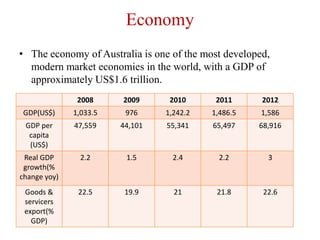
The document provides an overview of Australia, including its history, geography, culture, government, economy, and iconic wildlife. Key details include Australia being the world's smallest continent yet largest island, with a diverse landscape and culture. The economy relies heavily on natural resources like coal, gas, and minerals, with major exports including iron ore, coal, and gold. Kangaroos are one of Australia's most iconic animals and the country has a commercial kangaroo meat industry.