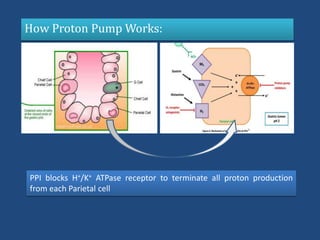
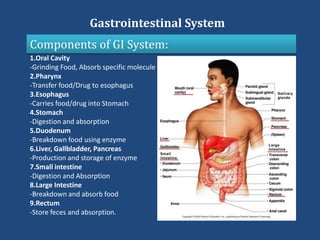
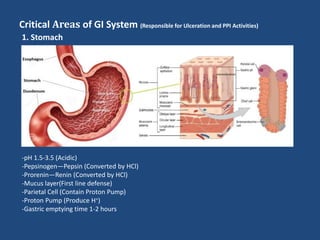
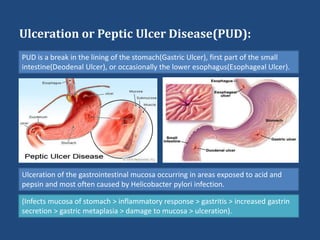
This document discusses the gastrointestinal (GI) system, ulceration, and the role of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) in managing ulcers. It provides an overview of the components and functions of the GI system. Ulceration, or peptic ulcer disease, is defined as a break in the stomach or intestine lining caused by factors like H. pylori infection or NSAID use. Risk factors for ulcers are outlined. PPIs are described as the most potent acid reducers that irreversibly block proton pumps in the stomach, promoting ulcer healing. The roles of other acid controllers like antacids, H2 blockers, cytoprotectives, and antibiotics are summarized. Treatment approaches for different ulcer







![HCl + Antacid [Al(OH)3+Mg(OH)2] = Neutralize HCl
-Used for symptomatic relief
-Not used to Healing ulcer
Antacid:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-150524171453-lva1-app6891/85/GI-System-Ulceration-and-Role-of-PPI-11-320.jpg)