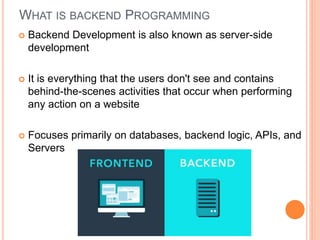
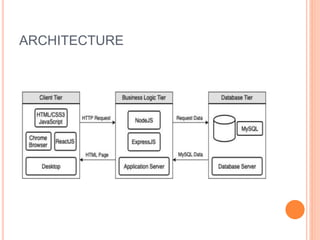
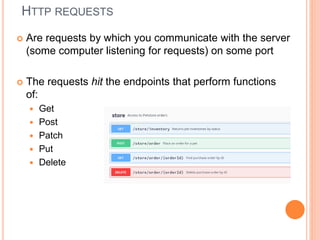
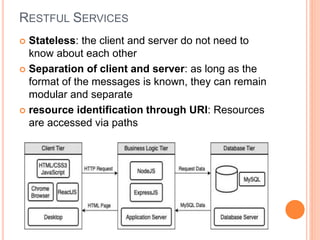
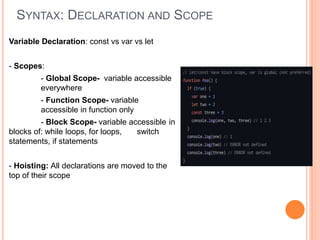
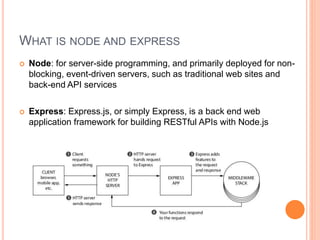
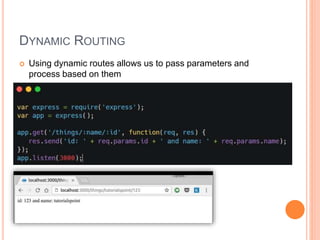
The document outlines a workshop on backend development using RESTful APIs and Express.js, emphasizing the importance of server-side programming. It explains key concepts such as HTTP requests and responses, JavaScript syntax, Node.js, Express framework, routing, and middleware functions. The content is tailored for teaching participants how to set up and manage a server to build robust applications.