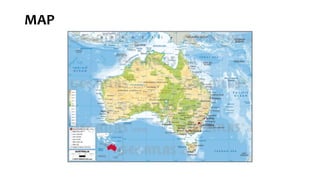
Australia is a country encompassing the mainland of the Australian continent, Tasmania, and several smaller islands, making it the sixth-largest country by total area. It is a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a diverse economy primarily driven by mining, agriculture, and services, and has a population of approximately 24.2 million people, predominantly urbanized along the coast. The nation boasts rich biodiversity, a variety of landscapes, and significant historical indigenous presence, while facing environmental challenges and high per capita carbon emissions.