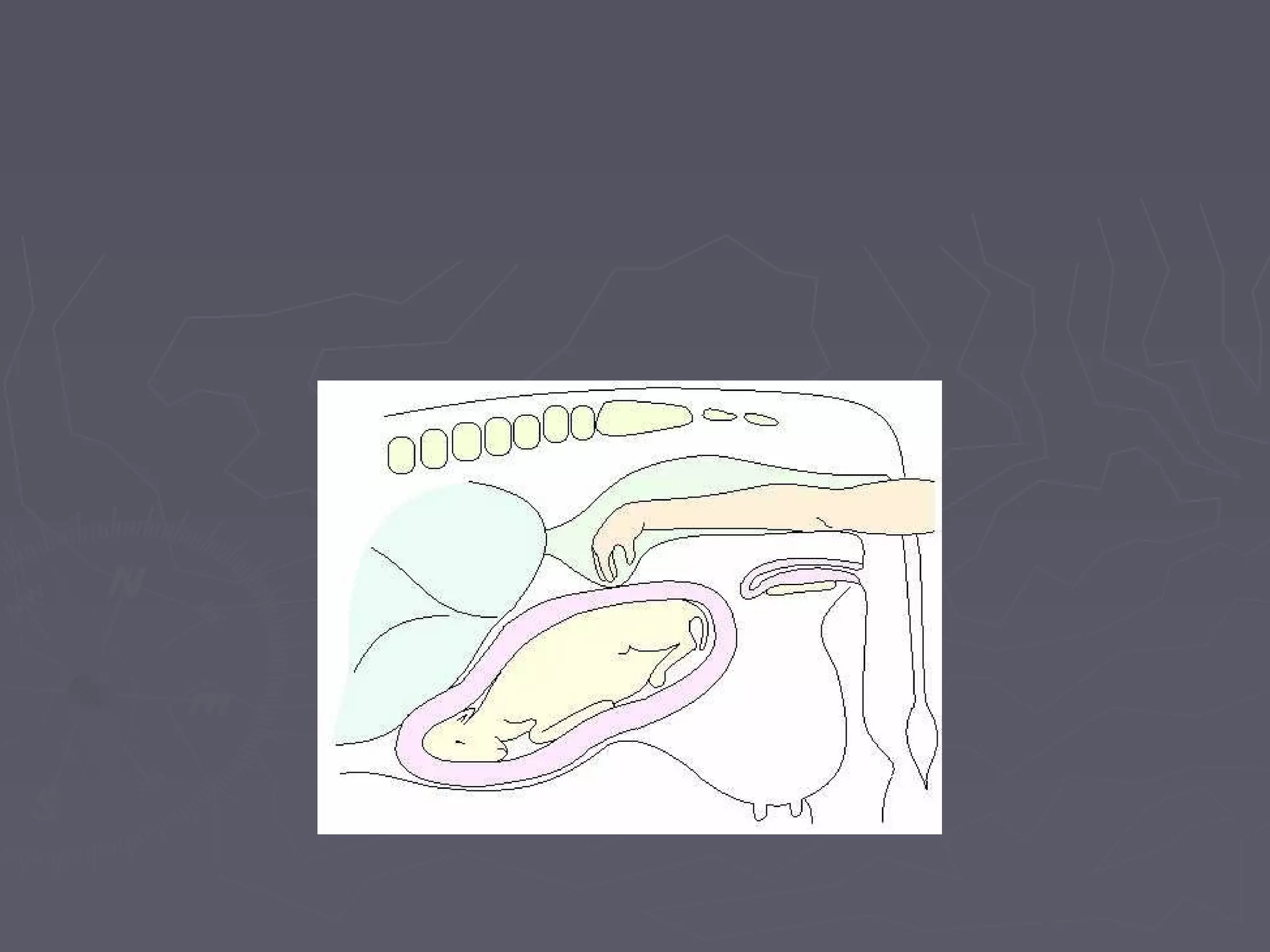
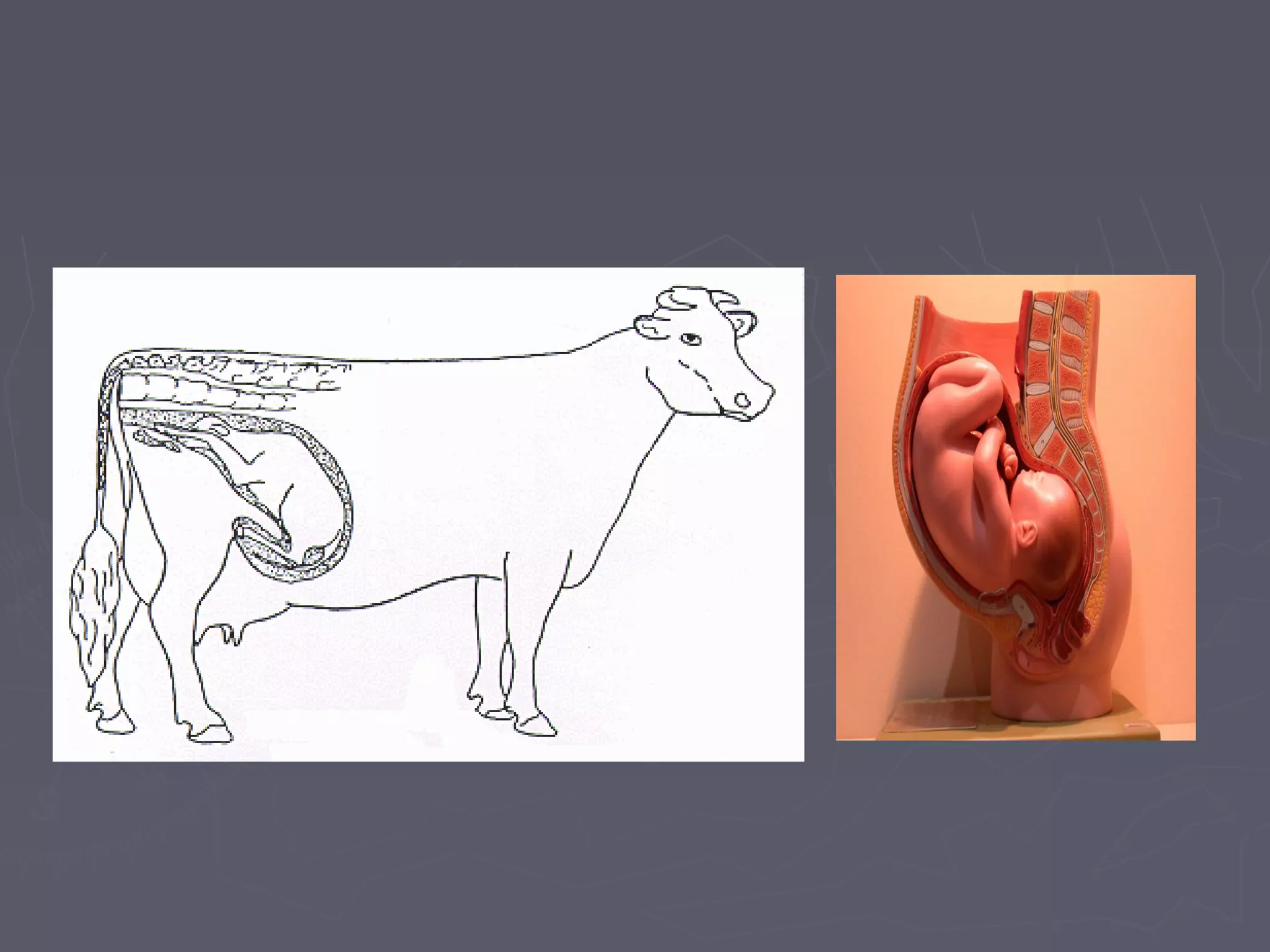
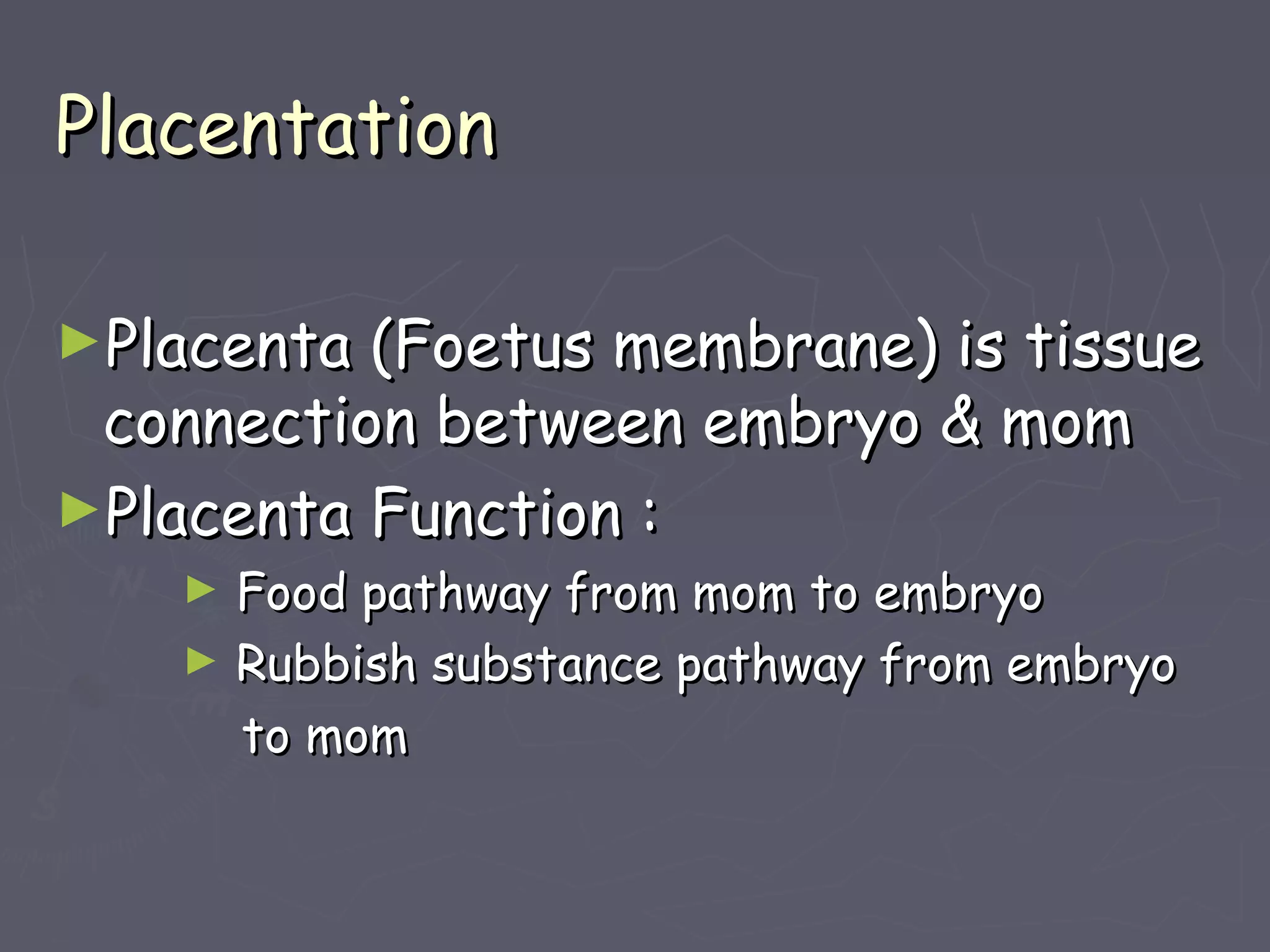
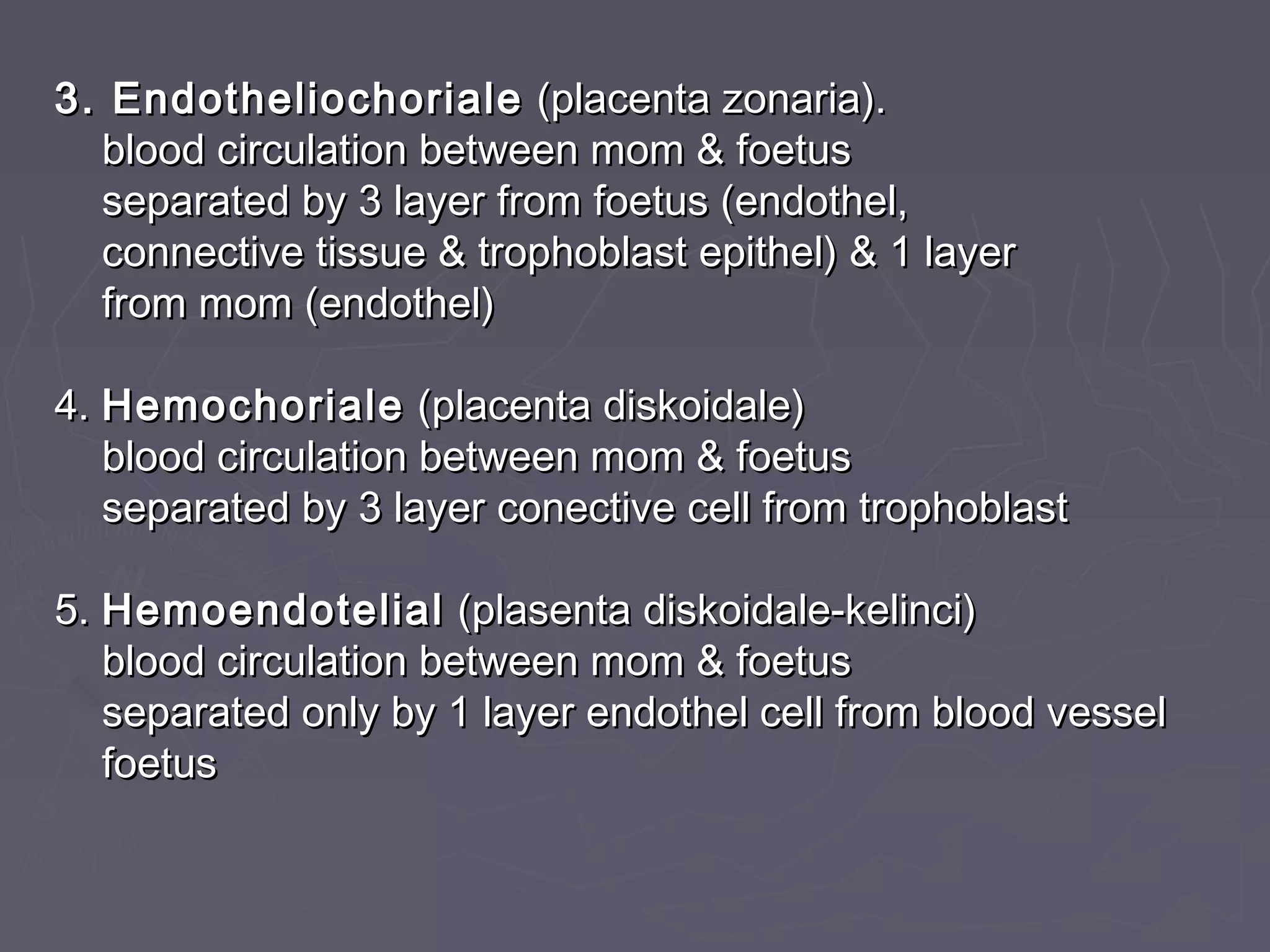
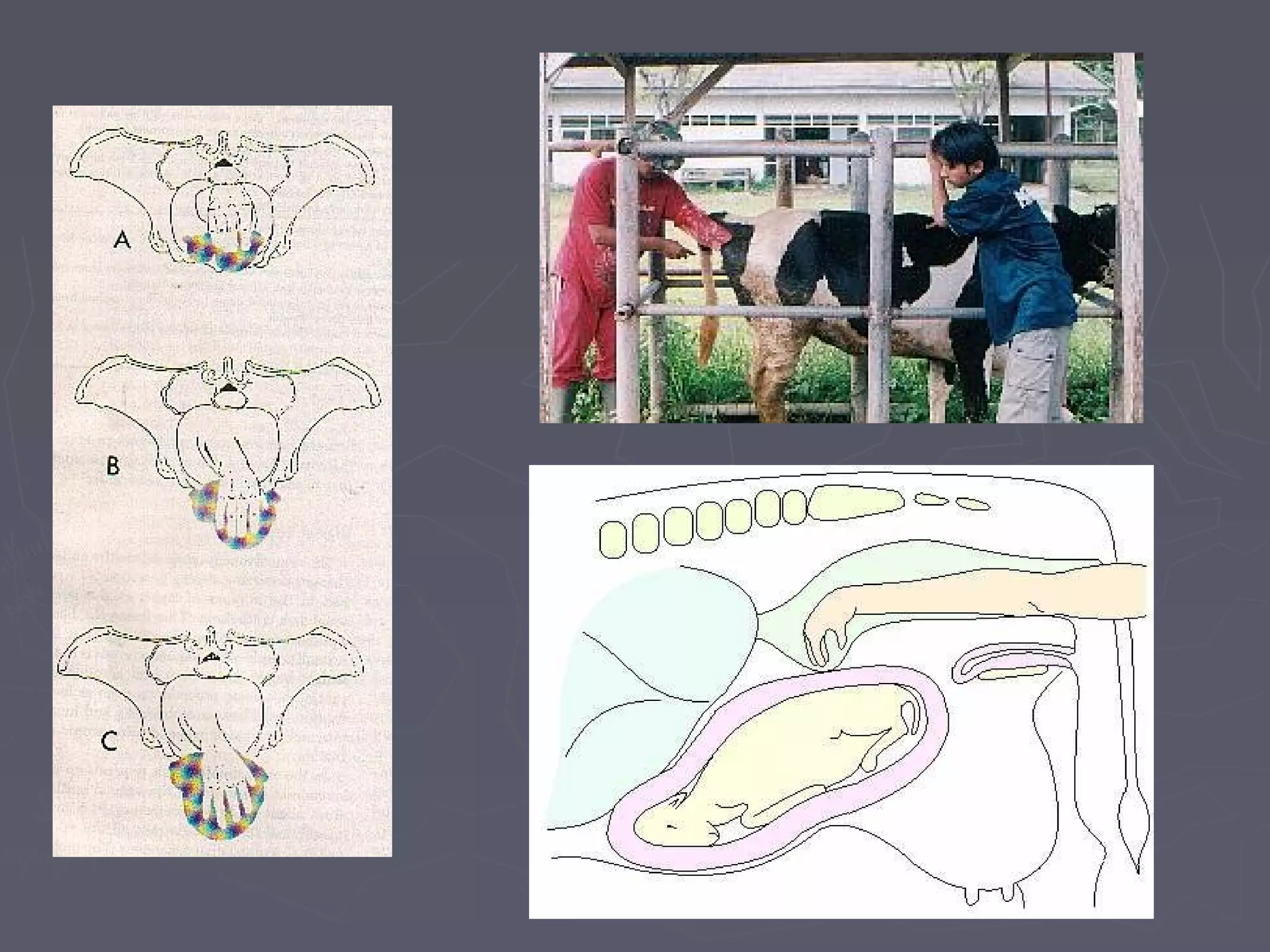
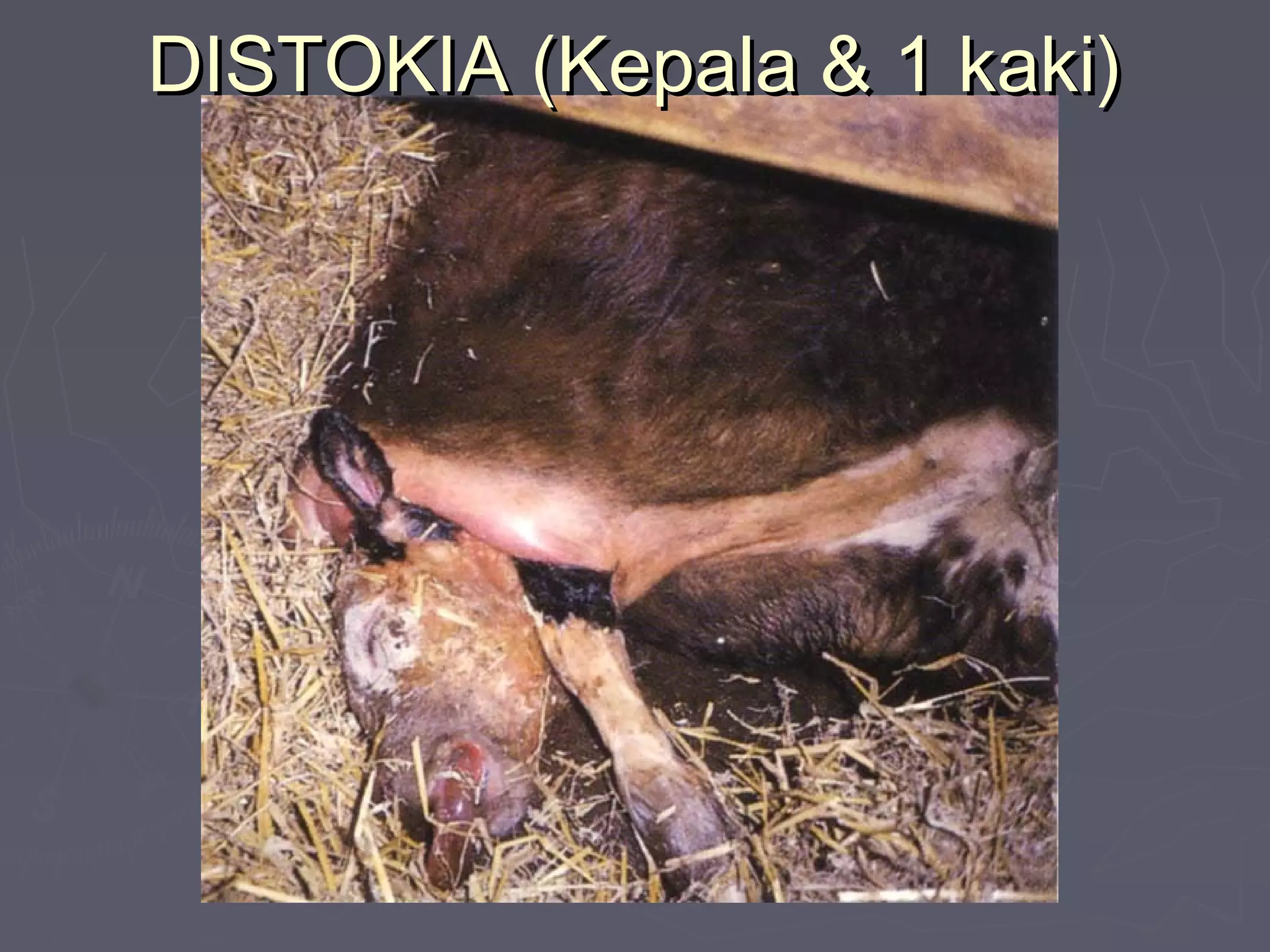
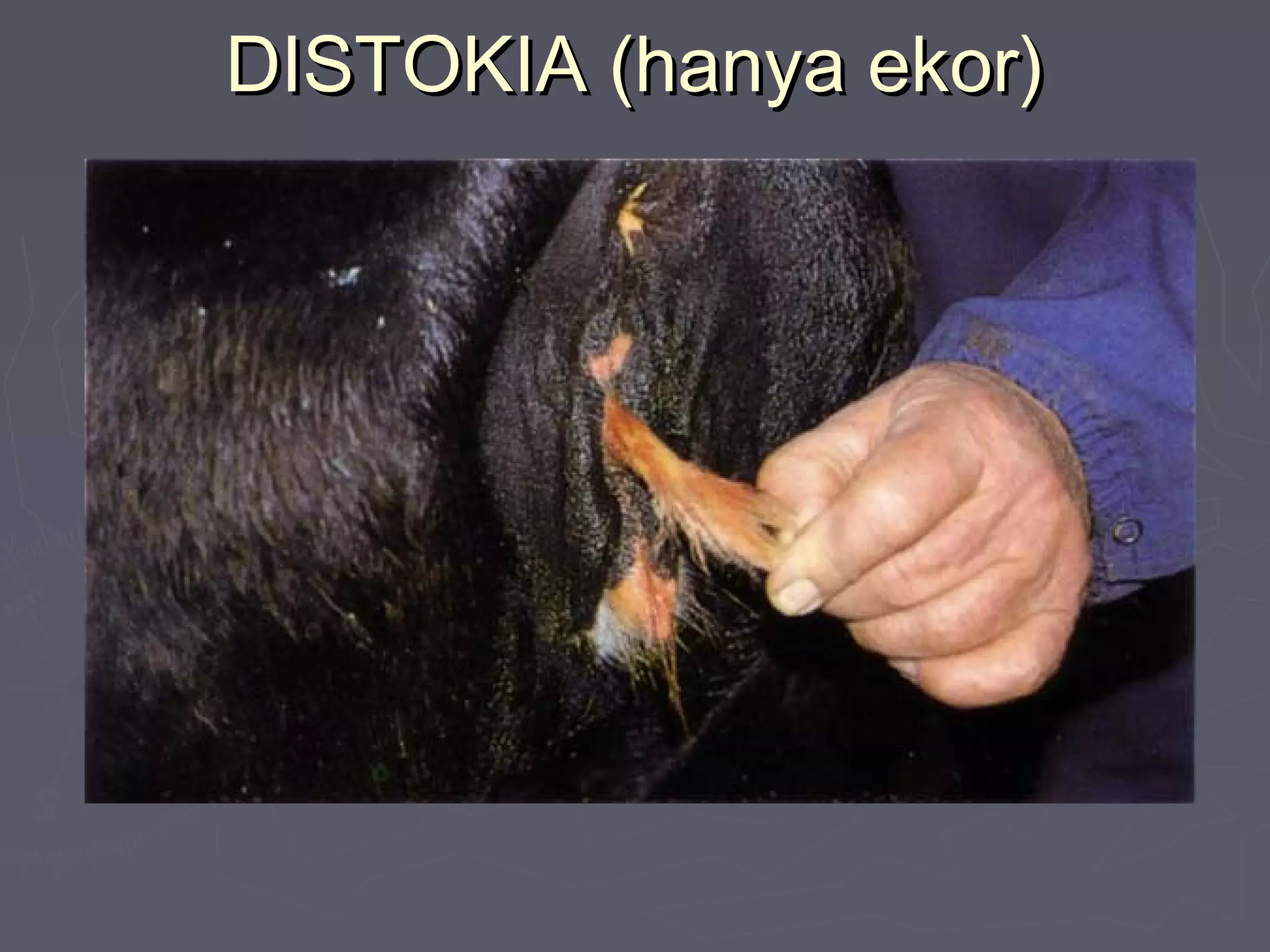
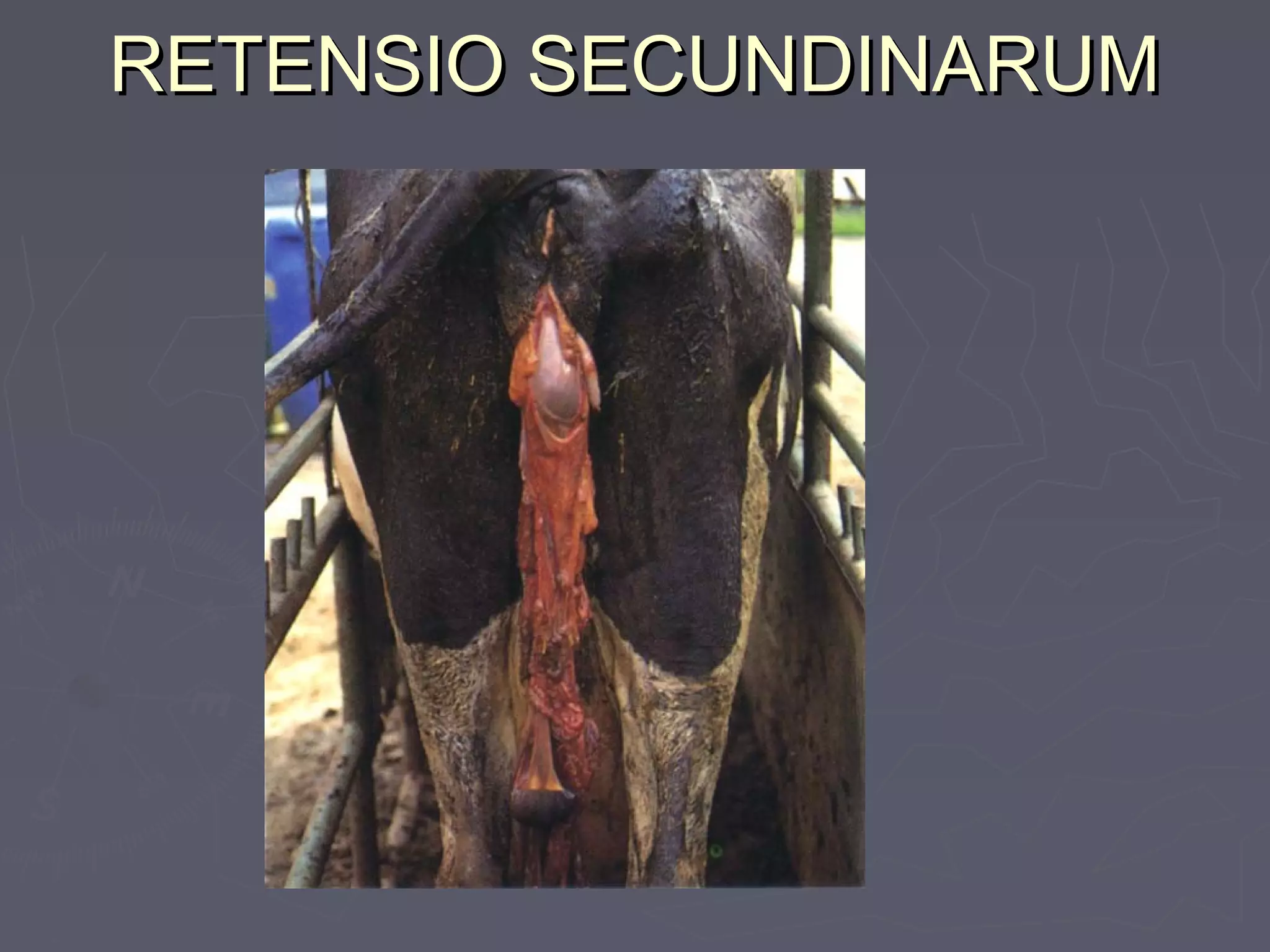
The document discusses gestation periods in farm animals. It describes gestation as consisting of three classes: the ovum period from fertilization to implantation, the embryo period from implantation to early organ formation, and the fetus period from organ formation to birth. The roles of the placenta, hormones, and changes to the female genital organs during gestation are also examined. Factors influencing the length of gestation and methods for examining gestation in farm animals are outlined.