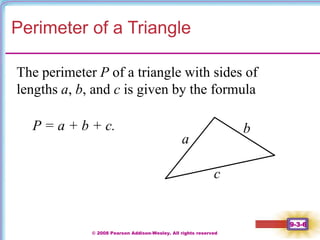
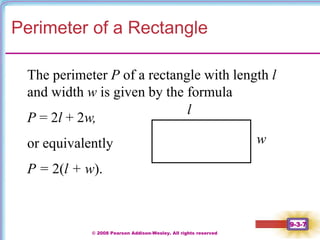
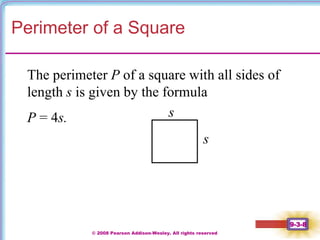
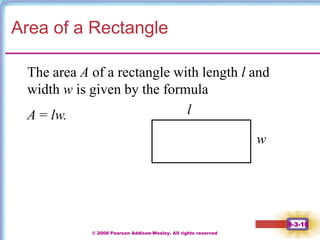
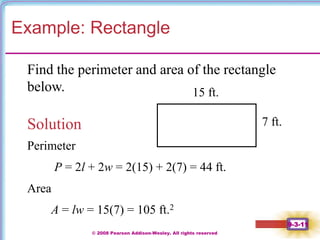
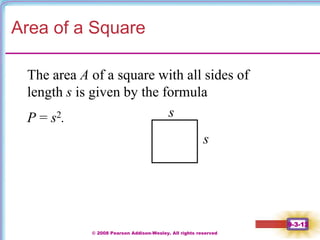
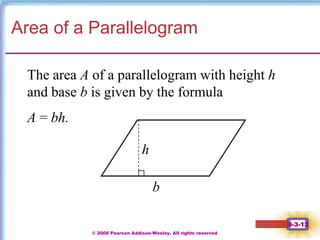
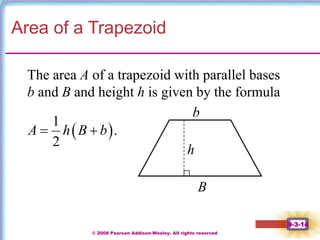
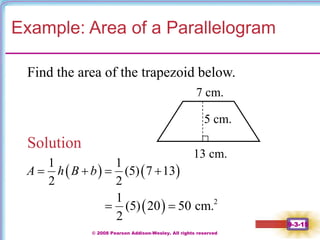
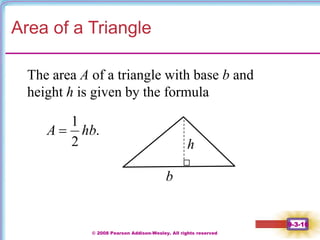
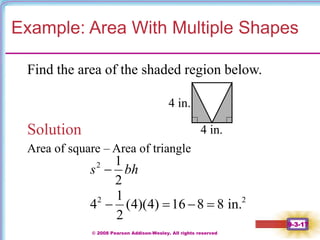
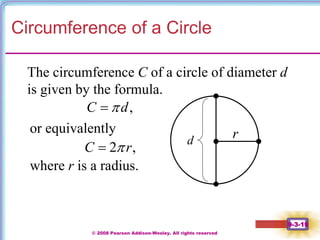
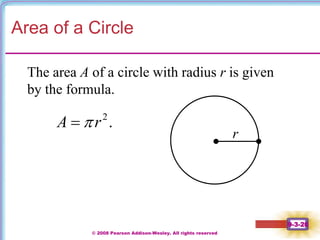
This document contains notes on perimeter, area, and circumference from a geometry textbook chapter. It defines perimeter as the distance around a shape and area as the surface covered. Formulas are provided for calculating the perimeter and area of polygons like triangles, rectangles, squares, parallelograms, and trapezoids. Circumference is defined as the distance around a circle, and formulas show circumference is equal to pi times the diameter or twice pi times the radius. The area of a circle is equal to pi times the radius squared. Examples demonstrate calculating perimeter, area, and circumference for various shapes.