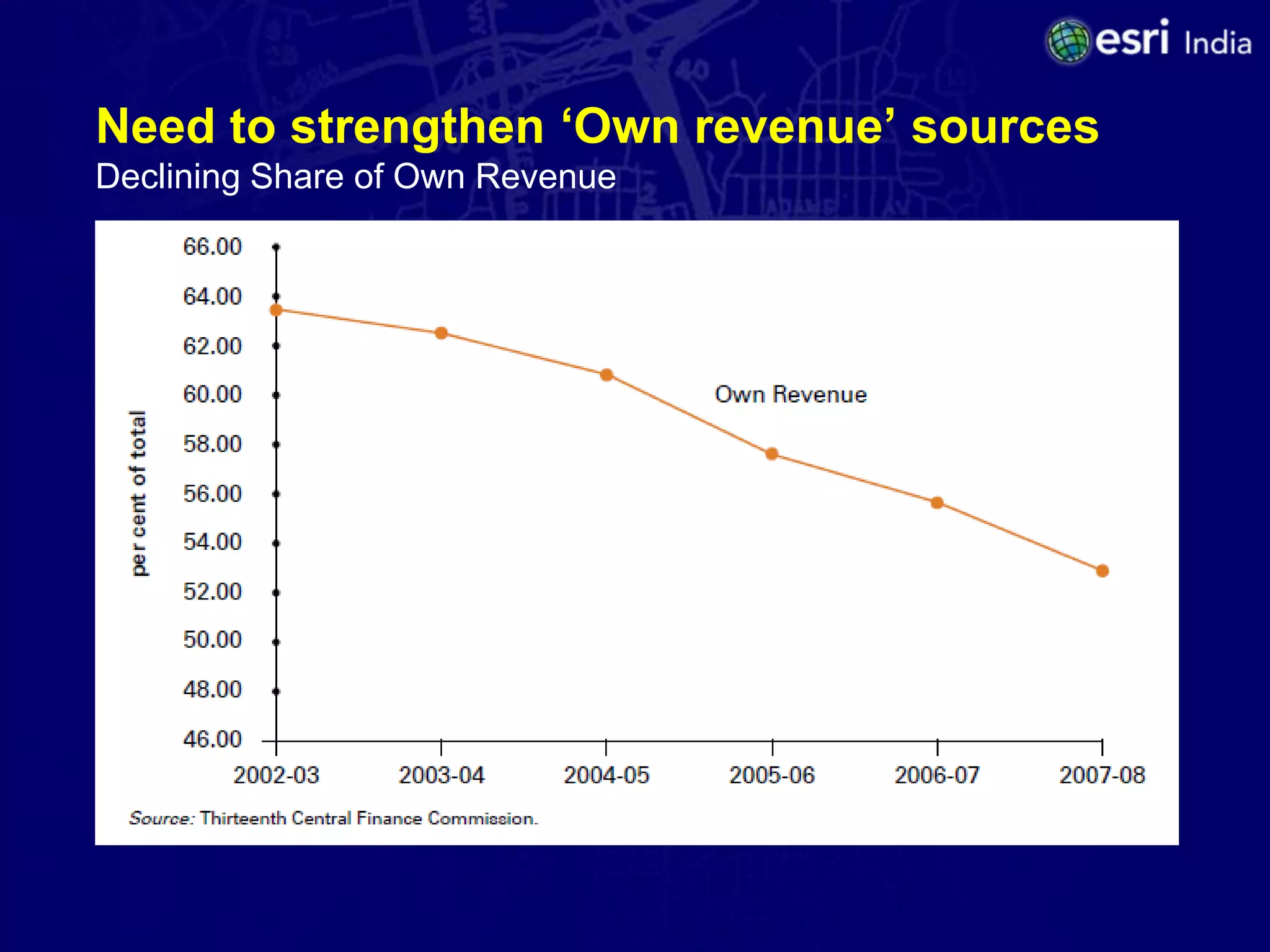
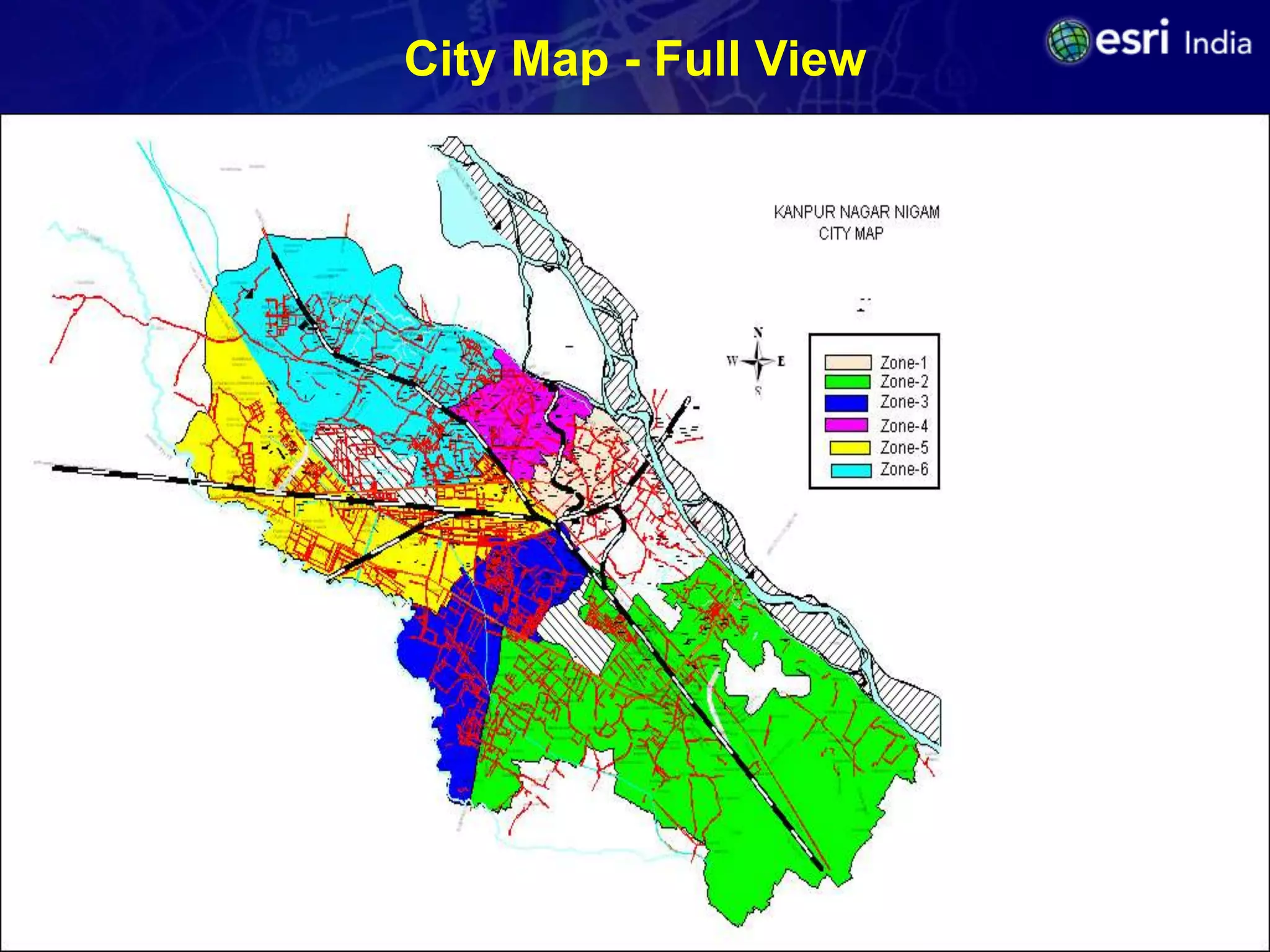
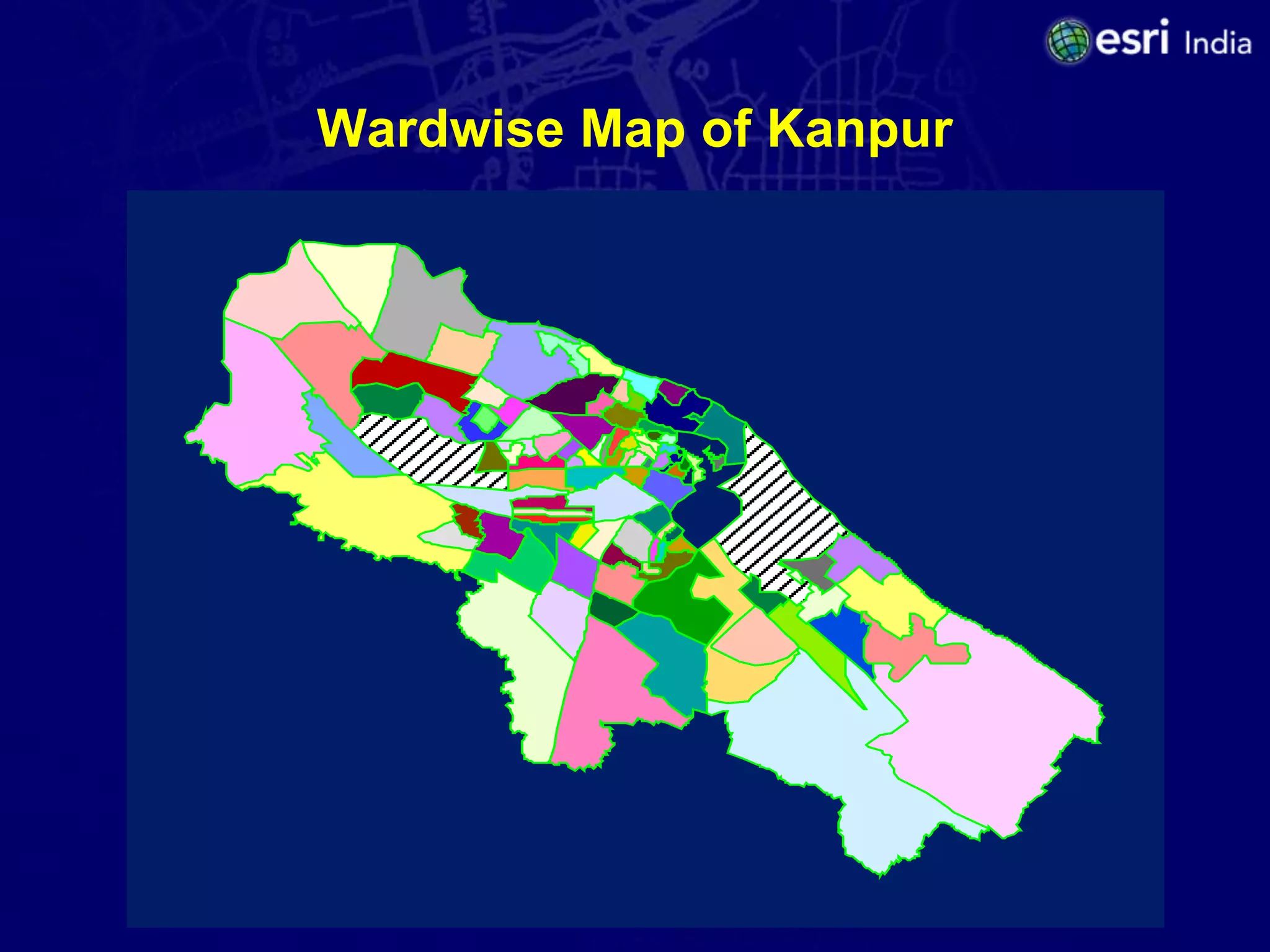
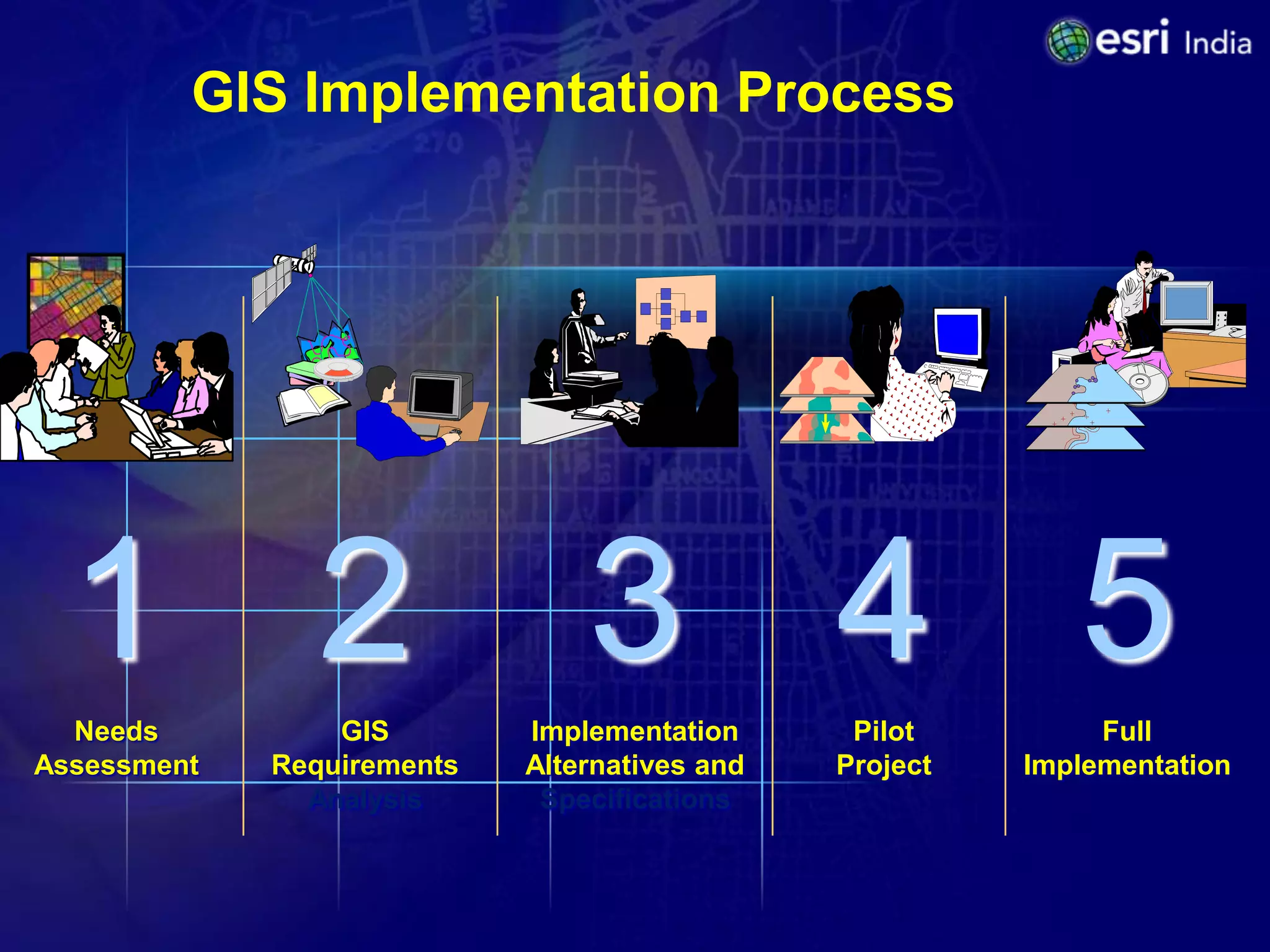
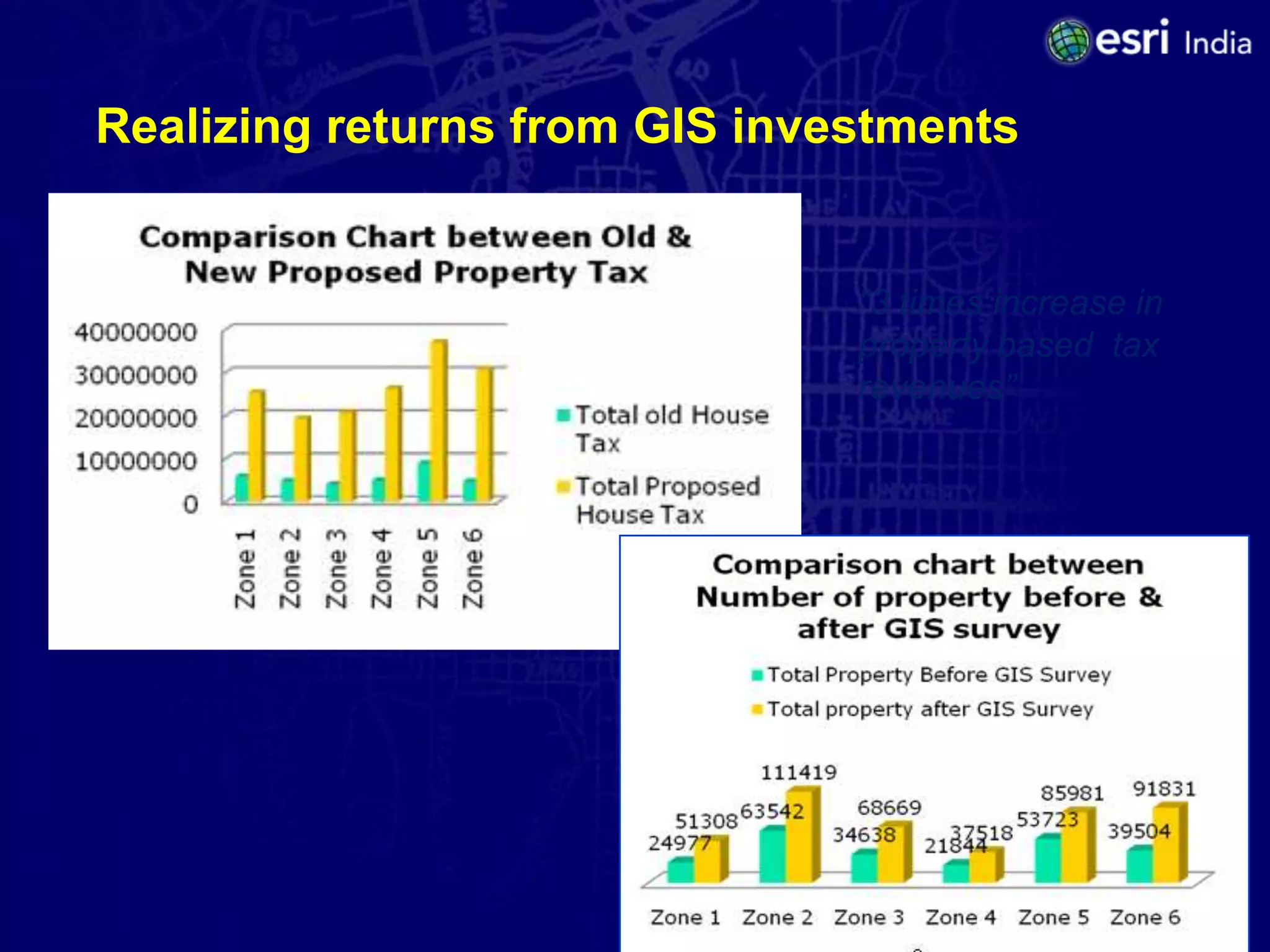
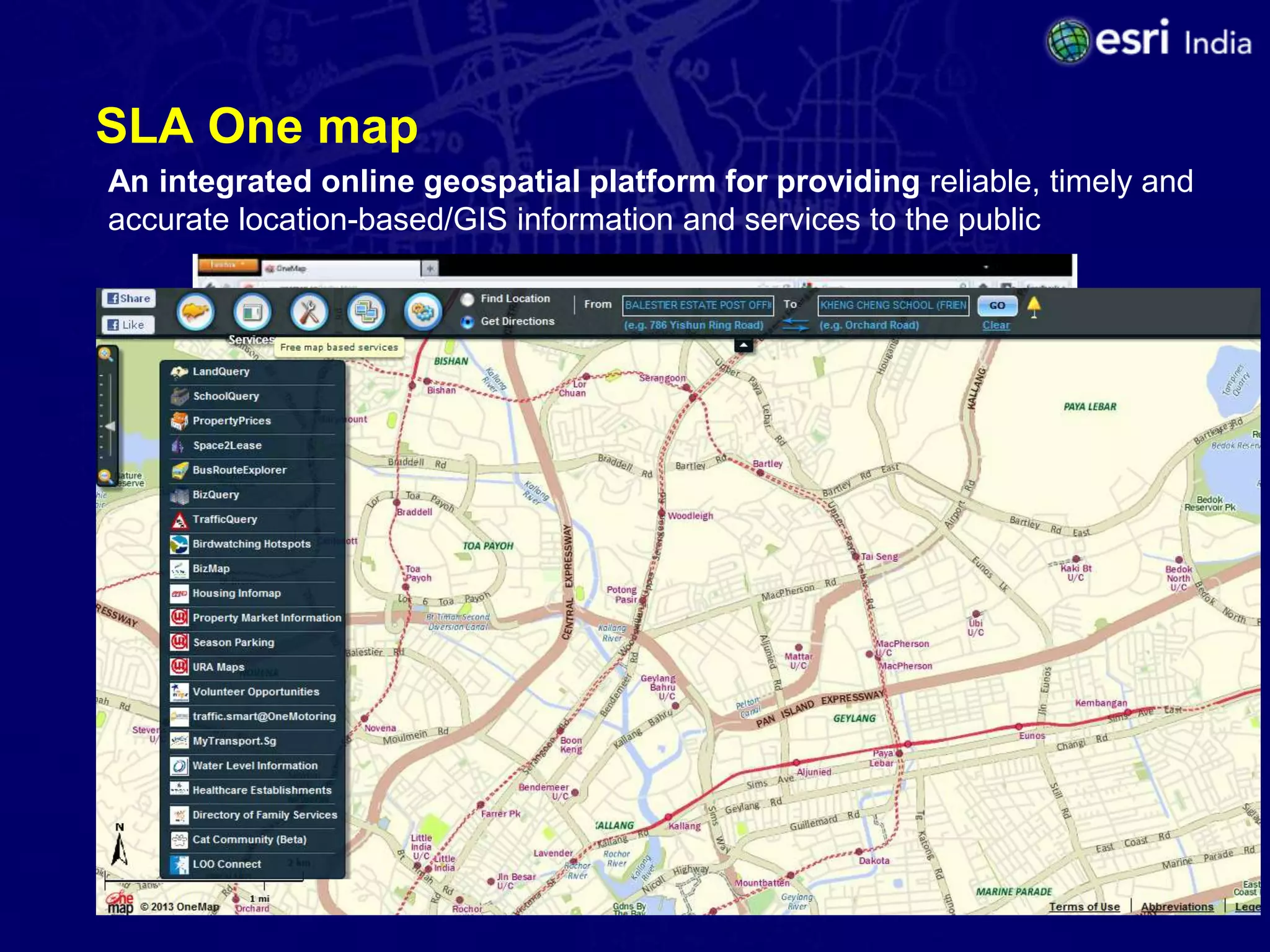
The document discusses the potential of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in enhancing revenue collection and management for municipal corporations, particularly focusing on property tax realization in urban areas. It highlights challenges such as poor assessment rates and weak collection efficiency, and presents a case study of Kanpur Nagar Nigam, illustrating how a GIS-based spatial property database can improve tax collection processes. Recommendations include re-engineering business processes, maintaining accurate taxpayer databases, and leveraging GIS for broader governance initiatives.