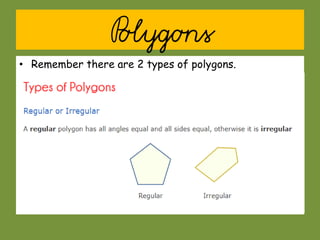
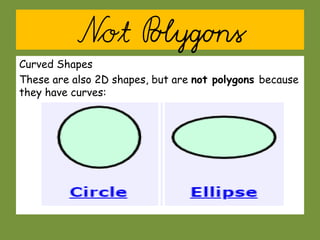
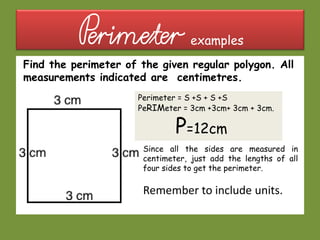
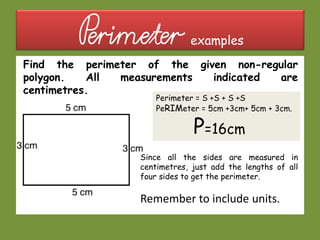
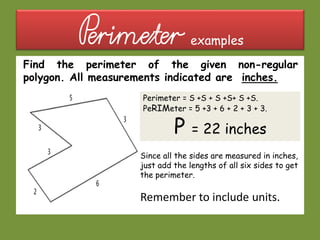
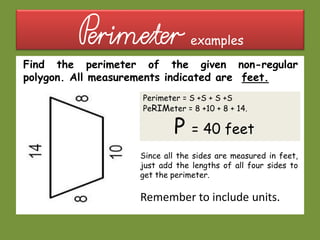
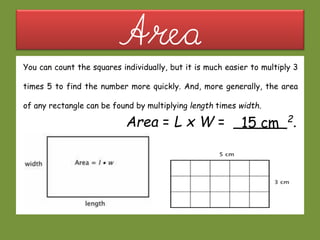
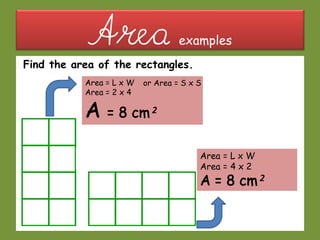
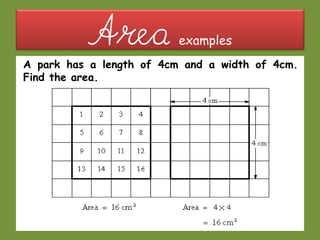
This document provides information about polygons, perimeter, and area. It defines a polygon as a 2D shape with straight sides. There are two types of polygons: regular and irregular. Perimeter is defined as the distance around a 2D shape and is measured by adding up the lengths of all sides. Area is the amount of surface a shape covers and is measured in square units. Formulas are provided to calculate the perimeter and area of common polygons like squares, rectangles, and triangles. Examples are given to demonstrate calculating perimeter and area using the appropriate formulas and units of measurement.