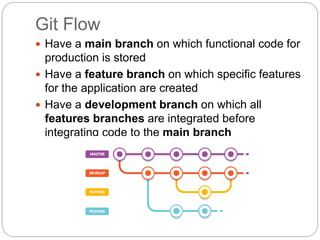
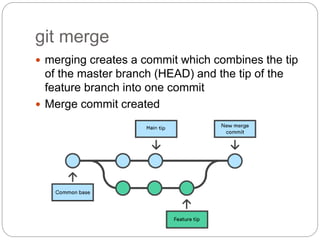
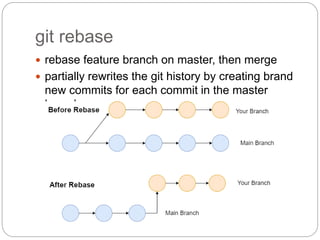
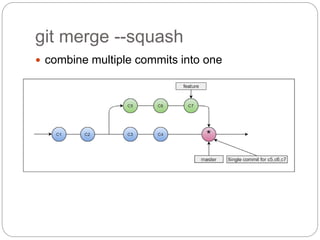
This document outlines the basics of using Git and GitHub, emphasizing the distributed version control system's features which allow local repositories, branching, and committing changes. It discusses commands for repository management, including cloning, staging, committing, and merging changes. Additionally, it covers the workflow of forking and submitting pull requests for collaborative contributions.