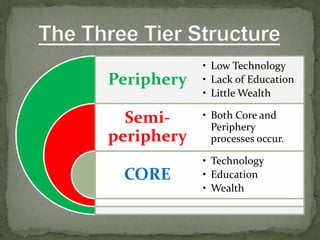
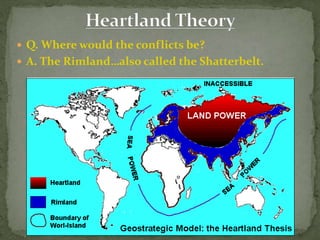
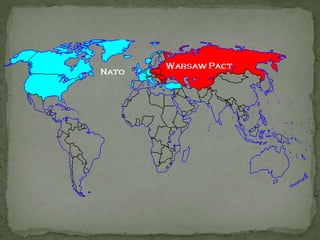
This document discusses several theories of geopolitics, including those proposed by Wallerstein, Ratzel, Mackinder, and Spykman. It analyzes their similarities and differences in explaining the arrangements and forces transforming the global political landscape. Wallerstein's world-systems theory describes a three-tier global economic structure of core, periphery, and semi-periphery states. Mackinder's heartland theory claims that whoever controls Eastern Europe and Siberia could dominate the world. Spykman modified this view, arguing that control of the rimland regions surrounding Eurasia would be key to global power.