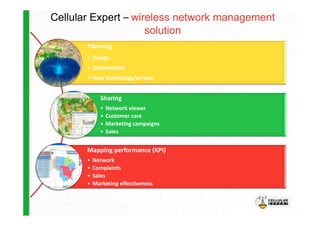
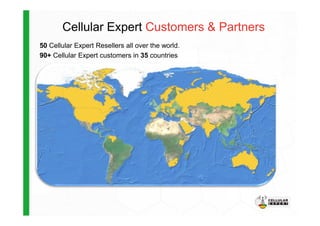
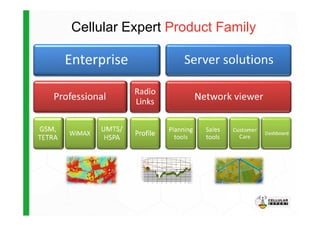
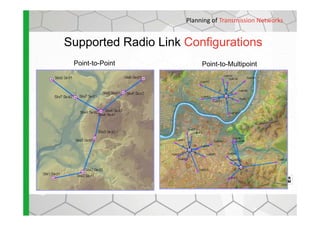
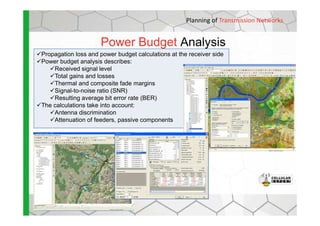
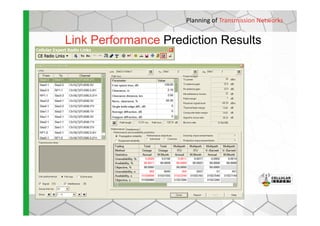
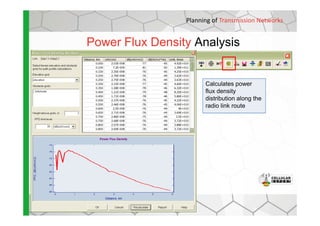
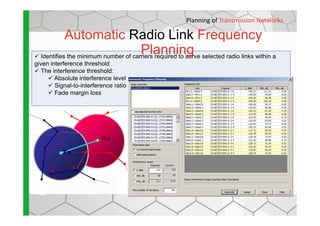
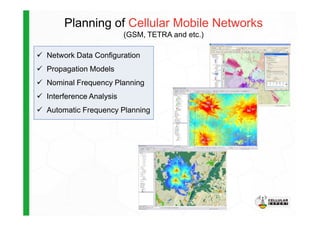
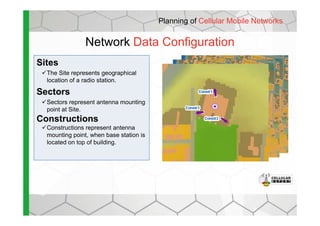
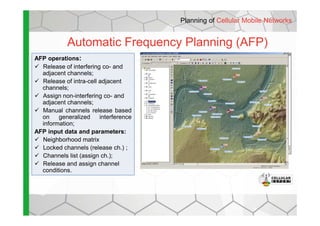
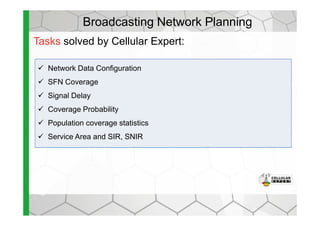
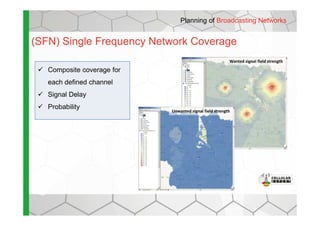
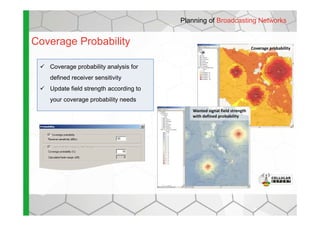
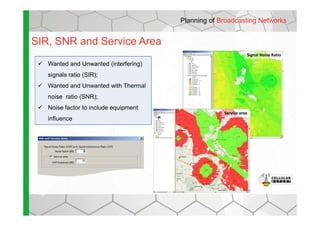
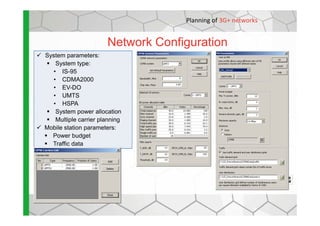
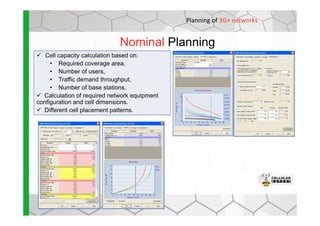
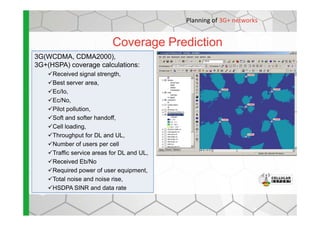
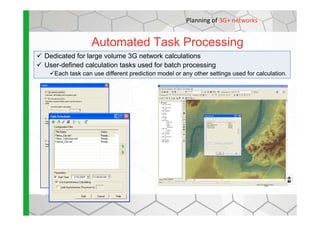
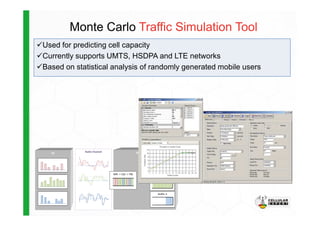
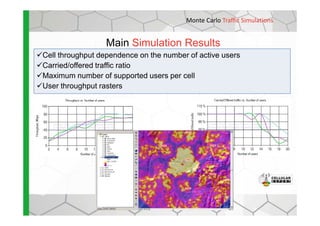
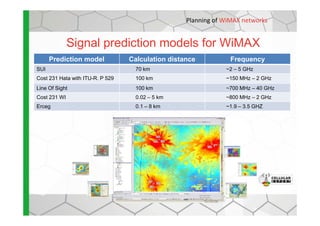
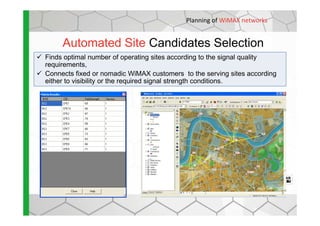
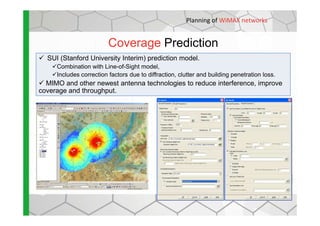
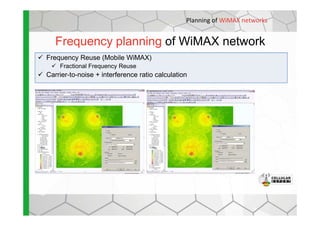
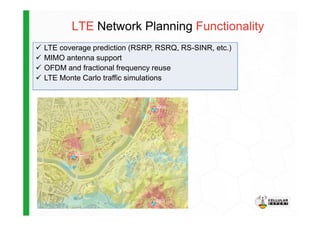
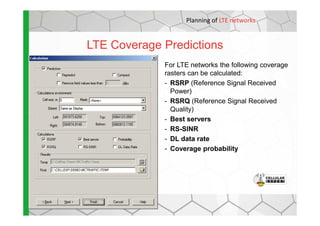
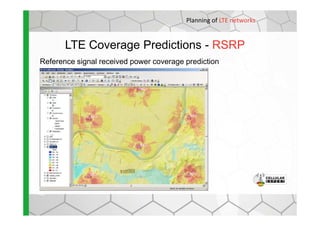
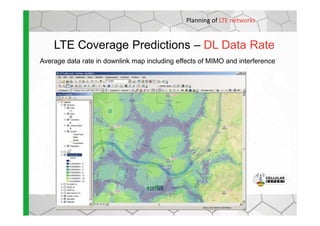
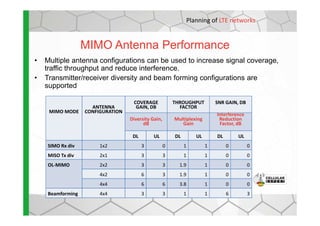
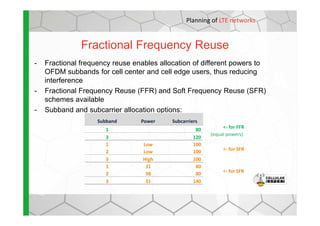
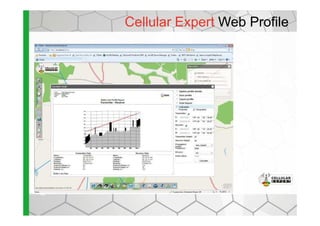
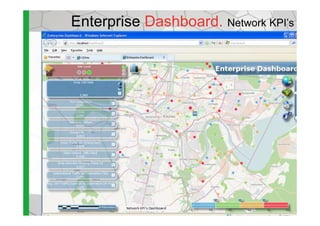
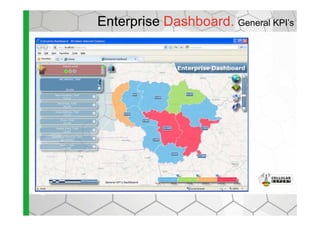
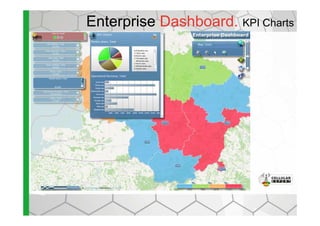
The document discusses the Cellular Expert software solution for wireless network planning, optimization, and management. It provides the following key details:
- Cellular Expert can be used by mobile network operators, telecom companies, and other wireless network owners to plan, optimize, and manage their networks.
- It supports various wireless technologies including GSM, UMTS, LTE, microwave, and broadcasting networks.
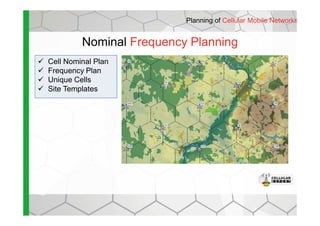
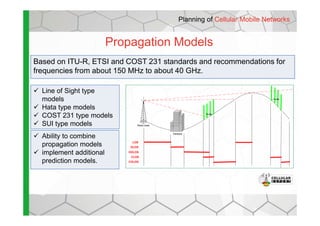
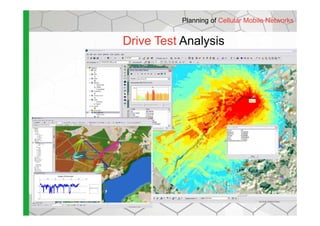
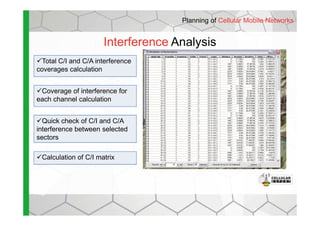
- The software provides tools for network configuration, coverage prediction, interference analysis, frequency planning, and other tasks important for wireless network deployment and management.