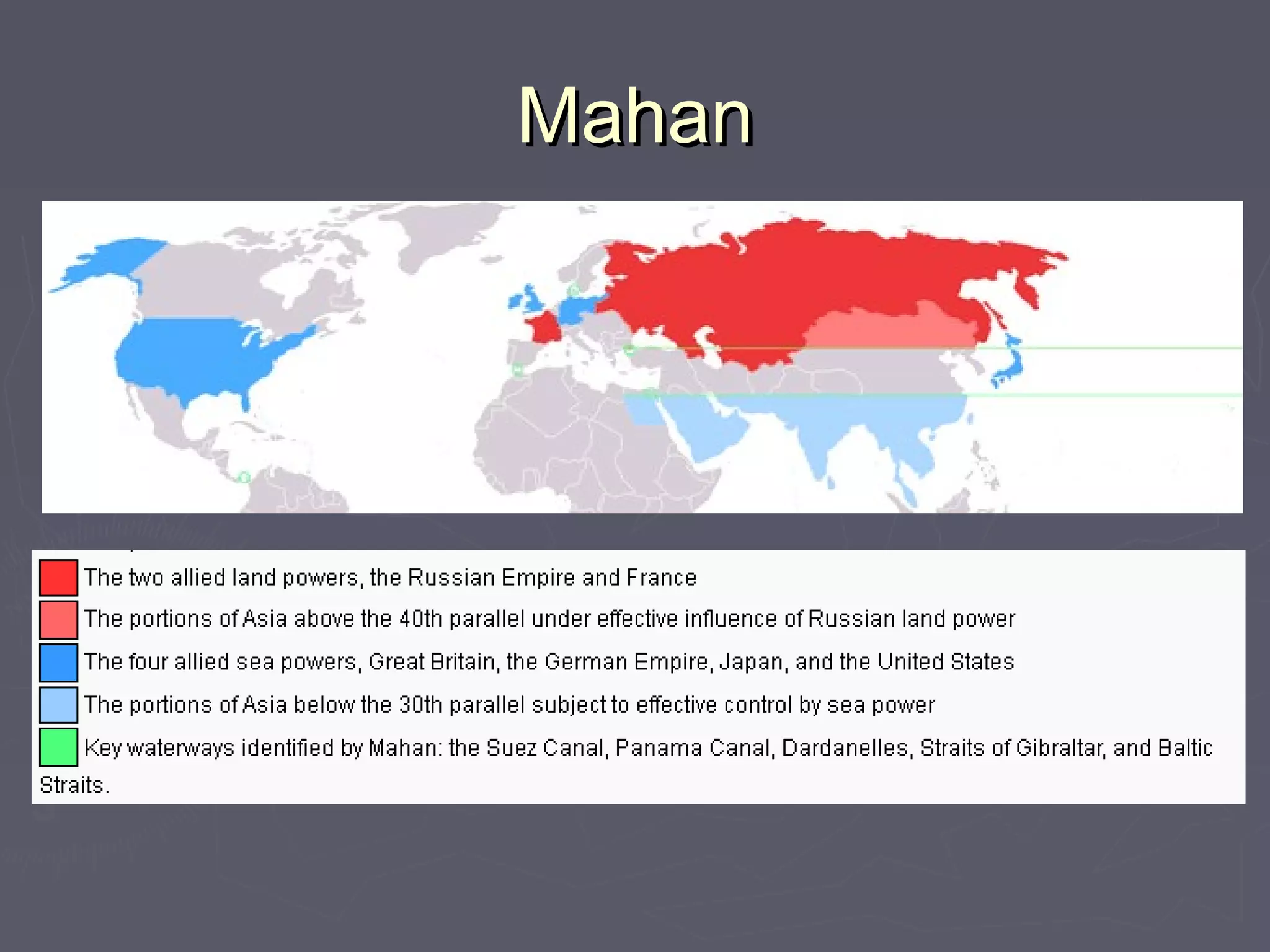
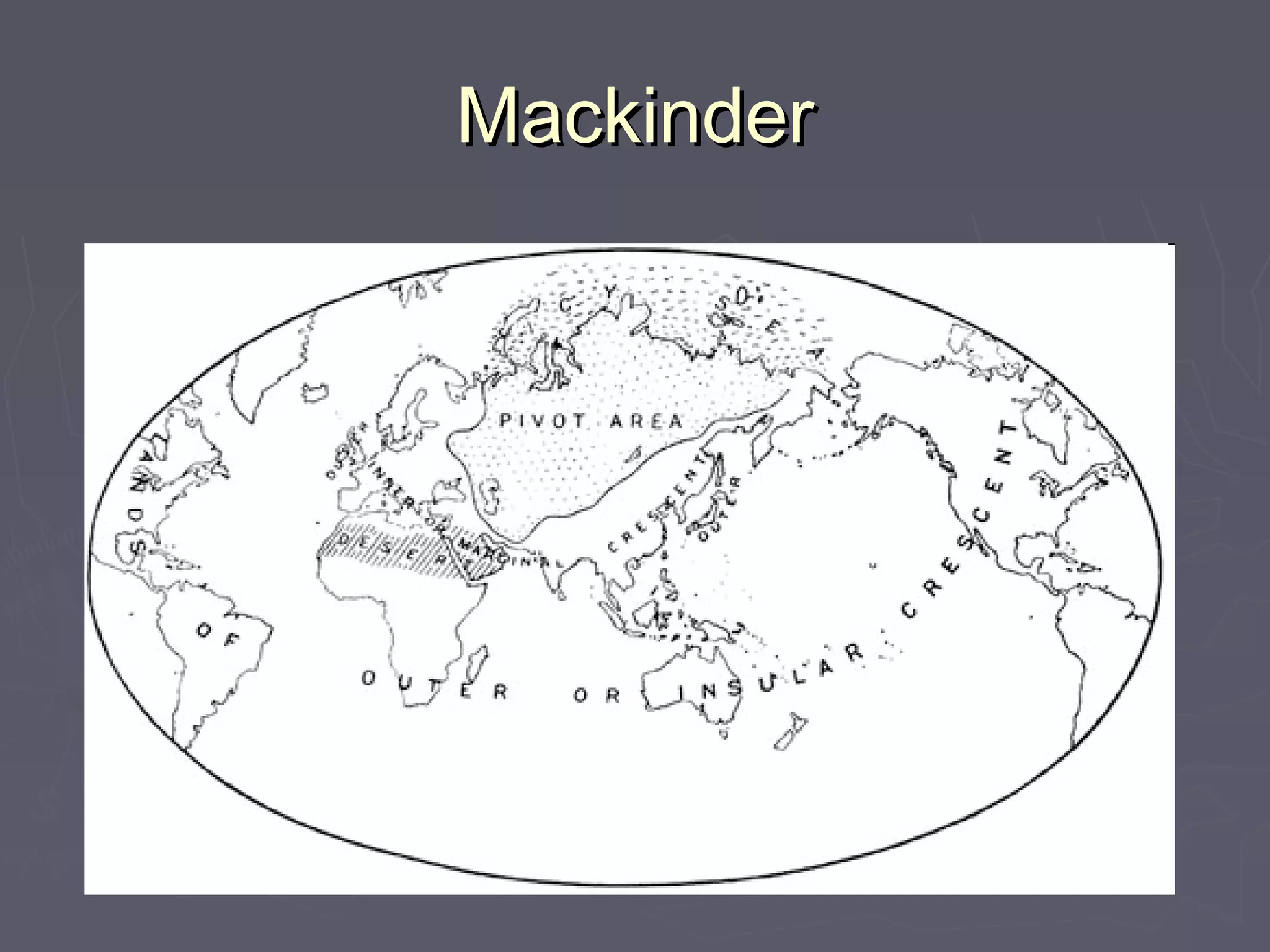
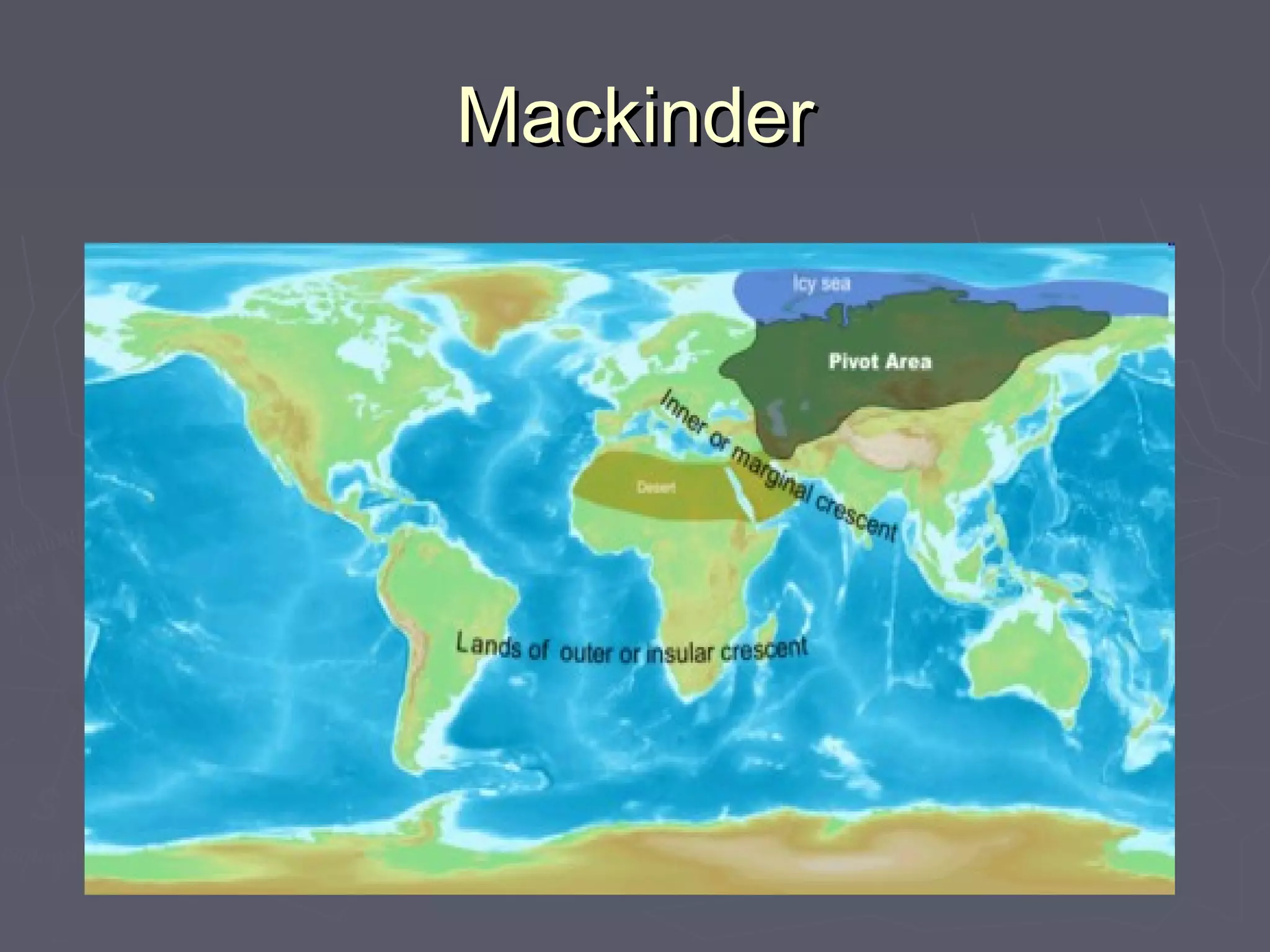
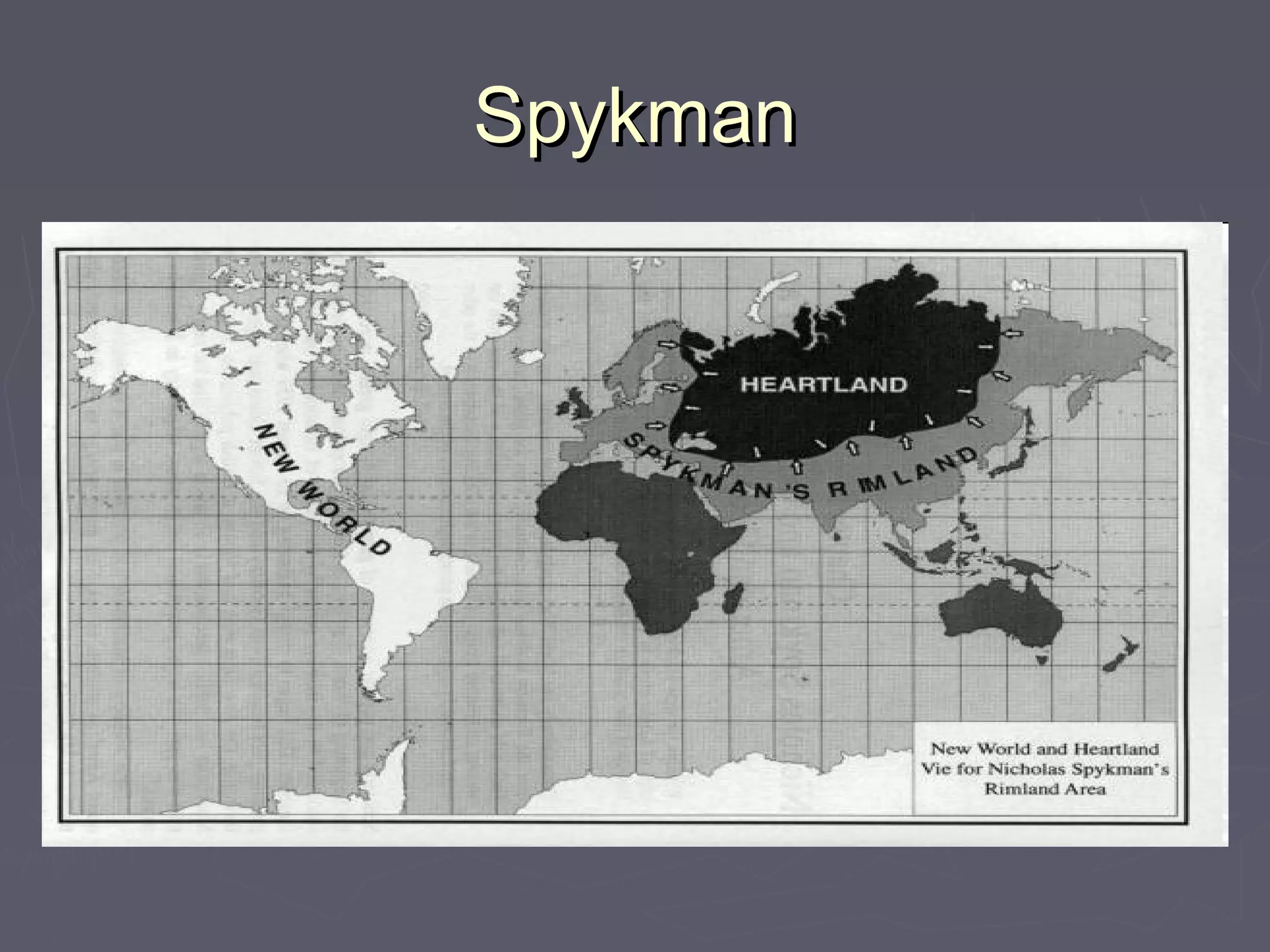
Geopolitics is the study of how geographical factors like territory, population, resources, and location influence international politics and relations between states. Key thinkers in geopolitical theory include Alfred Thayer Mahan who argued sea power was essential for trade and power, Halford Mackinder who developed the Heartland Theory that control of the Eurasian core landmass meant control of the world, and Nicholas Spykman who argued control of the rimlands of Europe and Asia was more important than the heartland. Immanuel Wallerstein viewed the global political economy as consisting of core states that exploited peripheral states, with semi-peripheral states acting as buffers between them.