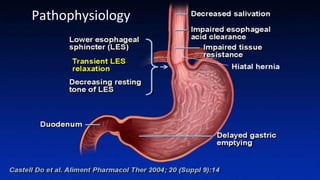
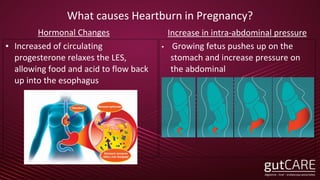
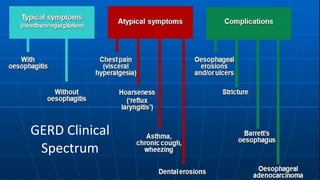
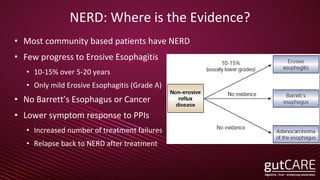
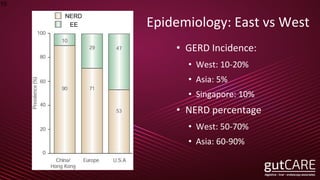
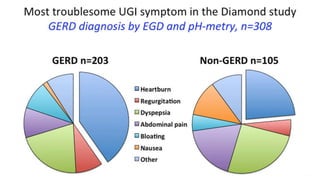
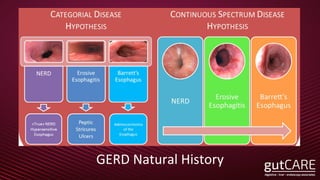
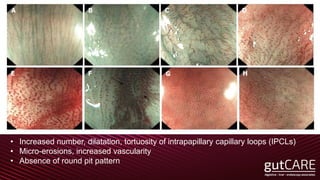
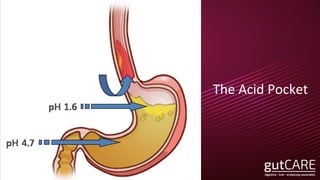
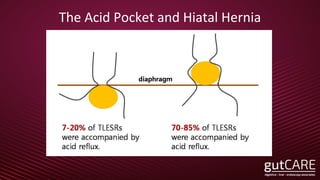
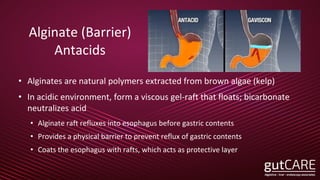
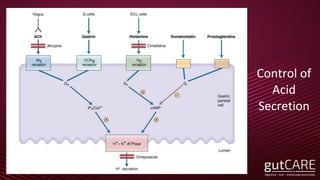
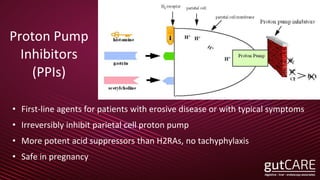
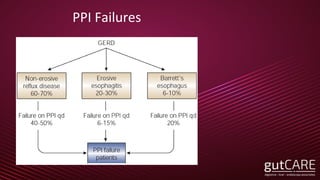
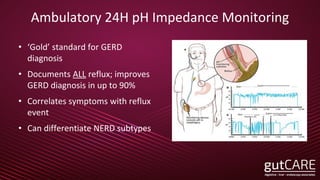
The document discusses the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), focusing on its prevalence among pregnant women and the spectrum of the condition. Key points include the evaluation of heartburn symptoms for diagnosis, the limited role of endoscopy, and various treatment options, including lifestyle changes and medications like proton pump inhibitors. It also highlights emerging treatments and the evolution of GERD paradigms over the last two decades.












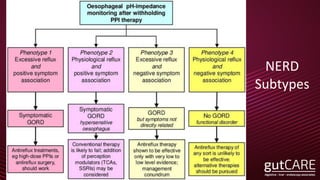


![24 hours gastric pH4 HTR (Study V-E: Vonoprazan 20mg and Esomeprazole 20mg administered)
Vonoprazan 20 mg group (n=10)
Esomeprazole 20 mg group (n=10)
100
0
day 1 of administration day 7 of administration
80
60
40
20 23.9
61.2
71.4
85.8
pH4HTR
Average value ±standard deviation
pH4 HTR: pH≧4 Holding Time Ratio (Holding time ratio is greater than pH 4)
Difference between both
drugs (%) [95% CI]
47.5 [35.5, 59.4] Difference between both
drugs (%) [95% CI]
24.6 [16.2, 33.1]
Sakurai Y, et al: Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 42 (6): 719-730
(%)
Target and method: In a randomized, open-label 2-period crossover study of 20 adult Japanese males with CYP2C19 genotype EM
(including hetero EM, homo EM), once daily dose of Vonoprazan 20mg and Esomeprazole 20mg (Study V-E, n=10), Vonoprazan
20mg and Rabeprazole 10mg (Study V-R, n=10) was administered for 7 days.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gerdaug18v2-180809133415/85/GERD-Current-Paradigms-36-320.jpg)
![Difference between both
drugs (%) [95% CI]
58.2 [43.6, 72.9]
Difference between both
drugs (%) [95% CI]
28.8 [17.2, 40.4]
24 hours gastric pH4 HTR (Study V-R: Vonoprazan 20mg and Rabeprazole 10mg administered)
Vonoprazan 20 mg group (n=7)
Rabeprazole 10 mg group (n=7)
Average value ±standard deviation
pH4 HTR: pH≧4 Holding Time Ratio (Holding time ratio is greater than pH 4)
100
(%)
0
day 1 of administration day 7 of administration
80
60
40
20
pH4HTR
26.3
65.1
93.8
84.2
Target and method: In a randomized, open-label 2-period crossover study of 20 adult Japanese males with CYP2C19 genotype EM
(including hetero EM, homo EM), once daily dose of Vonoprazan 20mg and Esomeprazole 20mg (Study V-E, n=10), Vonoprazan
20mg and Rabeprazole 10mg (Study V-R, n=10) was administered for 7 days.
Sakurai Y, et al: Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 42 (6): 719-730. More figures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gerdaug18v2-180809133415/85/GERD-Current-Paradigms-37-320.jpg)

