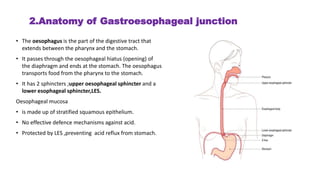
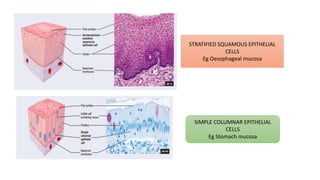
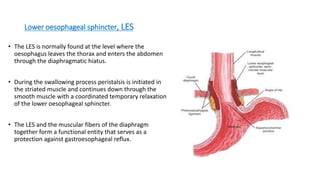
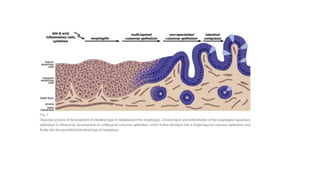
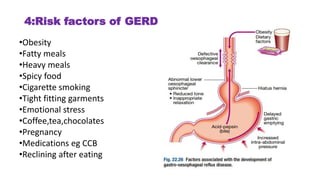
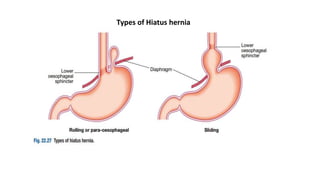
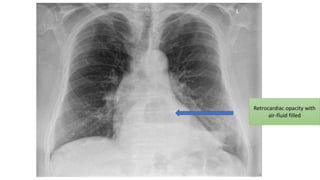
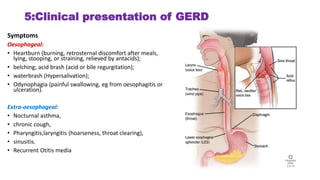
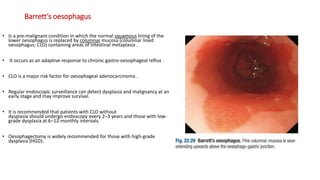
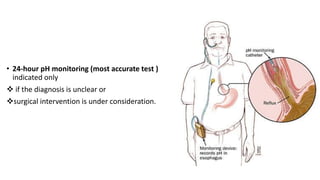
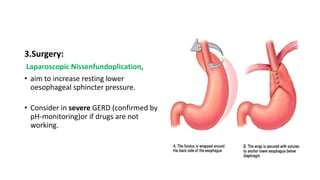
The document provides a comprehensive overview of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), including its definition, anatomy, pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical presentations, complications, investigations, differential diagnoses, and management strategies. GERD is characterized by the retrograde flow of stomach contents into the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn and complications like Barrett's esophagus and adenocarcinoma. Management includes lifestyle modifications, medication (antacids and proton pump inhibitors), and, in severe cases, surgical options.