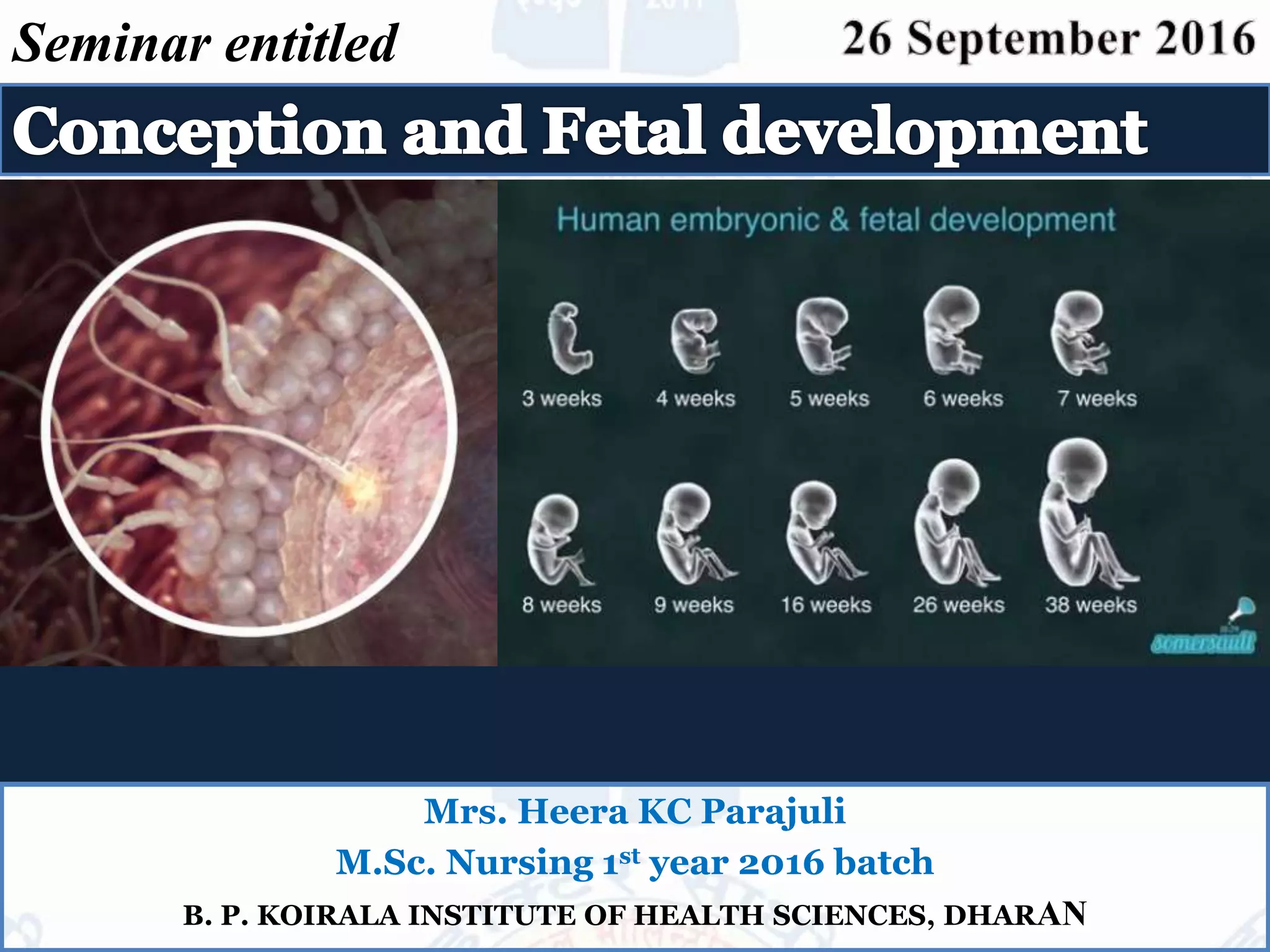
This document summarizes Heera KC Parajuli's seminar on conception and fetal development. It begins with an overview of gametogenesis - the processes of sperm and egg formation. It then discusses ovulation, explaining how a mature ovarian follicle ruptures monthly to release an egg. The next section covers fertilization, describing the steps where a sperm and egg fuse together in the fallopian tube to form a zygote. The document concludes with an introduction to the development of the zygote and early embryo.