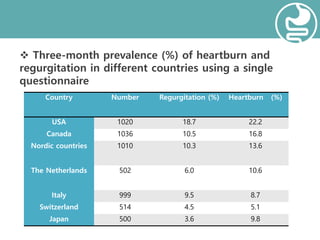
This document summarizes information about Dexlansoprazole (DEXILANT), a proton pump inhibitor used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It notes that GERD is common worldwide, with prevalence rates ranging from 5-48% depending on the country. DEXILANT contains two types of pellets that release at different pH levels to provide dual delayed release of the drug. It is indicated for healing erosive esophagitis, maintaining healing of EE, and treating heartburn from symptomatic non-erosive GERD. The document reviews dosage forms, advantages like flexibility with timing, potential off-label uses, and common side effects like gas and nausea.